The Evolution of Renewable Energy Reporting Frameworks
Early Voluntary Efforts
The initial push towards renewable energy often involved voluntary initiatives from businesses and individuals. These early adopters recognized the environmental benefits and potential economic advantages of transitioning away from fossil fuels. Many companies established internal sustainability programs, implementing energy-efficient practices and exploring renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines for their operations. These voluntary actions, while impactful on a smaller scale, laid the groundwork for future legislation and industry standards.
Early voluntary efforts also focused on developing industry standards and best practices. Organizations like the Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21) played a crucial role in promoting knowledge sharing and collaboration among stakeholders. These standards addressed areas like energy efficiency, renewable energy technologies, and sustainable resource management, creating a common understanding and framework for future development.
Emergence of Governmental Support
As the awareness of climate change grew and the need for a more sustainable energy system became more apparent, governments started to implement policies to encourage and support renewable energy development. These policies often took the form of tax incentives, subsidies, and mandates for renewable energy procurement. These governmental interventions significantly accelerated the adoption of renewable energy technologies, fostering a more favorable investment environment and driving innovation in the sector.
Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives also played a key role in promoting renewable energy. These efforts helped to disseminate information about the environmental benefits of renewable energy, its economic potential, and the steps individuals could take to contribute to the transition. This combination of governmental support and public awareness created a more supportive environment for renewable energy to flourish.
Industry Collaboration and Standardization
The development of industry standards and certifications became critical to ensure the quality, reliability, and safety of renewable energy technologies. This involved collaborations between manufacturers, researchers, and regulatory bodies. Standardized testing procedures and performance metrics helped to build trust and confidence in the technologies, which, in turn, fostered wider adoption. Stronger industry standards also help to ensure consistency and interoperability across different renewable energy systems, simplifying integration and maintenance.
Furthermore, collaborative efforts between businesses and research institutions led to significant advancements in renewable energy technologies, including cost reductions and improved performance. These collaborations often involved joint research projects, technology transfer agreements, and the sharing of best practices, creating a dynamic environment for innovation and progress in the sector. This collaborative spirit is essential to accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Expanding Scope: Integrating Environmental and Social Factors

Expanding Environmental Considerations
Integrating environmental considerations into business strategies is no longer a niche practice; it's becoming a fundamental necessity. Companies that ignore environmental factors risk not only reputational damage but also significant financial penalties and legal repercussions. Environmental regulations are evolving rapidly, and businesses must adapt to stay compliant and competitive. This includes adopting sustainable practices, reducing waste, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
Understanding and addressing environmental impacts is crucial. A deeper analysis of supply chains, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life product disposal is essential to identify and mitigate potential environmental harm. This proactive approach fosters long-term sustainability and builds a positive brand image.
Sustainable Supply Chains
Sustainable supply chains are critical to minimizing environmental impact. This means scrutinizing every stage of the process, from raw material sourcing to the final product delivery. Transparency and traceability are key elements in building a sustainable supply chain. Tracing materials back to their origin helps ensure ethical sourcing and reduce the risk of environmental damage or exploitation throughout the chain.
Businesses must actively seek out suppliers who share their commitment to sustainability. This collaborative approach fosters a shared responsibility for environmental protection and helps build a more resilient and responsible supply network. This also creates an opportunity for innovation in sustainable materials and practices.
Innovation in Green Technologies
Innovation in green technologies and sustainable materials is a significant driver of environmental progress. Companies can lead by investing in research and development of environmentally friendly solutions. This includes exploring alternative energy sources, developing more efficient manufacturing processes, and creating biodegradable or recyclable products.
Embracing green technologies not only reduces environmental impact but also opens new avenues for growth and innovation. The market for sustainable products and services is expanding rapidly, providing opportunities for businesses to capitalize on this trend and maintain a competitive edge in the long term. This dynamic approach fosters both environmental and economic benefits.
Measuring and Reporting Environmental Impact
Accurate measurement and transparent reporting of environmental impact are essential components of any comprehensive sustainability strategy. This requires establishing clear metrics to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Implementing robust data collection systems and transparent reporting mechanisms is crucial for demonstrating accountability and building trust with stakeholders.
Regularly assessing and reporting on environmental performance helps companies identify areas where they can reduce their impact and improve their environmental stewardship. This process provides valuable insights into operational efficiency and allows for targeted interventions to minimize environmental damage. Ultimately, this detailed approach fosters a culture of environmental responsibility.
The Future of Renewable Energy Reporting: Data Transparency and Collaboration
Data Transparency: A Cornerstone of Trust
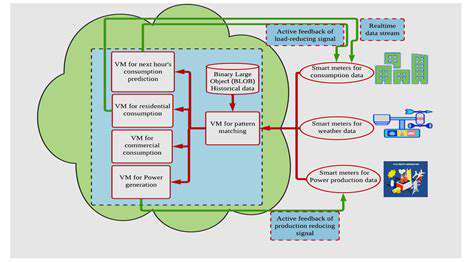
Data transparency is paramount in fostering public trust and enabling informed decision-making regarding renewable energy projects. Detailed, accessible data on energy production, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness is crucial. This transparency should extend to the entire lifecycle, from material sourcing and manufacturing processes to the operational efficiency and decommissioning procedures of renewable energy facilities. Open data standards and easily understandable formats are essential for ensuring that stakeholders, from investors and policymakers to community members and environmental groups, can access and analyze this information effectively.
Collaboration Across Sectors: Driving Innovation
The transition to a renewable energy future hinges on collaboration among various stakeholders. Governments, industry leaders, research institutions, and community groups must work together to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Collaborative platforms and initiatives can facilitate the exchange of data and expertise, accelerating innovation in renewable energy technologies and deployment strategies. This cross-sectoral collaboration will be critical in overcoming technological hurdles and addressing logistical challenges associated with integrating renewable energy sources into existing energy grids.
Standardized Reporting Frameworks: Ensuring Comparability
To facilitate meaningful analysis and comparisons of renewable energy projects, standardized reporting frameworks are essential. These frameworks should encompass key metrics such as energy production, carbon emissions, land use, and economic impacts. Establishing common standards will allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the performance and potential of different renewable energy technologies and deployment strategies. This will enable policymakers to make informed decisions about incentives and regulations.
Improving Data Collection Methods: Enhancing Accuracy
Accurate and reliable data collection methods are critical for producing meaningful renewable energy reports. This includes employing advanced sensor technologies to monitor energy generation and consumption in real-time. Leveraging data analytics and machine learning algorithms can further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of data collection and analysis, providing insights into performance trends and potential areas for improvement. Robust data quality assurance procedures are also necessary to ensure the reliability and integrity of the collected information.
Enhancing Public Engagement: Fostering Understanding
Public engagement is essential for building support for renewable energy projects and ensuring their long-term success. Clear and accessible communication of data and findings is key to effectively engaging communities in the renewable energy transition. Interactive dashboards, educational materials, and public forums can help ensure that the public has a clear understanding of the benefits and challenges of renewable energy projects. Community input and feedback can also play an important role in the design and implementation of these projects.
Technological Advancements: Driving Efficiency
Technological advancements are crucial for improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy systems. Innovations in energy storage, grid management, and smart technologies can significantly enhance the reliability and integration of renewable energy sources into existing infrastructure. Robust data collection and analysis will be essential to track the performance of these technologies and identify opportunities for further improvement. This will contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Accessibility and Interoperability: Breaking Down Barriers
Ensuring data accessibility and interoperability is crucial for maximizing the value of renewable energy reports. Open data platforms and standards will facilitate the sharing of information among stakeholders. Clear data formats and standardized APIs will enable seamless data exchange and integration into existing systems. This will promote collaboration and knowledge sharing, ultimately accelerating the transition to a sustainable energy future and fostering a more informed energy policy landscape.