Offshore Wind and Green Shipping
Harnessing the Power of the Ocean
Coastal winds have long been recognized as a formidable natural resource, but only in recent decades have we developed the technology to harness them effectively. Unlike their land-based counterparts, offshore turbines benefit from stronger, more consistent breezes that sweep across open waters. This reliability translates to higher energy output and fewer fluctuations in power generation. Engineers have made significant strides in designing turbines that can withstand harsh marine conditions while maximizing energy capture.
The evolution of installation techniques has been equally impressive. Specialized vessels now deploy massive turbine components with precision, while advanced anchoring systems ensure stability in deep waters. These innovations have slashed maintenance costs and extended operational lifespans, making offshore projects increasingly attractive to investors. As grid connection technologies improve, we're seeing more efficient ways to deliver this clean energy to population centers.
Environmental Considerations and Impacts
Marine ecosystems present unique challenges for wind farm developers. Careful environmental impact assessments now precede every major project, examining potential effects on everything from seabird migration routes to benthic habitats. Modern mitigation strategies include turbine placement algorithms that avoid critical migration corridors and the use of noise-reducing installation methods to protect marine mammals.
Interestingly, some wind farms have inadvertently created artificial reefs, attracting diverse marine life to their submerged structures. Ongoing monitoring programs track these ecological interactions, providing valuable data for future projects. This commitment to environmental stewardship helps balance energy needs with ocean conservation.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
Port cities are experiencing revitalization as they become hubs for offshore wind operations. The sector has created thousands of skilled positions in turbine manufacturing, maritime operations, and electrical engineering. Local businesses benefit from increased demand for housing, catering, and transportation services as workforce populations grow.
Some coastal communities have established training programs to prepare residents for these new career opportunities. The economic ripple effects extend far beyond the wind farms themselves, with supply chains spanning multiple industries. Revenue sharing agreements are increasingly common, allowing municipalities to fund infrastructure upgrades and public services.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The race to develop larger, more efficient turbines continues unabated. Recent prototypes feature aerodynamic blade designs inspired by natural forms, while modular construction techniques streamline manufacturing. Perhaps most exciting are the floating turbine platforms that unlock wind resources in deeper waters where fixed foundations aren't feasible.
Grid Integration and Energy Storage
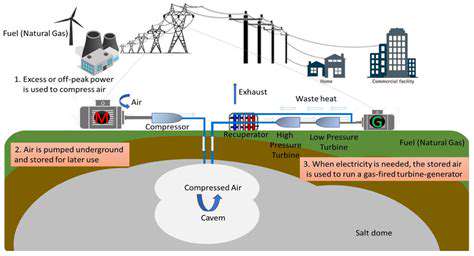
Utilities are developing sophisticated forecasting models to manage wind power's variable nature. Some regions are experimenting with hybrid systems that pair offshore wind with other renewables or storage solutions. Pumped hydro facilities and next-generation batteries help smooth out supply fluctuations, ensuring reliable power delivery.
Advanced high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines now efficiently move offshore power over long distances, minimizing energy losses. These innovations are crucial for integrating large-scale wind generation into national grids.
Policy Support and Regulatory Frameworks
Forward-thinking governments are implementing streamlined permitting processes to accelerate project development while maintaining environmental safeguards. Many have established clear decommissioning guidelines and liability frameworks to ensure responsible end-of-life management.
International cooperation has led to standardized safety protocols and best practices for offshore operations. These policy frameworks provide the stability needed for long-term investment in clean energy infrastructure.
The Technological Advancements Driving the Transition

The Rise of Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning systems are demonstrating remarkable capabilities in pattern recognition and predictive analytics. Healthcare applications now include AI-assisted diagnostics that can detect subtle anomalies in medical imaging, often catching conditions human practitioners might miss. Financial institutions employ similar technology to monitor transactions for fraudulent activity in real time.
Natural language processing has reached a point where AI can generate coherent, context-aware responses that mimic human conversation. This breakthrough has transformed customer service operations across multiple industries. Meanwhile, autonomous systems are becoming increasingly adept at navigating complex environments, from warehouse floors to urban streets.
Enhanced Communication Technologies
The rollout of 5G networks has enabled unprecedented data transfer speeds with minimal latency. This infrastructure supports everything from telemedicine to augmented reality applications. Satellite internet constellations now provide high-speed connectivity to remote regions, bridging the digital divide.
Collaboration platforms have evolved beyond simple video calls to include virtual workspaces with shared whiteboards and real-time document editing. These tools have fundamentally changed how distributed teams coordinate projects across time zones.
Biotechnology Innovations
Gene therapy has moved from experimental treatment to clinical reality, with customized therapies addressing previously untreatable genetic disorders. Researchers are developing techniques to precisely edit DNA sequences, offering hope for curing inherited diseases. The field continues to advance at a remarkable pace, with new applications emerging regularly.
Nanomedicine represents another frontier, with engineered particles delivering drugs directly to target cells while minimizing side effects. These microscopic systems can also serve as diagnostic tools, detecting disease markers at extremely low concentrations.
Sustainable Energy Solutions
Solar panel efficiency continues to climb while production costs decline, making photovoltaic systems accessible to more consumers. Wind turbine designs incorporate advanced materials that withstand extreme weather while maximizing energy capture. Geothermal plants are becoming more efficient at converting Earth's heat into usable electricity.
Energy storage technology has seen particularly dramatic improvements. Next-generation batteries offer greater capacity, faster charging, and longer lifespans - crucial for stabilizing grids with high renewable penetration. These innovations are accelerating the transition away from fossil fuels.
Challenges and Future Outlook

Economic Pressures
Supply chain disruptions continue to affect production timelines across industries. Manufacturers face difficult decisions about reshoring operations versus diversifying international suppliers. Volatile commodity prices complicate long-term planning and investment decisions.
Workforce availability presents another challenge, with skilled labor shortages in many technical fields. Companies are investing more in training programs and considering automation solutions to fill capability gaps.
Technological Advancements
The breakneck pace of digital transformation requires constant adaptation. Organizations must balance the need to adopt new technologies with the practical realities of implementation. Cybersecurity concerns grow more pressing as operations become increasingly connected.
Ethical considerations around AI deployment are sparking important discussions about accountability and transparency. Establishing governance frameworks for emerging technologies remains an ongoing challenge.
Environmental Concerns
Regulatory requirements for sustainability reporting are becoming more stringent. Companies must track and disclose their environmental impact across entire supply chains. Carbon offset programs are evolving, with greater emphasis on verifiable, permanent emissions reductions.
Consumer expectations around corporate environmental responsibility continue to rise, influencing purchasing decisions and brand loyalty. Companies leading in sustainability often see tangible benefits in recruitment and retention as well.
Competition and Market Dynamics
The digital economy has lowered barriers to entry in many sectors, intensifying competition. Established players must innovate continuously to maintain market share against agile startups. Customer expectations for personalized experiences and rapid service continue to escalate.
Differentiation increasingly depends on combining product quality with exceptional service and authentic brand values. Companies that successfully anticipate market shifts can gain significant competitive advantages.
Regulatory Hurdles
Data protection regulations vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating compliance challenges for global operations. Labor laws continue to evolve, particularly regarding remote work arrangements and gig economy workers.
Environmental regulations are becoming more comprehensive, often requiring significant operational adjustments. Proactive compliance strategies can turn these requirements into opportunities for process improvement.
Social and Ethical Considerations
Workforce diversity and inclusion initiatives have moved from optional to essential. Employees and consumers alike expect companies to demonstrate meaningful commitment to social justice causes. Responsible sourcing practices now extend beyond basic compliance to include broader human rights considerations.
Organizations that authentically align their operations with societal values often enjoy stronger employee engagement and customer loyalty. This alignment requires ongoing effort and genuine organizational commitment.