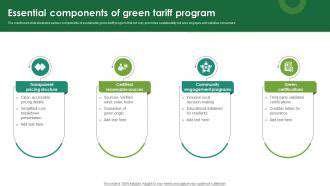
Driving Innovation with Corporate Renewable Procurement
Technological Breakthroughs Reshaping the Sector
The renewable energy landscape has transformed dramatically through continuous innovation. Modern photovoltaic systems achieve efficiencies unthinkable a decade ago, while next-generation wind turbines harness energy from previously untappable wind speeds. Perhaps most remarkably, these advancements coincide with dramatic cost reductions—solar panel prices have plummeted by over 80% since 2010, fundamentally altering the energy economics equation.
Policy Frameworks Driving Change
Forward-thinking governments are implementing multifaceted approaches to accelerate the energy transition. Innovative mechanisms like renewable portfolio standards and production tax credits have proven particularly effective, creating stable investment environments while gradually phasing out fossil fuel subsidies. These policies don't merely encourage adoption—they're restructuring entire energy markets to favor sustainable solutions.
Strategic public investments in R&D are yielding remarkable dividends, with national laboratories and university partnerships producing breakthroughs in energy storage and smart grid technologies. This public-private synergy represents perhaps our most potent tool for achieving long-term sustainability goals.
The New Energy Economy Emerges
The renewable revolution is generating economic benefits that extend far beyond the energy sector itself. Skilled manufacturing jobs are returning to regions that lost traditional industrial employment, while rural communities benefit from new revenue streams through land leases for renewable projects. Energy independence is becoming tangible for nations that previously relied on volatile fuel imports.
Environmental Impacts Beyond Carbon
While climate change mitigation remains paramount, renewables offer additional ecological benefits often overlooked. Compared to fossil fuel extraction, renewable energy projects demonstrate dramatically lower impacts on water resources, air quality, and land use—benefits that compound over project lifespans measured in decades. These advantages extend to public health, with studies showing measurable reductions in respiratory illnesses near renewable installations.
A Global Movement Takes Shape
The renewable transition has become truly global, with developing nations leapfrogging directly to distributed renewable systems rather than replicating Western fossil fuel dependence. International knowledge-sharing platforms and technology transfer agreements are accelerating this process, creating a virtuous cycle of innovation and implementation across borders. This collaborative approach represents our best hope for meeting climate targets while supporting equitable development.
Beyond the Greenwashing: Real Impact Through Procurement
Identifying Authentic Sustainability
Greenwashing remains an unfortunate reality in corporate sustainability claims. The gap between marketing rhetoric and operational reality can be substantial, requiring stakeholders to develop sophisticated evaluation frameworks. True sustainability requires verifiable metrics—third-party certifications, supply chain transparency, and auditable performance data—rather than vague commitments or aspirational statements.
Several red flags indicate potential greenwashing: overemphasis on minor initiatives while ignoring core impacts, reliance on undefined terms like eco-friendly, and absence of time-bound commitments. Savvy organizations now employ specialized auditors to validate sustainability claims throughout their value chains.
The Transparency Imperative
Genuine sustainability requires radical transparency—not just in final products but across entire production cycles. Leading companies now publish detailed environmental impact assessments for major product lines, including full lifecycle analyses from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. This level of disclosure, while challenging, builds authentic credibility with increasingly sophisticated consumers and investors.
The transparency movement is creating ripple effects throughout supply chains. When major purchasers demand verified sustainability data, entire industries adapt—as seen in the textile sector's response to water usage disclosure requirements. This market-driven approach often proves more effective than regulation alone.
Quantification as a Competitive Advantage
Progressive organizations are moving beyond qualitative claims to rigorous quantification. Advanced tools now enable precise measurement of carbon footprints, water usage, and other environmental impacts at the product level. This data-driven approach allows for targeted improvements and credible progress reporting—transforming sustainability from a marketing exercise into a core operational metric.
Sourcing as a Strategic Lever
Innovative procurement teams are reimagining supplier selection criteria to prioritize verifiable sustainability performance. Some forward-thinking manufacturers now require suppliers to demonstrate annual reductions in energy intensity or waste generation as a condition of continued business. This approach creates powerful market incentives for continuous environmental improvement throughout supply chains.
The most advanced organizations are developing supplier sustainability scorecards—comprehensive evaluation frameworks that assess multiple environmental dimensions while accounting for regional differences in infrastructure and capabilities.
Procurement-Led Innovation
Strategic sourcing has emerged as an unexpected driver of technological innovation. By articulating clear sustainability requirements, procurement professionals create market pull for emerging solutions. Several breakthrough technologies—from plant-based packaging to low-carbon concrete—gained critical early adoption through such procurement-led innovation programs.
Collaborative Ecosystems for Impact
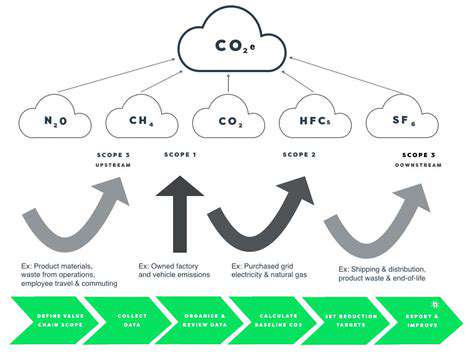
The most significant sustainability gains often emerge from pre-competitive collaboration. Industry consortia are pooling resources to address shared challenges like circular economy implementation or Scope 3 emissions reduction. These collaborative platforms accelerate learning while avoiding redundant investments—a pragmatic approach to systemic challenges that no single organization can solve alone.
Measuring What Matters
Leading organizations are evolving beyond basic sustainability reporting to integrated impact measurement frameworks. These systems connect environmental performance to financial and operational metrics, demonstrating how sustainability initiatives create tangible business value. Such approaches help secure ongoing executive support and investment for ambitious sustainability programs.
Unlocking Growth Opportunities: From Cost Savings to New Markets
Strategic Cost Optimization
Modern cost reduction strategies blend operational efficiency with sustainability gains. Energy efficiency projects, for instance, simultaneously reduce expenses and carbon footprints—a dual benefit that sophisticated organizations now quantify in their capital allocation processes. Waste reduction initiatives similarly create financial and environmental returns, particularly when adopting circular economy principles.
Emerging Market Strategies
Successful market expansion requires nuanced understanding of local sustainability contexts. In developing economies, distributed renewable solutions often prove more viable than replicating centralized grid models. Cultural factors significantly influence adoption rates—for instance, rooftop solar penetration varies dramatically based on local ownership patterns and financing availability.
Technology as an Enabler
Digital transformation is amplifying sustainability gains across operations. IoT-enabled equipment provides real-time energy usage data, allowing for precision optimization. Blockchain solutions are emerging for supply chain transparency, while AI-driven analytics identify unexpected efficiency opportunities. These technologies create compounding benefits when integrated into comprehensive sustainability strategies.
Product Innovation Pathways
The most successful sustainable product launches address multiple consumer needs simultaneously. Electric vehicles succeed not just through environmental benefits but via superior performance and lower operating costs. Similarly, energy-efficient appliances gain market share through quiet operation and smart features alongside energy savings. This multidimensional value proposition is key to mainstream adoption.
Cultivating an Innovation Culture
Sustained innovation requires intentional cultural development. Leading organizations create structured ideation processes while allowing space for experimentation. Some implement innovation sandboxes where teams can prototype solutions without immediate ROI pressures. Others establish clear pathways for employee-driven sustainability initiatives, recognizing that frontline staff often identify the most practical improvement opportunities.
Building a Sustainable Future: Collaboration and Policy Support
Cross-Industry Synergies
The energy transition creates unexpected opportunities for industry convergence. Automotive manufacturers are becoming energy storage providers, while tech companies evolve into energy management platforms. These boundary-crossing innovations often yield the most transformative solutions, as seen in vehicle-to-grid technologies that turn electric car batteries into grid assets.
Policy as a Catalyst
Effective policy frameworks balance ambition with pragmatism. Carbon pricing mechanisms, when properly designed, create consistent market signals without disruptive shocks. Renewable energy standards provide certainty for long-term investments. The most successful policies evolve through regular review cycles, incorporating technological advancements and market feedback.
Investing in Breakthroughs
Strategic R&D investment requires focus on both incremental improvements and moonshot technologies. While efficiency gains in existing renewables remain important, parallel investment in emerging solutions like green hydrogen and advanced nuclear ensures a diversified energy portfolio. Public funding often proves most effective when structured as matching grants that leverage private sector participation.
Engaging Communities
Successful sustainability initiatives increasingly recognize the importance of local context. Community solar programs demonstrate how participatory models can accelerate adoption while ensuring equitable access. Indigenous knowledge is proving invaluable in renewable project siting and ecological impact mitigation. This place-based approach builds enduring support for the energy transition.