The Environmental Benefits of Local Decentralization of Energy Generation
Enhancing Energy Accessibility
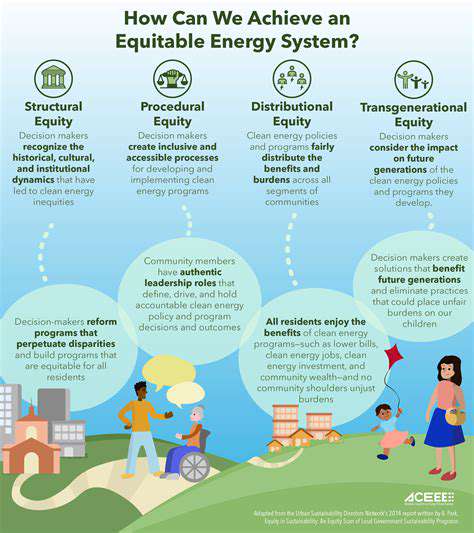
Expanding Energy Availability
Universal energy access represents a fundamental requirement for economic progress and poverty alleviation. Reliable electricity provision transforms communities, enabling access to modern conveniences like food preservation that improve living standards. Expanded energy availability also stimulates local enterprise, creating employment opportunities and fostering regional development.
Transitioning to clean energy sources simultaneously addresses environmental concerns. Renewable solutions like solar home systems and microgrids offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. Energy conservation programs complement these solutions by promoting efficient usage patterns. This combined strategy supports both human development and ecological preservation.
Closing the Energy Divide
Equitable energy distribution remains a critical social justice issue. Vulnerable populations frequently experience energy insecurity, which limits educational attainment, healthcare access, and economic mobility. Targeted policy interventions must address these disparities through customized solutions.
Policy measures should focus on making energy both available and affordable for underserved groups. Supporting community-led energy projects and local capacity building helps create sustainable solutions tailored to specific regional needs.
Sustainable Energy Strategies
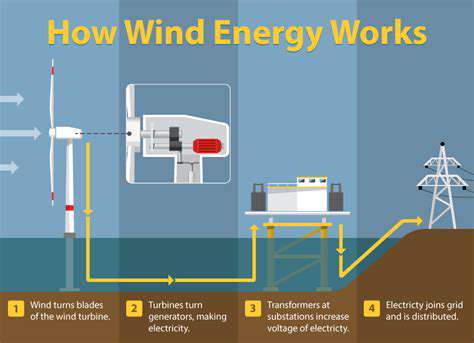
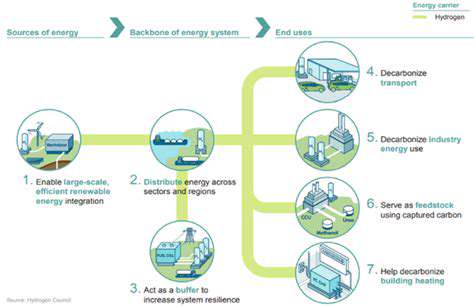
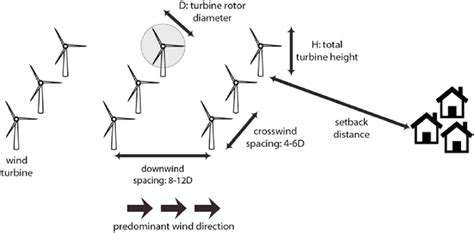
The shift to renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro power is essential for climate protection and energy independence. Strategic investments in renewable technology and supporting infrastructure form the foundation for sustainable energy systems.
Implementing energy efficiency measures and deploying smart grid technologies optimize resource use while minimizing environmental impact. These approaches offer both ecological benefits and economic advantages through job creation and operational savings.
Infrastructure Development
Modern energy systems require robust physical networks and human capital. This includes transmission infrastructure, generation facilities, and distribution channels. Substantial infrastructure investment ensures reliable energy delivery to all communities.
Workforce training programs equip local populations with the technical skills needed to operate and maintain energy systems. Such capacity building empowers communities to manage their own energy futures effectively.
Economic Advantages of Sustainable Energy
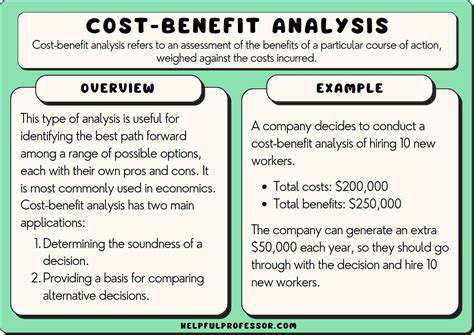
Healthcare Cost Analysis
Evaluating healthcare investments requires careful consideration of both expenses and outcomes. Comprehensive assessments examine direct medical costs alongside secondary impacts like lost work productivity. Truly effective analysis must account for long-term consequences beyond initial expenditure.
Methodologies like incremental cost-effectiveness ratios enable precise measurement of value. These analytical tools inform policy decisions, ensuring optimal use of healthcare resources. Systematic comparison of alternatives guarantees efficient resource allocation.
Chronic Disease Economics
Conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease create substantial financial strain through ongoing treatment needs and reduced productivity. The complete economic picture includes both medical expenses and quality-of-life impacts.
Comprehensive management strategies must address prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. Only integrated approaches can effectively reduce the economic burden of chronic illnesses.
Long-term support services represent another cost dimension, ranging from home care to rehabilitation programs. Understanding these cumulative expenses is essential for developing sustainable healthcare policies. Targeted interventions are crucial for mitigating chronic disease costs.
Economic Decision Factors
Financial considerations influence healthcare choices at individual and systemic levels. Patients balance treatment costs against potential benefits, considering insurance coverage and personal budgets. Thoughtful cost-benefit analysis informs better healthcare decisions.
Providers and policymakers similarly weigh financial implications when selecting treatments and allocating resources. Budget constraints, cost projections, and potential savings all factor into strategic planning. Understanding the relationship between costs and outcomes enables more effective healthcare strategies.