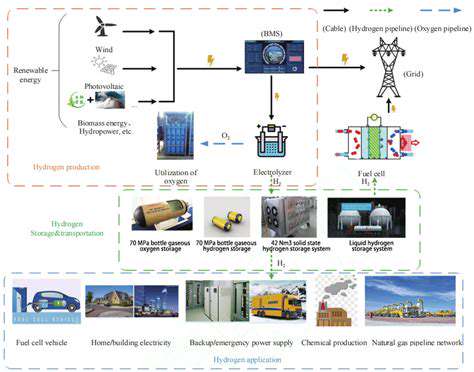
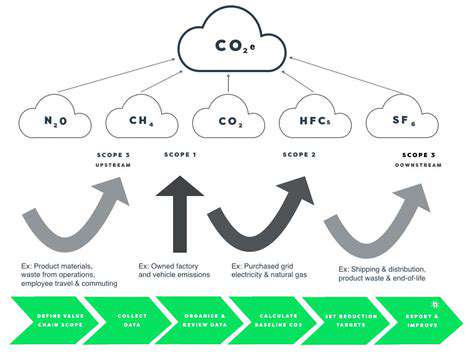
The Role of Cloud Computing in Renewable Energy Data Management
Enhanced Data Processing and Analytics Capabilities
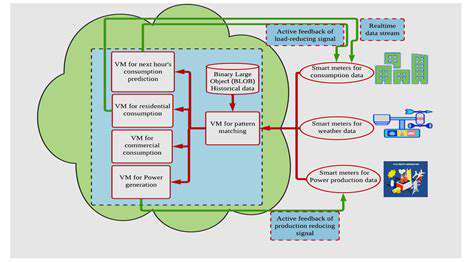
Data Ingestion and Transformation
Efficient data ingestion forms the backbone of any robust data analysis framework. Organizations extract information from diverse sources including relational databases, REST APIs, and CSV files, then standardize it into unified formats for analytical processing. Proper data transformation eliminates inconsistencies while preserving semantic meaning across datasets. Common standardization tasks involve imputing missing values, normalizing measurement units, and resolving schema conflicts.
Comprehensive validation protocols serve as quality checkpoints throughout the transformation pipeline. By implementing automated verification rules, teams can intercept anomalies before they compromise analytical results. This systematic approach to data verification maintains fidelity across the entire analytical workflow. Regular audits of transformation logic further ensure ongoing alignment with business requirements.
Advanced Analytical Techniques
Modern analytics employs sophisticated methodologies including ensemble learning and Bayesian inference to extract meaningful signals from complex datasets. These approaches reveal subtle correlations that traditional statistical methods might overlook, enabling more accurate forecasting and anomaly detection. The application of deep neural networks has particularly revolutionized pattern recognition in high-dimensional data spaces.
Supervised learning models trained on historical observations demonstrate remarkable predictive capabilities for operational planning. When properly validated, these models support data-driven decision making with quantifiable confidence intervals. Their implementation often yields measurable improvements in key performance indicators across various business functions.
Data Visualization and Reporting
Strategic information presentation bridges the gap between technical analysis and executive decision-making. Well-designed visual encodings – from heatmaps to network diagrams – translate multivariate relationships into intuitive representations. These graphical summaries enable stakeholders to quickly grasp complex system dynamics without specialized training.
Interactive analytical interfaces take this further by supporting exploratory data analysis through dynamic filtering and drill-down capabilities. Such self-service tools democratize data access while maintaining governance controls. When integrated with automated reporting systems, they provide timely insights that keep pace with rapidly evolving business conditions.
Data Security and Governance
Protecting sensitive information requires a multi-layered security strategy encompassing encryption, access controls, and activity monitoring. Regular security audits assess vulnerability to emerging threats while ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory standards. Responsible data stewardship builds organizational trust and mitigates legal exposure.
Formal governance frameworks document data lineage, ownership, and permissible use cases. These policies balance analytical needs with privacy requirements through role-based access controls and data masking techniques. Continuous validation checks maintain data integrity throughout its lifecycle, preventing analytical errors from propagating through decision systems.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Leveraging Cloud-Based Analytics for Enhanced Monitoring
Cloud-native monitoring solutions provide unparalleled visibility into distributed renewable energy assets. By processing telemetry streams with subsecond latency, these systems detect operational anomalies as they emerge. Custom dashboards synthesize performance metrics like power conversion efficiency and bearing temperatures into actionable intelligence, enabling rapid response to emerging issues.
The cloud's elastic computing resources facilitate sophisticated pattern recognition across geographically dispersed installations. Advanced change-point detection algorithms identify subtle deviations from expected operating envelopes, often flagging maintenance needs before measurable performance degradation occurs. This capability transforms maintenance strategies from reactive to anticipatory.
Predictive Maintenance Models for Optimized Downtime
Modern prognostic systems combine physics-based modeling with machine learning to forecast equipment reliability. By analyzing multivariate time-series data – including vibration spectra, lubrication quality, and environmental conditions – these models predict remaining useful life with increasing accuracy. Maintenance planners leverage these forecasts to schedule interventions during planned production pauses, avoiding costly unplanned outages.
The financial impact of this approach compounds over time as avoided failures and extended asset lifecycles reduce capital expenditure requirements. Empirical studies demonstrate 30-50% reductions in maintenance costs when transitioning from calendar-based to condition-based maintenance regimes in renewable energy applications.
Remote Monitoring and Expert Support
Geospatial independence proves particularly valuable for offshore wind farms and remote solar installations. Cloud-based monitoring eliminates physical access barriers by streaming operational data to centralized expert teams. Remote diagnostics tools enable engineers to investigate issues using virtual instrumentation, often resolving problems without costly site visits.
Integrated knowledge bases and case-based reasoning systems capture institutional expertise, allowing less experienced personnel to leverage collective organizational knowledge. This institutional memory preservation becomes increasingly valuable as experienced workforces transition toward retirement.
Data Security and Compliance in Cloud-Based Systems
Renewable energy operators must balance operational visibility with cybersecurity requirements. Cloud providers implement defense-in-depth strategies including hardware security modules and network microsegmentation to protect critical infrastructure data. Regular third-party audits validate compliance with NERC CIP, ISO 27001, and other relevant standards.
Data sovereignty considerations influence architecture decisions, particularly for international deployments. Hybrid cloud configurations allow sensitive operational data to remain on-premises while still benefiting from cloud-based analytical capabilities. These implementations demonstrate how modern monitoring solutions can satisfy both operational and regulatory requirements simultaneously.