Unlocking the Power of Renewable Energy
Harnessing the Sun's Power
Solar power, a renewable energy source derived from the sun's radiant energy, presents a compelling alternative to traditional fossil fuels. This clean energy solution taps into an abundant and virtually limitless resource, offering hope for combating climate change and securing a sustainable energy future. Recent technological breakthroughs have dramatically improved solar power systems, making them more efficient and affordable for residential, commercial, and community applications.
The Science Behind Solar Panels
Photovoltaic (PV) cells, commonly known as solar panels, operate on a fascinating principle called the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the silicon-based semiconductor material within these panels, photons transfer their energy to electrons, creating an electrical current. This carefully engineered process allows for direct conversion of sunlight into usable electricity. Different panel technologies offer varying levels of efficiency and cost-effectiveness, giving consumers multiple options to meet their energy needs.
Types of Solar Energy Systems
The solar energy landscape offers diverse solutions tailored to specific requirements. Residential setups typically feature rooftop panels connected to inverters that transform DC electricity into household AC power. In contrast, utility-scale solar farms deploy vast arrays of panels in sun-rich locations to supply electricity to entire communities. Off-grid solar solutions provide complete energy independence, storing power in batteries for use in remote areas or regions with unreliable grid connections.
The Environmental Benefits of Solar Power
Solar energy delivers significant ecological advantages by dramatically reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. Unlike conventional power plants, solar installations produce zero harmful emissions during operation, contributing to cleaner air and water. While the manufacturing process does have environmental implications, ongoing innovations in production techniques and recycling programs continue to minimize this footprint.
The Economic Implications of Solar Adoption
The solar industry has become a major economic driver, creating employment opportunities across manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors. Over time, solar power can lead to substantial energy cost savings, particularly in regions with abundant sunshine. Government incentives like tax credits and rebates have further accelerated adoption, making solar increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources while stimulating local economies.
Wind Power: Tapping into the Kinetic Energy of the Atmosphere

Harnessing the Power of the Wind
Wind energy has emerged as a clean and renewable power source of growing global importance. This technology captures atmospheric kinetic energy to generate electricity, reducing dependence on finite fossil fuels while addressing climate change concerns. Modern wind turbines represent engineering marvels, achieving unprecedented efficiency through aerodynamic blade designs and sophisticated control systems that optimize energy capture from varying wind conditions.
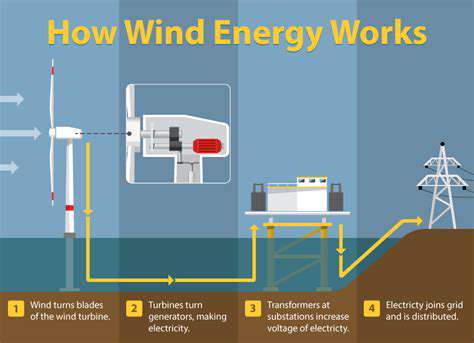
The Mechanics of Wind Turbines
At the core of wind power generation, turbines convert rotational motion into electricity through an intricate mechanical-electrical process. The design of rotor blades represents a triumph of materials science, combining lightweight composites with structural integrity to maximize energy capture. The nacelle houses precision components that ensure smooth operation and maintenance accessibility, contributing to the system's reliability and longevity.
Environmental Benefits of Wind Power
Wind energy offers substantial environmental advantages by eliminating greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Unlike fossil fuel plants, wind turbines produce no particulate emissions that degrade air quality. The transition to wind power has demonstrated measurable improvements in public health outcomes, particularly in reducing respiratory illnesses associated with air pollution.
Economic Impacts of Wind Power Development
The wind energy sector has become a significant economic engine, generating employment across manufacturing, construction, and operations. Investments in wind infrastructure stimulate regional development, creating skilled jobs and supporting ancillary businesses. Many communities have experienced revitalization through wind farm development, with local economies benefiting from increased tax revenue and land lease payments.
Challenges and Future of Wind Power
While promising, wind energy faces technical challenges including intermittency and grid integration issues. Advanced energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies are addressing these limitations. Continued innovation in turbine design and materials promises to further enhance efficiency and reliability, positioning wind power as a cornerstone of future energy systems.
Creating an ideal living space requires careful consideration of both functionality and aesthetics. Thoughtful furniture arrangement and creative use of vertical space can transform any room's ambiance, while decluttering promotes mental clarity and visual harmony.
Beyond Solar and Wind: Exploring Other Renewable Energy Options
Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth's Heat
Geothermal systems utilize the Earth's internal thermal energy, offering consistent and reliable power generation. This technology benefits from stable underground temperatures, making it particularly valuable for baseload power in geologically active regions. While environmental impacts are generally lower than fossil fuels, careful site selection remains crucial to minimize potential ecosystem disturbances.
Hydropower: Harnessing the Power of Water
Water-based energy systems range from massive hydroelectric dams to small-scale micro-hydro installations. While large projects can significantly impact aquatic ecosystems, smaller systems offer sustainable alternatives for rural electrification. Modern engineering approaches aim to balance energy production with environmental protection through fish-friendly turbine designs and improved flow management.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Bioenergy systems convert organic materials into usable energy while addressing waste management challenges. Sustainable biomass operations carefully manage feedstock sources to prevent deforestation and maintain soil health. Advanced conversion technologies continue to improve efficiency while reducing emissions from biomass combustion.
Ocean Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Tides and Waves
Marine energy technologies capture the immense power of ocean movements, though commercial development remains in relatively early stages. Tidal and wave energy converters show particular promise for coastal communities. Ongoing research focuses on improving device durability and reducing maintenance costs in harsh marine environments.
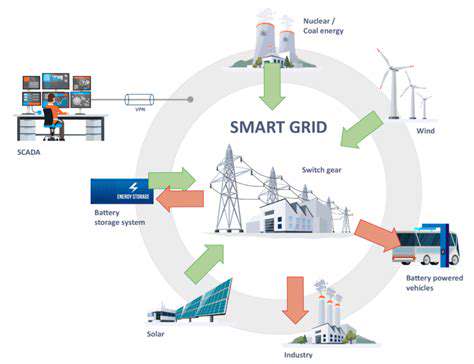
The Crucial Role of Energy Storage and Grid Integration
Enhanced Reliability and Resilience
Advanced energy storage solutions are transforming grid stability by mitigating renewable energy variability. These systems provide critical backup power during outages or generation shortfalls, ensuring uninterrupted electricity supply. Storage technologies have become indispensable for maintaining grid reliability as renewable penetration increases across power networks.
Optimizing Grid Operations and Efficiency
Energy storage enables more efficient grid management by shifting surplus renewable generation to periods of high demand. This capability reduces reliance on peaking power plants and improves overall system efficiency. Storage-integrated smart grids facilitate greater renewable energy utilization while maintaining power quality and reliability standards.