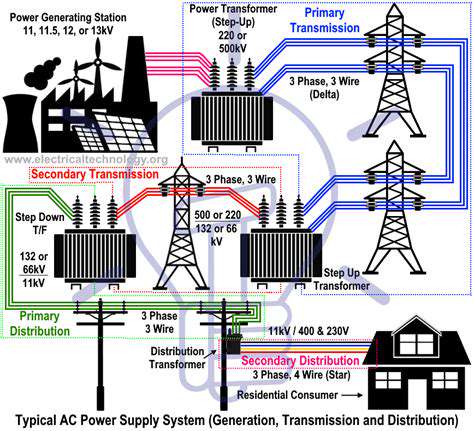
Corporate Renewable Procurement for Multi National Companies
Wind power, another prominent renewable energy source, harnesses the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines, strategically placed in areas with consistent wind patterns, convert wind energy into electrical power. This technology has advanced significantly, leading to more efficient turbines and improved energy capture.
The consistent and predictable nature of wind resources, coupled with the decreasing costs of wind turbine technology, makes wind power an increasingly attractive option for large-scale energy production. This consistency, coupled with the potential for significant energy generation, makes wind power a crucial component in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Hydropower: Harnessing the Power of Water
Hydropower, utilizing the energy of flowing water, has been a significant source of renewable energy for decades. Dammed rivers create reservoirs, and the controlled release of water drives turbines to generate electricity. This method, while established, plays a vital role in many countries' energy mix.
However, the environmental impact of large-scale hydropower projects needs careful consideration. The construction of dams can alter river ecosystems and displace communities, necessitating careful planning and mitigation strategies. Careful environmental assessments and community engagement are essential for responsible hydropower development.
Geothermal Energy: Tapping into Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, converting it into usable energy. Heat from deep within the Earth can be used to generate electricity or directly heat buildings. This technology presents a potentially significant source of renewable energy, particularly in geologically active regions.
While geothermal energy is a powerful option, it's important to note that the accessibility and feasibility of extraction vary greatly depending on geological conditions. Proper assessment of these conditions is crucial for successful geothermal energy projects.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as wood, agricultural residues, and municipal waste, to produce energy. These sources can be converted into biofuels or burned directly to generate heat and electricity. This method offers an alternative source of energy in regions with readily available biomass resources.
However, the sustainability of biomass energy relies heavily on responsible sourcing and management practices. Unsustainable harvesting practices can negatively impact ecosystems and food security. Carefully managed and sustainable biomass practices are crucial to the long-term viability of this renewable energy source.
Ocean Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Tides and Waves
Ocean energy sources, including tidal and wave energy, offer the potential for harnessing the immense power of the oceans. Tidal currents, predictable and consistent in many locations, can be used to generate electricity. Similarly, wave energy, derived from the motion of waves, can also be converted into usable energy.
Despite the potential, ocean energy technologies are still developing and face challenges related to cost-effectiveness and technological advancement. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of this renewable energy source.
The Future of Renewable Energy: A Bright Outlook
The future of renewable energy is undoubtedly bright. Continued advancements in technology, coupled with increasing public awareness and governmental support, are driving the transition toward a sustainable energy system. This transition is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change and securing a more stable and environmentally conscious future for all.
The integration of Renewable energy sources is not just an environmental necessity; it's also a significant economic opportunity. Job creation, economic growth, and improved energy security are all potential benefits of a global shift towards renewables.
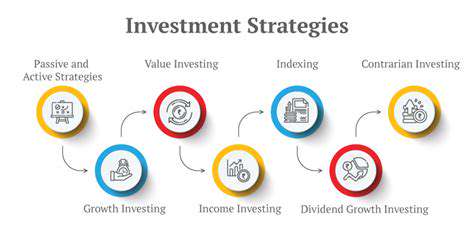
Developing a Robust Renewable Procurement Strategy
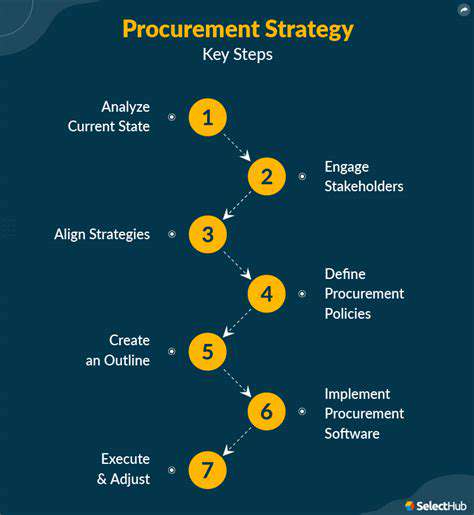
Understanding the Fundamentals of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources, like solar, wind, and hydro, are crucial for a sustainable future. These resources are replenished naturally, unlike fossil fuels, and their use significantly reduces our reliance on finite resources. Understanding the core principles behind these technologies is essential for developing effective and efficient renewable energy systems. This involves examining the mechanisms of energy conversion and storage, the environmental impacts, and the economic viability.
Renewable energy sources are not without their challenges. Intermittency, for example, is a significant hurdle in solar and wind power, requiring innovative solutions for energy storage and grid management. Furthermore, the initial investment costs for some renewable projects can be substantial, posing a financial barrier for widespread adoption.
Assessing the Technical Viability of Projects
A crucial aspect of renewable project development is a thorough technical assessment. This involves evaluating the site's suitability for different renewable technologies, considering factors like sunlight hours, wind speeds, and water flow rates. Accurate data collection and analysis are vital for predicting the long-term performance and output of the project.
Detailed engineering designs are essential for ensuring the project's technical feasibility and safety. This includes careful consideration of the project's environmental impact, including potential habitat disruption and the need for mitigation strategies.
Economic Considerations for Renewable Energy Projects
The financial viability of renewable energy projects is a critical factor in their success. This includes analyzing the upfront capital costs, operational expenses, and potential returns on investment. Project financing strategies and government incentives play a crucial role in making renewable energy projects economically attractive. The long-term cost-benefit analysis is also a key element to consider.
Understanding the market demand for the energy generated is crucial. Factors like the cost of competing energy sources, the regulatory environment, and the availability of incentives all impact the profitability of the project.
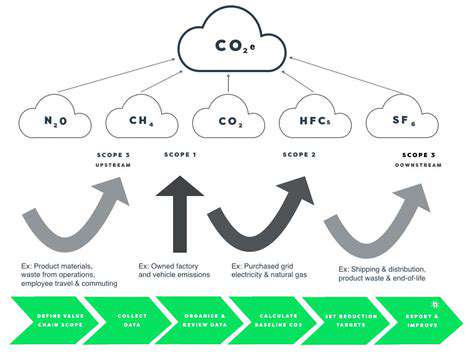
Environmental Impact Assessment and Mitigation
Environmental impact assessments are essential for identifying and mitigating the potential environmental consequences of renewable energy projects. This includes analyzing the project's impact on local ecosystems, water resources, and air quality. Careful planning and implementation of mitigation strategies are necessary to minimize negative impacts on the surrounding environment.
Minimizing the project's impact on biodiversity and habitats is paramount. This might involve careful site selection, habitat restoration, or the implementation of noise control measures. These environmental safeguards are essential for long-term sustainability.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the development and deployment of renewable energy. Favorable policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, can significantly encourage investment in renewable projects. Regulations regarding permitting, environmental standards, and grid integration are also critical elements.
Understanding the nuances of local and national regulations is crucial for navigating the complexities of project development. This includes staying informed about potential changes in policy and adapting project plans accordingly.
Community Engagement and Stakeholder Management
Successful renewable energy projects require strong community engagement and effective stakeholder management. This involves proactively engaging with local communities to address concerns and build trust. Open communication and transparency are vital for ensuring that projects are perceived as beneficial and sustainable. Addressing concerns about potential impacts on property values, noise, and visual aesthetics is crucial for project acceptance.
Community involvement can lead to innovative solutions and encourage collaborative problem-solving. Building strong relationships with local residents and businesses is a crucial step in the project development process.
Financing and Investment Strategies
Securing adequate financing is a critical step in developing renewable energy projects. This involves exploring various financing options, including government grants, private investment, and public-private partnerships. Attracting investors requires showcasing the project's long-term viability and potential returns. Developing a robust financial model is essential for demonstrating the project's profitability and securing funding.
Understanding different investment structures and the associated risks is crucial. Due diligence and careful risk assessment are essential components of a successful financing strategy.