Advanced Materials for Wind Turbine Blades: Lighter, Stronger, Recyclable
Addressing the Recyclability Challenge: Designing for Circularity
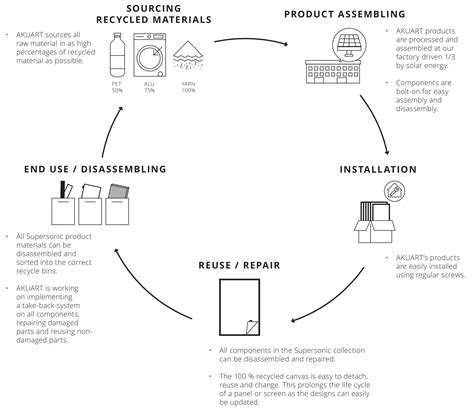
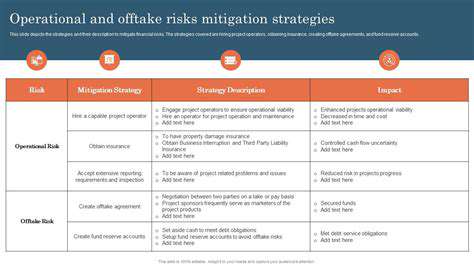
Understanding the Complexity of Recyclable Materials
The recyclability of materials is a multifaceted issue, encompassing a wide range of factors from the composition of the material itself to the infrastructure available for collection and processing. Different materials exhibit varying degrees of recyclability, and this complexity often leads to challenges in efficient and effective recycling programs. Understanding these complexities is crucial to developing sustainable solutions for waste management.
Numerous factors influence the recyclability of a material, including the presence of contaminants, the manufacturing process used, and the overall design of the product. For instance, a plastic bottle containing food residue or a metal container with paint residue might be difficult to recycle because of the contamination.
The Impact of Contamination on Recycling
Contamination is a significant obstacle to successful recycling. Even small amounts of non-recyclable materials can render an entire batch of recyclables unusable, resulting in significant economic and environmental losses. Contaminated recyclables often end up in landfills, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion.
Contamination can be introduced at various stages of the recycling process, from improper sorting at the source to inadequate cleaning procedures at processing facilities. Minimizing contamination requires a multi-faceted approach, including educating consumers about proper recycling practices and investing in advanced sorting technologies.
The Role of Design in Material Recyclability
Product design plays a critical role in determining the recyclability of materials. Products that are designed with recyclability in mind are more likely to be effectively recycled and contribute to a circular economy. For example, the use of standardized materials, modular designs, and easily separable components can significantly enhance recyclability.
The Importance of Infrastructure for Recycling
Adequate infrastructure is essential for efficient recycling. This includes well-maintained collection systems, processing facilities, and markets for recycled materials. Without sufficient infrastructure, recycling efforts can be hampered, resulting in lower recycling rates and increased waste generation.
Investing in infrastructure improvements, including upgrading sorting technologies and expanding processing capacity, is crucial for enhancing recycling rates and achieving a more sustainable future.
Economic Incentives and Barriers to Recycling
Economic factors significantly influence recycling rates. The market price of recycled materials can affect the profitability of recycling programs, and fluctuating prices can create instability in the industry. Government policies and subsidies can play a crucial role in promoting recycling activities and creating a more favorable economic environment.
Incentivizing consumers to participate in recycling programs, such as providing rebates or deposit-refund schemes for specific materials, can also stimulate recycling rates.
Consumer Awareness and Education
Consumer awareness and education are fundamental to effective recycling programs. Educating consumers about proper sorting techniques, the types of materials that can be recycled, and the importance of minimizing contamination is crucial for improving recycling rates. Clear and accessible information about recycling guidelines can significantly impact consumer behavior and promote sustainable practices.
Public awareness campaigns and educational programs can play a significant role in raising awareness and fostering a culture of responsible waste management.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Technological advancements offer promising solutions for enhancing recycling processes. New sorting technologies, advanced materials analysis techniques, and innovative recycling methods are constantly being developed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling. These advancements have the potential to significantly reduce contamination rates, improve material recovery, and create new markets for recycled materials.
Continued research and development in the field of recycling technology are crucial for driving further innovation and achieving greater sustainability in resource management.