Solar Energy Advancements for Remote Power
Perovskite Solar Cells: A Promising Future
Perovskite solar cells are gaining attention for their potential to boost efficiency and lower costs. Made from hybrid organic-inorganic materials, these cells absorb light exceptionally well. Researchers are working to improve their stability for broader use. Their low production costs and high efficiency could make them a game-changer.
Organic Solar Cells: Flexibility and Low-Cost Potential
Organic solar cells (OSCs) use carbon-based materials, offering flexibility and lightweight designs. They can be produced cheaply using solution-based methods, making them ideal for niche applications. However, improving their efficiency and longevity remains a focus for researchers.
Concentrated Photovoltaics (CPV): Maximizing Energy Capture
CPV systems use lenses to focus sunlight onto small, high-efficiency cells. This method achieves greater efficiency than traditional panels, especially in sunny regions. While initial costs are higher, CPV’s energy output per area makes it a strong contender for specific applications.
Ongoing research aims to lower costs and improve scalability, broadening CPV’s potential.
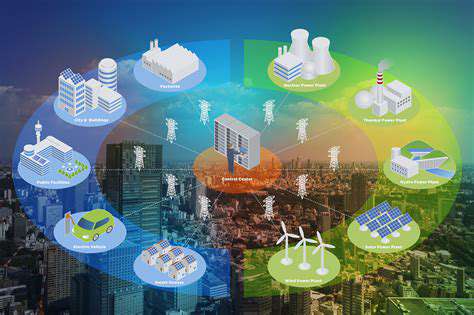
Smart Grid Integration and Remote Monitoring: Optimizing Solar Systems

Smart Grid Integration: A Necessity for Modern Infrastructure
The adoption of smart grids is critical for modern energy systems. These grids use digital technology to optimize power distribution, enhance reliability, and integrate renewable sources like solar. Real-time monitoring allows for proactive energy management, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Remote Monitoring and Control Capabilities
Remote systems enable operators to manage power grids from a central location. This real-time oversight minimizes outages and ensures stable energy delivery. It also allows for dynamic adjustments based on demand, saving costs for both utilities and consumers.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite their benefits, smart grids face obstacles like high upfront costs and cybersecurity risks. Protecting these systems from attacks is essential to maintaining grid reliability. Collaboration among stakeholders is key to overcoming these challenges.
Economic Benefits of Smart Grids
Smart grids reduce operational costs and lower electricity bills. They also support renewable energy growth, creating jobs and boosting the economy. Improved grid resilience further safeguards against financial losses from outages.
Future Trends and Innovations
Artificial intelligence and blockchain are set to revolutionize smart grids. AI will enhance predictive capabilities, while blockchain could enable decentralized energy trading. These innovations promise a more efficient and sustainable energy future.
Future Trends and Applications: Expanding the Reach of Solar Power
Harnessing the Power of AI for Optimized Solar Systems
AI-driven analytics can optimize solar panel performance by analyzing weather and usage data. Predictive maintenance helps prevent failures, ensuring consistent energy output. AI also improves large-scale solar farm management, balancing energy distribution across the grid.
The Integration of Solar with Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grids are essential for managing solar energy’s variability. Real-time monitoring ensures stable integration with other energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This synergy supports a more sustainable power infrastructure.
Decentralized Solar Energy Systems: Empowering Communities
Local solar installations reduce dependence on centralized grids. These systems enhance energy security and affordability, particularly in remote areas. They also create local jobs, fostering economic growth.
Solar-Powered Transportation: Electrifying the Future of Mobility
Solar energy is making inroads in transportation, powering cars, buses, and ships. As technology advances, solar vehicles will play a bigger role in cutting emissions. Improved storage solutions will extend their range and practicality.
Advancements in Solar Panel Technology: Enhancing Efficiency and Affordability
Ongoing research is making solar panels more efficient and cheaper. Innovations in materials and manufacturing are driving down costs, making solar energy accessible to more people. These developments are accelerating the shift to renewable energy globally.