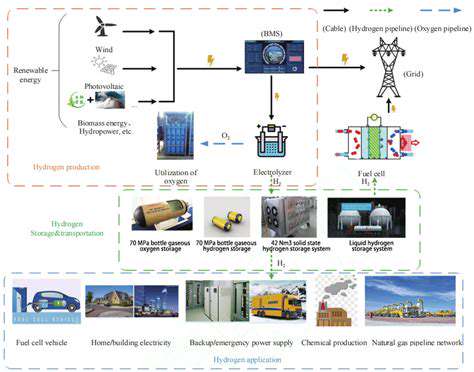
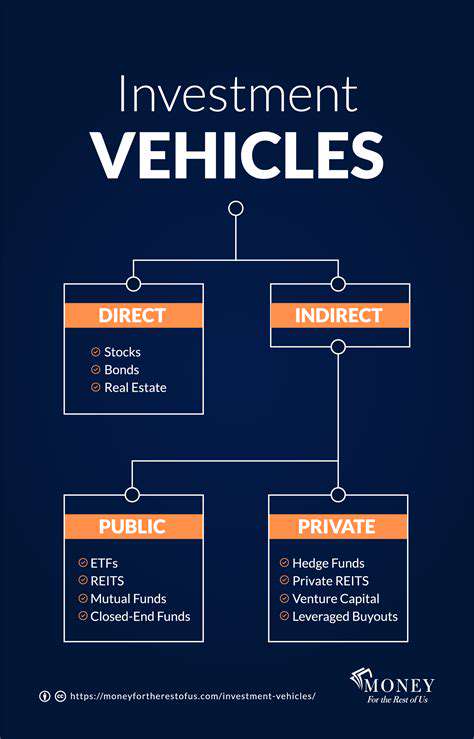
Scaling Up Decentralization of Energy Generation Initiatives

Overcoming Technological Barriers to Scalability
Defining Technological Barriers
Technological barriers to scalability in decentralized energy systems are complex and often interwoven. These obstacles span from existing hardware and software constraints to the intricate task of merging diverse energy sources and overseeing distributed energy resources. Tackling these foundational technological challenges is vital for the broad acceptance and sustainable expansion of decentralized energy solutions.
Concrete instances include current communication networks' bandwidth constraints, which may impede the smooth transfer of data needed for instantaneous grid management. Another pressing issue is the compatibility of various decentralized energy technologies, potentially causing inefficiencies when integrating different systems.
Data Management and Communication
Efficient data handling is critical for peak performance and scalability in decentralized energy setups. Instantaneous data sharing among distributed energy resources, storage systems, and the wider grid demands sturdy communication protocols and secure data storage solutions. Surmounting these hurdles entails crafting sophisticated data analytics tools and algorithms to manage large datasets and bolster smart grid operations.
Interoperability and Standardization
The absence of interoperability among diverse decentralized energy technologies presents a major obstacle to scalability. Uniform protocols and interfaces are indispensable for the smooth incorporation of assorted renewable energy sources, storage options, and smart grid elements. This standardization will pave the way for a more effective and dependable decentralized energy network.
Additionally, ensuring interoperability across various hardware and software platforms is key for the uninterrupted functioning of decentralized energy systems. This necessitates cooperation among stakeholders and the creation of universal standards that guarantee compatibility across different systems.
Energy Storage Solutions
Scalable and dependable energy storage options are essential to counterbalance the variable nature of renewable energy sources. Creating affordable and efficient storage technologies, such as next-gen batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal energy storage, is crucial for maintaining a steady energy supply and grid stability.
Further advancements in energy storage technology are imperative to improve the reliability and scalability of decentralized energy systems. This involves investigating novel methods to maximize storage capacity and cut expenses, making decentralized solutions more accessible.
Security and Privacy Concerns
The growing dependence on digital technologies in decentralized energy systems brings notable security and privacy issues. Strong cybersecurity protocols are needed to safeguard sensitive data, block unauthorized entry, and uphold the trustworthiness of energy transactions. A secure digital framework is fundamental for fostering trust in decentralized energy systems.
Computational Resources and Algorithms
The intricate dynamics and real-time operations within decentralized energy systems demand substantial computational power and sophisticated algorithms. Effective algorithms for optimizing energy distribution, managing storage, and responding to grid variations are pivotal for ensuring system stability and dependability. Developing scalable computational resources capable of handling rising data volumes and complexity is essential for future progress.
Cybersecurity Protocols and Standards
Creating robust cybersecurity protocols and standards is critical for protecting the integrity and security of decentralized energy systems. Deploying encryption methods, intrusion detection systems, and access control measures is vital to counter cyber threats and shield critical infrastructure. Ongoing monitoring and updates of cybersecurity practices are necessary to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches in decentralized energy systems.

Policy Frameworks and Regulatory Support
Policy Incentives for Renewable Energy
Governments can introduce appealing financial incentives to promote the uptake of renewable energy technologies. These incentives might include tax breaks, subsidies, and grants for investments in solar panels, wind turbines, and storage systems. Such measures not only spur private investment but also hasten the shift to a decentralized energy grid by enhancing the economic appeal of renewables over fossil fuels. This is key for expanding decentralized energy generation, fostering competition, and spurring innovation in the field.
Moreover, transparent regulatory frameworks should be established to simplify the permitting and grid connection of distributed energy resources (DERs). Smoother procedures will lessen bureaucratic hurdles and encourage broader involvement in decentralized energy generation, a critical factor in scaling this transformation.
Regulatory Clarity on Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Ambiguities in the regulatory framework for distributed energy resources (DERs) can stall the widespread adoption of decentralized energy generation. A clear and uniform regulatory landscape is needed to tackle issues like grid integration, net metering, and managing the variable energy supply from distributed sources. This clarity will offer vital certainty for investors and developers, boosting investment and innovation in this area.
Specific regulations should address the distinct challenges posed by decentralized generation, such as fluctuating power output, grid stability, and energy storage management. Resolving these issues through supportive policies will cultivate a more favorable environment for decentralized energy growth.
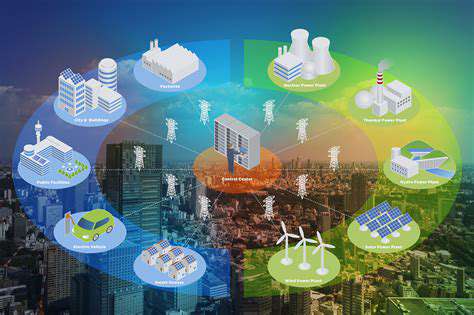
Grid Modernization and Interconnection Standards
Existing grid infrastructure often poses challenges for the seamless integration of decentralized energy sources. Upgrading current grid systems to accommodate variable renewables is essential. This includes modernizing transmission and distribution networks, enhancing grid stability, and deploying advanced control systems to manage energy flow from multiple distributed generation points. Investing in smart grid technologies will be crucial for the smooth incorporation of decentralized energy systems.
Support for Energy Storage Technologies
Decentralized energy systems frequently depend on intermittent renewables, making energy storage solutions necessary. Policies backing the advancement and deployment of storage technologies are vital for grid stability and reliability. This support could involve financial incentives for developing and implementing advanced battery technologies, pumped hydro storage, or other suitable solutions. This will enable better handling of power generation fluctuations from renewable sources.
Community-Based Energy Programs and Policies
Policies that promote and support community-based energy initiatives are pivotal for scaling up decentralized energy generation. These programs can empower communities to actively engage in the transition to renewables, fostering local ownership and control over energy resources. Policies should ease the establishment of community-owned renewable energy projects, allowing greater resident involvement in energy production and consumption decisions. Such measures can lead to a more sustainable and equitable energy future for communities.
Public Awareness and Education Initiatives
Boosting public understanding and engagement with decentralized energy solutions is crucial for successful implementation. Public education campaigns can clarify misconceptions about the technology and emphasize its benefits. These efforts can cultivate public backing for policies that encourage decentralized energy generation. Providing clear, accessible information about the advantages of local energy production, cost savings, and environmental benefits is key to fostering public acceptance and driving broader adoption of decentralized energy systems. This will help create an informed and supportive public to champion this important shift.