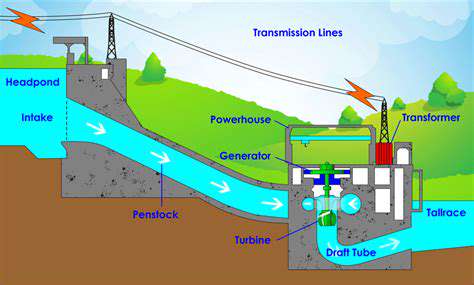
Offshore Wind Permitting Process
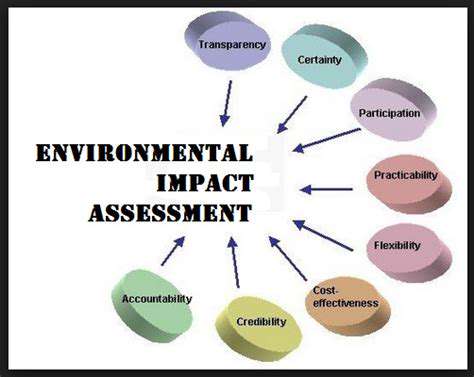
Understanding the Importance of Environmental Impact Assessments
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) serve as vital evaluation tools for proposed development projects. These systematic frameworks identify, predict, and mitigate potential ecological consequences. Through comprehensive analysis, EIAs promote sustainable development while minimizing environmental disruption. The assessment process facilitates informed decision-making that balances economic objectives with ecological preservation requirements.
EIA methodologies examine numerous environmental factors including air quality metrics, water purity levels, and biodiversity indexes. By analyzing complex ecological relationships, these assessments predict potential system disturbances and longitudinal effects.
Key Components of a Comprehensive EIA
Thorough EIAs incorporate several essential elements: detailed project descriptions, baseline environmental conditions, and projected post-implementation changes. Impact identification analyzes both beneficial and adverse effects across multiple environmental dimensions. This includes specialized evaluations of potential human health implications and community wellbeing factors.
Robust mitigation strategy development represents a fundamental EIA component, demonstrating proactive environmental stewardship. Final assessments provide concise conclusions with actionable recommendations for project modification.
EIA and Sustainable Development
Environmental assessments directly support sustainable development principles. Sustainability requires meeting current needs without compromising future generations' resource availability. EIAs mediate between development requirements and environmental protection mandates through comprehensive analysis.
Incorporating sustainability metrics throughout project lifecycles enhances long-term ecological outcomes. Assessments should evaluate all phases from initial planning through final decommissioning procedures.
EIA and Public Participation
Stakeholder involvement significantly strengthens environmental assessment processes. Including community members, advocacy groups, and technical experts ensures diverse perspective integration. Transparent communication protocols establish essential trust throughout assessment phases, while public forums enable comprehensive concern addressing.
Regulatory Frameworks and EIA
Jurisdictional regulations mandate EIAs for specific project categories, with requirements varying by location and project scope. Compliance with established procedures maintains assessment integrity. Adherence to regulatory timelines and reporting standards ensures EIA process effectiveness.
Challenges and Future Directions
EIA implementation faces ongoing challenges including data collection limitations in dynamic environments. Advanced analytical techniques improve impact prediction accuracy and mitigation strategy development. Future assessments must incorporate emerging scientific research while expanding stakeholder participation mechanisms.
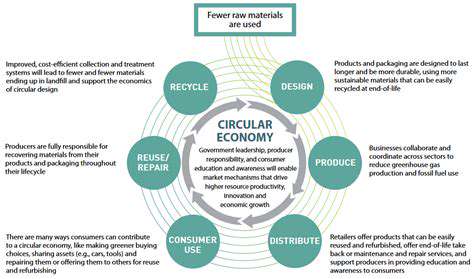
Transitioning to circular economic models offers multiple benefits: decreased environmental degradation, enhanced resource stability, and novel economic opportunities. Waste reduction strategies help protect ecosystems while addressing climate change concerns. The economic potential proves particularly significant as circular systems generate innovative markets for recycled materials and specialized services.
Community Engagement and Stakeholder Consultation
Community Outreach Initiatives
Effective community engagement establishes essential relationships for organizational success. Proactive outreach involves direct resident interaction, need assessment, and demonstrated commitment to community welfare. Participation in local activities and sponsorship of community programs builds mutual trust. Visible community investment fosters shared responsibility and regional vitality.
Establishing accessible communication channels facilitates resident input through multiple formats. Transparent information exchange ensures community members feel valued and respected, strengthening organizational-community bonds and collaborative potential.
Stakeholder Collaboration
Successful stakeholder integration creates synergistic operational environments. Recognizing diverse stakeholder perspectives enables comprehensive solution development. Open discussion forums and active listening techniques incorporate varied viewpoints into project planning.
Strategic partnerships with local enterprises facilitate resource sharing and cooperative initiatives. Collaborative approaches amplify project impacts while delivering community-wide benefits.
Building Trust and Transparency
Trust development requires consistent, transparent community interaction. Clear communication of organizational objectives and decision rationales establishes essential credibility. Regular updates and accessible feedback mechanisms demonstrate accountability and responsiveness.
Measuring Impact and Adapting Strategies
Continuous evaluation of engagement initiatives enables performance optimization. Data collection on participation metrics and community impacts identifies successful approaches and improvement areas. Strategy adaptation based on collected data ensures ongoing relevance to evolving community needs, demonstrating organizational flexibility and commitment.
Project Timeline and Cost Considerations
Project Timeline
Offshore wind development timelines vary significantly based on location-specific factors. The multi-phase process includes site evaluations, feasibility analyses, permit acquisitions, financing arrangements, construction phases, and operational commencement. Precise timeline projections enable effective resource management and financial planning.
Permitting Process Timeline
Permitting procedures often require multiple years for completion due to regulatory complexity. Local requirements, environmental reviews, and public consultation processes influence duration. Early regulatory engagement and detailed preparation help minimize potential delays.
Cost Considerations: Initial Investment
Substantial upfront investments cover site assessments, engineering designs, environmental studies, and permitting expenses. Offshore infrastructure development including port facilities and transmission systems represents significant capital requirements.
Cost Considerations: Construction and Operations
Construction expenditures encompass turbine fabrication, marine installation, and supporting infrastructure. Long-term operational budgets must account for maintenance requirements, personnel costs, and potential repairs. Material cost fluctuations necessitate flexible financial planning.
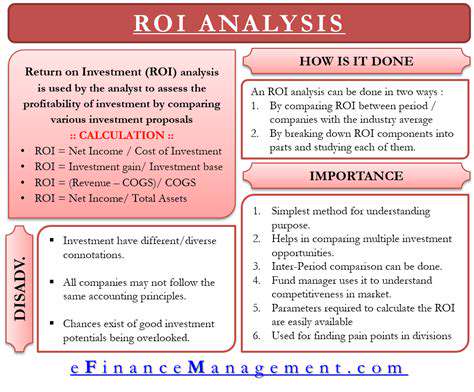
Financial Projections and Risk Assessment
Comprehensive financial models evaluate project viability by analyzing all cost components against projected revenues. Risk evaluations consider energy price volatility, regulatory changes, and technological developments.
Contingency Planning and Budget Management
Contingency reserves address potential cost overruns and schedule delays. Continuous expenditure monitoring and financial reporting maintain fiscal control throughout project implementation.