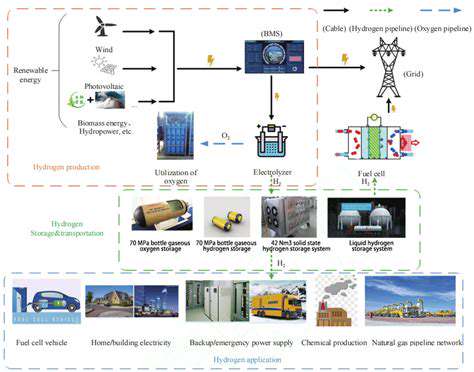
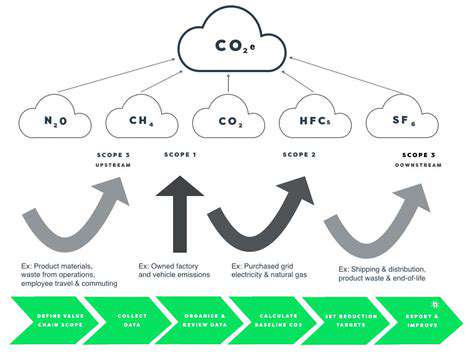
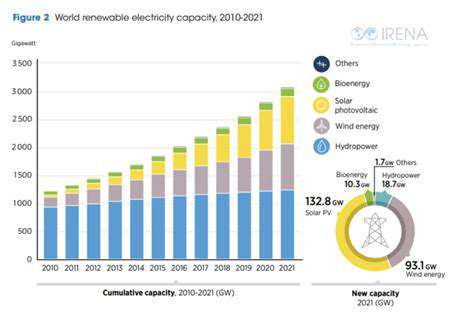
Microgrids: Building Decentralization of Energy Generation
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): Solar arrays, wind turbines, and fuel cells
- Storage Systems: Lithium-ion battery banks and flywheel energy storage
- Smart Controls: AI-driven management systems that balance supply/demand in milliseconds
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology's microgrid demonstrates this integration perfectly. Its neural network controller processes 15,000 data points per second to optimize power flows between solar canopies, battery banks, and building loads.
Challenges in Microgrid Development
Despite advantages, deployment hurdles persist. Interoperability remains the Achilles' heel—when a New York microgrid attempted to integrate three different battery brands, engineers spent six months developing custom interfaces. Upfront costs also deter adoption; a typical community microgrid requires $2-5 million initial investment.
Regulatory ambiguity compounds these challenges. In Texas, conflicting municipal and state codes delayed a microgrid project for 18 months. Standardized policies and creative financing models—like Connecticut's Green Bank partnerships—are proving essential for scaling adoption.
Future of Microgrids in Energy Systems
The microgrid revolution is accelerating. Market analysts project 20% annual growth through 2030, driven by climate concerns and grid vulnerabilities exposed during recent blackouts. Emerging technologies like solid-state batteries and hydrogen fuel cells promise to enhance future systems.
California's wildfire-prone communities provide a glimpse of this future. After 2020 blackouts, 47 towns installed microgrids; when fires struck again in 2022, these communities maintained power while surrounding areas went dark. This resilience—coupled with plunging renewable costs—ensures microgrids will anchor tomorrow's decentralized energy infrastructure.
Beyond Grid Reliance: Enhanced Resilience and Reliability
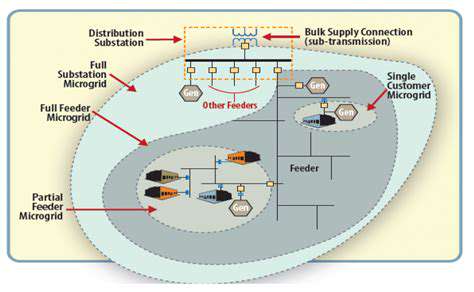
Beyond the Limitations of Traditional Grids
Conventional power grids resemble spiderwebs—efficient until damaged. When Hurricane Maria devastated Puerto Rico, the centralized grid took 11 months to fully restore, while the Adjuntas microgrid powered critical services within hours. This vulnerability stems from centralized architecture where single points of failure can collapse entire regions.
Embracing Flexibility and Adaptability
Modern microgrids employ military-grade resilience strategies. The U.S. Army's Fort Bragg microgrid, designed to withstand electromagnetic pulses, showcases this adaptability. Its hybrid design seamlessly switches between solar, generators, and batteries—maintaining operations during 72-hour grid outages.
Leveraging Advanced Layout Techniques
Cutting-edge microgrids now incorporate predictive analytics. Using weather data and usage patterns, Hawaii's Maui microgrid anticipates cloud cover 30 minutes ahead, pre-charging batteries to smooth solar output. This precision control reduces diesel backup needs by 40%.
Exploring New Frontiers in Design
The next evolution involves swarm grids—independent microgrids that can interconnect dynamically. In Bangladesh, 100+ solar microgrids now form adaptive clusters, sharing power across villages based on real-time needs. This biological approach to grid design may revolutionize rural electrification.
Economic Benefits and Community Engagement
Economic Benefits of Decentralized Microgrids
Microgrid economics defy conventional wisdom. While initial investments average $3,000 per kW, Alaskan villages recoup costs in 3-5 years by eliminating costly diesel shipments. Brooklyn's TransActive Grid demonstrates how peer-to-peer energy trading can yield 15-20% returns for residential participants.
Community Engagement and Empowerment
When Puerto Rico's Casa Pueblo community built their solar microgrid, they didn't just gain electricity—they gained agency. Residents now manage the system through a cooperative model, reinvesting profits in local schools. This participatory approach has been replicated in 12 other communities.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable integration reaches new heights in microgrids. The Falkland Islands' 3MW wind-diesel hybrid system achieves 60% renewable penetration—unthinkable in conventional grids. Advanced inverters enable this by maintaining stable frequency despite wind variability.
Improved Reliability and Resilience
Reliability metrics speak volumes. After installing microgrids, a Michigan hospital reduced generator runtime from 200 hours/year to just 6. For data centers, microgrids deliver five nines (99.999%) reliability—far surpassing the traditional grid's 99.97%.