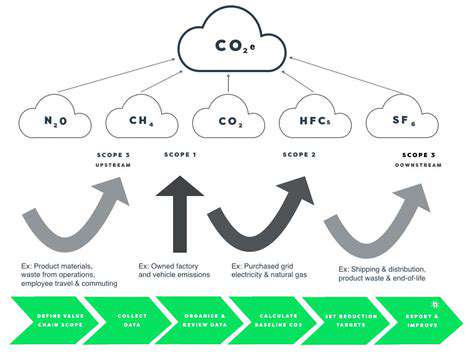
Energy Storage in Emerging Markets
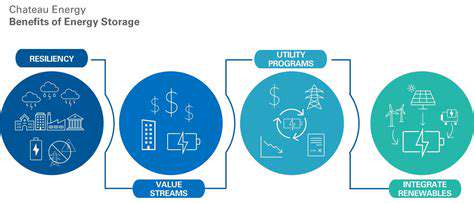
Global energy markets are witnessing unprecedented transformation as nations grapple with climate commitments. Renewable energy adoption accelerates daily, yet its variable output creates complex grid management challenges. Storage technologies now stand as the linchpin for successful renewable integration, allowing excess generation to be banked for later use. Engineers compare this to having a savings account for electrons rather than living paycheck to paycheck.
This storage imperative transcends technical specifications - it represents the missing link in our decarbonization puzzle. Grid operators increasingly view storage capacity as essential infrastructure, akin to transmission lines or substations. Recent blackout events in developing nations demonstrate how storage can prevent economic losses exceeding $100 million per incident.
Technological Breakthroughs Reshaping the Sector
Battery chemistry innovations occur at remarkable speed, with lithium-ion variants achieving 90% cost reductions since 2010. Researchers at MIT recently demonstrated solid-state prototypes with triple the energy density of conventional cells. These advancements enable storage solutions that were unimaginable a decade ago.
Traditional methods like pumped hydro continue evolving too. Norwegian engineers have developed modular underwater systems that use seawater instead of mountain reservoirs. Such adaptations make proven technologies viable in diverse geographical contexts.
Cross-Industry Transformation Underway
Transportation sectors experience the most visible storage revolution. Electric buses in Shenzhen now outnumber diesel models, each carrying battery packs equivalent to 50 Tesla vehicles. This shift creates ripple effects across mining and materials supply chains.
Home energy systems show equally dramatic changes. Australian suburbs now feature neighborhoods where 60% of households combine solar panels with wall-mounted batteries. These systems typically pay for themselves within seven years through bill savings and grid services revenue.
Market Dynamics and Emerging Opportunities
Storage investments surpassed $20 billion globally last year, with growth rates exceeding 30% annually. Analysts at BloombergNEF predict storage capacity will multiply fifteenfold by 2040, creating entirely new business models around energy arbitrage and grid services.
The coming decade will likely witness storage becoming the most dynamic segment of energy infrastructure. Novel approaches like gravity storage in abandoned mines and thermal storage in volcanic rock demonstrate the field's boundless creativity. These solutions promise to reshape how societies generate, distribute, and consume electricity.
Smart grid integration now reaches beyond theory, with pilot projects showing 40% improvement in renewable utilization through predictive storage dispatch.
Electrolysis technology achieves new milestones as renewable penetration increases. Modern membrane systems can now produce hydrogen at $3/kg when paired with offshore wind. Scotland's recent hydrogen initiative will use tidal energy to create emission-free fuel for ferries and distilleries, demonstrating the versatility of storage conversion technologies.
Innovative Capital Solutions for Emerging Businesses
Modern Financing Approaches for Growth-Stage Companies
Entrepreneurs today navigate a financial landscape radically different from previous generations. Where banks once dominated lending, now hundreds of specialized options exist. This democratization of capital access helps bridge the $5 trillion global funding gap for small enterprises.
Fintech platforms now use machine learning to assess creditworthiness through unconventional metrics, including social media engagement and supply chain relationships. These tools help lenders understand businesses beyond spreadsheet snapshots.
Digital Lending Platforms Revolutionizing Access
Online lenders process applications 80% faster than traditional institutions by automating risk analysis. Some platforms specialize in specific sectors - for instance, offering equipment financing to dental practices or inventory loans to craft breweries. This specialization creates better-aligned financial products.
Community Investment Models Gaining Traction
Local investment networks now allow neighborhoods to fund businesses they want to support. Portland's Main Street Fund lets residents invest as little as $100 in downtown shops, receiving both interest payments and store discounts. These models build economic resilience while providing capital.
Receivables Financing Evolves
Modern invoice platforms integrate directly with accounting software, advancing funds within hours of invoice generation. Seasonal businesses like holiday decor manufacturers report this as their most crucial financial tool, smoothing cash flow through predictable annual cycles.
Public Sector Support Programs
Progressive governments now offer first loss guarantees to encourage private lending to underserved sectors. Canada's small business financing program backs loans up to $1 million, reducing lender risk while expanding access. Such initiatives demonstrate how public-private partnerships can unlock capital without requiring direct government lending.
Microfinance Enters the Digital Age
Mobile-based microloans now reach rural entrepreneurs through simple USSD codes. Kenyan farmers access $500 loans for irrigation equipment via basic feature phones, repaying after harvest through mobile money. These innovations prove that appropriate-scale financing can transform livelihoods without requiring complex banking infrastructure.