The Financial Landscape of Renewable Energy Projects
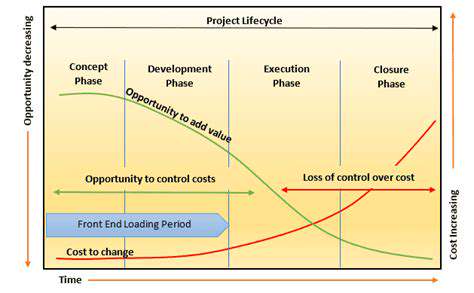
Project Initiation Costs
Project initiation costs represent the upfront expenses incurred during the initial stages of a project. These expenses lay the foundation for successful project execution, covering activities like feasibility studies, project planning, and initial documentation. Without proper initiation, projects face higher risks of misalignment with organizational goals and budget overruns. Teams must allocate sufficient time and resources to this phase to prevent costly revisions later.
During initiation, teams should thoroughly analyze project scope and requirements. Comprehensive planning and risk assessment become particularly important before advancing to subsequent phases. Neglecting these steps often results in timeline delays and financial strain throughout the project lifecycle. Establishing clear communication protocols and resource allocation strategies significantly improves initiation outcomes.
Development Costs
The development phase accounts for the majority of project expenses, covering the actual creation or construction of deliverables. These costs fluctuate based on project complexity, required resources, and technology choices. For software projects, development costs typically include programmer salaries, software licenses, and quality assurance testing expenses.
Selection of project management tools directly influences development expenditures. Appropriate tools can enhance workflow efficiency, improve team communication, and ultimately reduce overall costs. Skilled project management remains essential for controlling development expenses and maintaining project schedules.
Maintaining detailed cost records enables effective monitoring and management of development expenses. This practice allows for necessary budget adjustments during the project. Transparent tracking systems promote accountability and informed decision-making throughout development.
Project Closure Costs
Closure costs include final-stage expenses such as documentation completion, final testing, user training, and operational handoff. Many organizations underestimate these costs, yet they prove critical for successful project transition and value realization.
Comprehensive project documentation, including lessons learned, provides valuable insights for future initiatives. Proper handoff procedures prevent operational disruptions and ensure smooth integration of project deliverables. Post-implementation support often includes technical assistance, updates, and modifications to address evolving requirements. Strategic planning for closure activities prevents unexpected expenses and ensures project success.
Financing Mechanisms for Renewable Energy Initiatives

Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments play a crucial role in renewable energy adoption through financial incentives like tax credits, grants, and direct payments. These targeted incentives stimulate innovation and investment in specific technologies. For example, solar panel tax credits substantially reduce homeowner installation costs, increasing renewable energy accessibility.
Subsidies help bridge cost disparities between renewable and traditional energy sources, particularly during early technology development phases. By lowering financial barriers, subsidies accelerate the transition to sustainable energy solutions.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) combine public sector support with private sector expertise and capital. These collaborations prove especially effective for large-scale projects like wind farms or solar plants, where shared risk facilitates infrastructure development.
Debt Financing Mechanisms
Loans from banks and financial institutions provide essential capital for renewable energy projects. Debt financing enables companies to invest in necessary infrastructure while managing cash flow through structured repayment plans. Loan terms significantly impact project viability, requiring careful financial planning.
Venture Capital and Private Equity
These investment forms support innovative renewable energy startups and technologies. Venture capital focuses on high-growth potential companies, accelerating technological advancements through substantial R&D funding. Investors typically accept higher risk for potential long-term returns.
Crowdfunding Platforms
Crowdfunding enables community participation in renewable energy projects through small individual contributions. This approach fosters local engagement and expands funding sources beyond traditional channels. While not typically primary funding, it effectively complements other financing methods.
Smart inverters represent critical components in contemporary solar energy systems, converting panel output into usable household electricity. Beyond basic conversion, these devices incorporate advanced features that optimize system performance and longevity through real-time monitoring and adjustment algorithms.
Analyzing Return on Investment (ROI) and Financial Performance Metrics
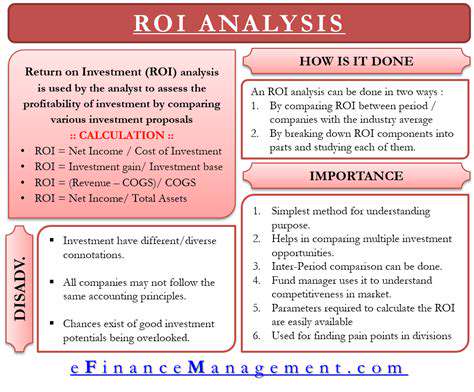
Understanding the Core Concept of ROI
Return on Investment measures investment profitability by comparing gains to costs. This fundamental metric informs resource allocation decisions and profitability assessments. High ROI indicates successful investments, while negative ROI signals potential issues requiring attention. The metric enables direct comparison between investment opportunities.
Calculating ROI: A Step-by-Step Guide
The standard ROI formula (Net Profit / Investment Cost) × 100% provides clear profitability assessment. Accurate calculation requires comprehensive cost inclusion and precise revenue tracking. Reliable ROI figures support sound financial decision-making across organizational levels.
Factors Influencing ROI
Market conditions, competition, and economic factors significantly impact ROI outcomes. Economic fluctuations particularly affect investment returns, emphasizing risk assessment importance. Execution quality and strategic planning also substantially influence final ROI results.
Applying ROI in Different Industries
ROI analysis applies universally across sectors. In technology, it evaluates software development returns, while healthcare assesses medical equipment value. Cross-industry ROI comparisons inform strategic investment decisions and resource allocation.
ROI and Decision-Making
ROI analysis drives data-driven investment decisions. Quantifying potential returns helps prioritize projects and minimize financial risk. Comparative ROI analysis ensures optimal resource distribution for maximum organizational benefit.
Improving ROI: Strategies and Techniques
Operational optimization and process improvements enhance ROI. Cost reduction measures and efficiency gains directly increase investment returns. Continuous performance monitoring allows timely strategy adjustments to maintain optimal ROI.
The Role of Government Policies and Incentives
Government Support for Renewable Energy
Policy frameworks significantly influence renewable energy adoption through subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory measures. These approaches reduce technology costs while stimulating sector innovation and employment. Feed-in tariffs and renewable portfolio standards exemplify effective policy tools for achieving climate objectives.
Incentivizing Investment in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Stable regulatory environments attract private investment to renewable energy projects. Streamlined permitting and tax incentives lower financial barriers, accelerating infrastructure development. Public-private partnerships combine sector strengths for optimal project outcomes.
Addressing Renewable Energy Intermittency
Energy storage solutions mitigate renewable energy variability. Government investment in battery and pumped hydro technologies ensures consistent power supply despite generation fluctuations.
Promoting Research and Development
Government-funded R&D drives renewable technology advancements. Support for academic-industrial collaborations accelerates innovation in solar efficiency, battery storage, and turbine design. Continuous technological improvement remains vital for renewable energy competitiveness.
Energy Efficiency Policy Frameworks
Complementary energy efficiency policies reduce overall consumption, enhancing renewable energy impact. Building codes and appliance standards create synergistic effects that maximize sustainability benefits while lowering consumer costs.
Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
Carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems improve renewable energy economics by internalizing fossil fuel externalities. Revenue reinvestment in renewable projects creates positive feedback loops for sustainable energy transition.