Blockchain for Decentralization of Energy Generation Trading: Secure and Transparent
Introduction to Decentralized Energy Trading
Understanding Decentralization in Energy Trading
Decentralized energy trading represents a paradigm shift away from traditional centralized power grids. This shift involves distributing energy generation and trading amongst various participants, rather than relying on a single entity to manage the entire process. This distributed approach offers numerous advantages, including increased resilience to outages, enhanced market efficiency, and greater participation from diverse energy sources.
Centralized systems often face vulnerabilities due to single points of failure. A disruption at a central hub can cripple the entire network. Decentralization, in contrast, creates redundancies and alternative pathways for energy flow, making the system more robust and less susceptible to widespread outages. Furthermore, a decentralized model empowers smaller producers and consumers, enabling them to participate actively in the energy market.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in enabling decentralized energy trading. Its cryptographic security and transparency features are essential for establishing trust and accountability among diverse participants in the energy ecosystem. Each transaction, from generation to consumption, is recorded on an immutable ledger, providing a verifiable and auditable record of all energy exchanges.
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity controls the data or the process. This fosters trust and eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining transactions and reducing administrative overhead. The inherent security features of blockchain make it ideal for managing sensitive energy data and ensuring the integrity of transactions.
Benefits of Decentralized Energy Trading
Decentralized energy trading offers a plethora of benefits for both consumers and producers. Consumers gain access to a wider range of energy sources, potentially leading to lower prices and greater energy choice. The ability to directly interact with producers can foster greater transparency and empower consumers to make informed decisions.
Producers benefit from increased market access and direct engagement with consumers. This can lead to higher profitability and greater control over their energy assets. Decentralization also encourages innovation and the development of new energy technologies, as smaller players can enter the market more easily.
Challenges in Implementing Decentralized Systems
Despite the numerous advantages, implementing decentralized energy trading systems presents several challenges. Interoperability between different energy sources and storage solutions is crucial but can be complex to achieve. Standardization of data formats and communication protocols is essential for seamless integration within the decentralized network.
Regulatory frameworks need to adapt to accommodate the novel characteristics of decentralized energy markets. Furthermore, ensuring security and preventing fraud within a distributed system requires robust protocols and mechanisms.
Opportunities for Innovation and Growth
Decentralized energy trading opens up significant opportunities for innovation in the energy sector. Smart contracts can automate transactions, reducing administrative burdens and increasing efficiency. The integration of renewable energy sources becomes easier and more cost-effective within a decentralized framework.
The development of new energy storage solutions and the optimization of energy grids are driven by the needs of decentralized systems. This environment fosters innovation and creates new avenues for investment and growth in the energy sector.
The Future of Energy Trading
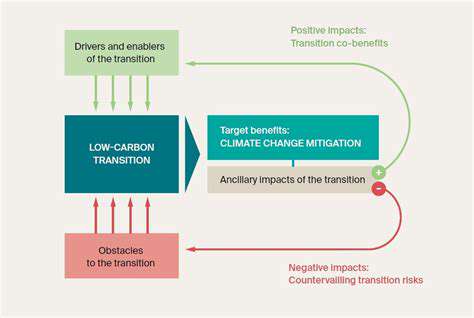
The future of energy trading is inextricably linked to decentralization. The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources necessitates a more flexible and responsive energy system. Decentralized models can adapt better to fluctuating energy supply and demand, enabling a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Blockchain technology will continue to play a critical role in facilitating these changes, enabling secure and transparent transactions, and empowering participants throughout the energy ecosystem. We can expect to see further development and integration of blockchain into energy markets in the years to come.
Blockchain's Advantages for Energy Trading
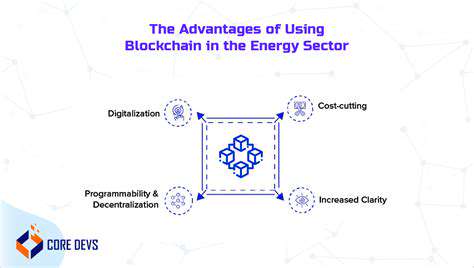
Decentralization and Transparency
Blockchain technology fundamentally alters the energy sector by enabling a decentralized system where no single entity controls the flow of data or energy. This decentralized nature fosters transparency, allowing all participants to view the entire energy transaction history. This enhances trust and accountability, crucial for building a more reliable and efficient energy ecosystem. Transparency in energy transactions can help prevent fraud and corruption, leading to more trust among participants. Moreover, this openness enables stakeholders to track energy production, distribution, and consumption with greater clarity, potentially leading to better resource allocation and reduced waste.
The decentralized nature of blockchain significantly reduces reliance on intermediaries, streamlining processes and potentially lowering costs. This direct interaction between producers and consumers can lead to greater efficiency and fairer pricing models. By cutting out intermediaries, blockchain technology can potentially reduce the cost of energy transactions, making it more accessible to a wider range of users.
Improved Security and Immutability
Blockchain's inherent security features are particularly valuable in the energy sector, which often involves sensitive data and complex transactions. The immutability of blockchain records makes tampering with data nearly impossible. This characteristic is crucial for maintaining the integrity of energy transactions, ensuring that all data is accurate and reliable. Cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms further enhance the security of energy transactions, safeguarding against unauthorized access and manipulation.
The immutable nature of blockchain records also enables a robust audit trail for energy transactions, creating a comprehensive history of all activities. This detailed audit trail can be invaluable for tracing energy sources, verifying compliance with regulations, and identifying potential inefficiencies in the system. This detailed audit trail significantly improves accountability and traceability, crucial for regulatory compliance and mitigating potential risks.
Enhanced Efficiency and Automation
Blockchain's potential to automate processes and enhance efficiency in energy management is substantial. Smart contracts on a blockchain platform can automate tasks like payment processing, contract fulfillment, and dispute resolution, reducing administrative overhead and increasing speed. This automation can significantly streamline energy transactions and improve overall operational efficiency, leading to cost savings for all involved parties.
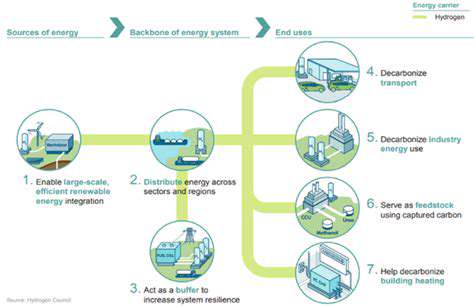
Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. By tracking the origin and quality of renewable energy, blockchain can ensure accurate compensation for producers and facilitate seamless integration into the existing energy infrastructure. This can lead to a more sustainable and resilient energy system, promoting environmental responsibility and long-term energy security.
Decentralized Energy Generation and Trading Platforms
Understanding Decentralized Energy Generation
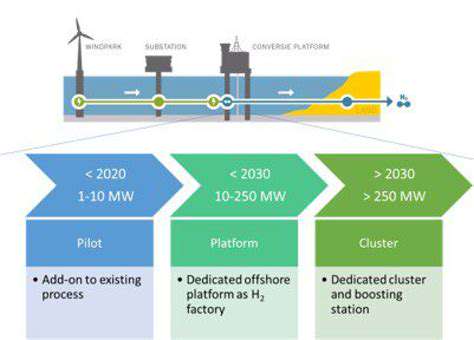
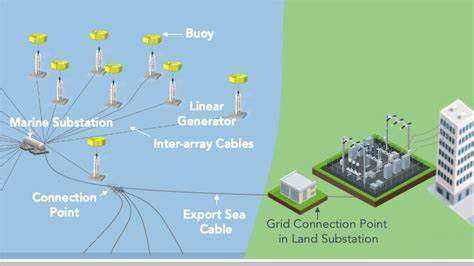
Decentralized energy generation involves producing electricity from various sources, like solar panels, wind turbines, and micro-hydro systems, at a local level, rather than relying solely on large-scale centralized power plants. This shift towards distributed energy resources (DERs) is crucial for enhancing grid resilience and reducing transmission losses. Furthermore, this localized approach fosters greater energy independence and empowers communities to actively participate in managing their energy needs.
The rise of renewable energy technologies and advancements in energy storage solutions are key drivers behind the growing popularity of decentralized energy generation. This approach offers significant environmental benefits by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Blockchain's Role in Facilitating Energy Trading
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for facilitating energy trading among decentralized energy producers and consumers. This decentralized system eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and improving efficiency. By recording transactions on a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain ensures accountability and trust among participants.
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written into the blockchain, can automate energy transactions, streamlining the process and reducing potential disputes. This automation can further enhance efficiency and reduce the administrative burden on all parties involved.
Decentralized Energy Platforms and their Architecture
Decentralized energy platforms typically employ a distributed ledger technology (DLT), like blockchain, to track energy production, consumption, and trading. This architecture ensures transparency and immutability of records, fostering trust and accountability among participants. These platforms often integrate with various DERs, enabling seamless data exchange and automated transactions.
The architecture of these platforms typically involves a network of nodes, each responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the ledger. This distributed approach enhances the platform's resilience and security, making it resistant to single points of failure.
Enhancing Transparency and Trust in Energy Markets
Blockchain technology fundamentally enhances transparency in energy markets by creating a publicly accessible and immutable record of all transactions. This open record-keeping fosters trust among participants, eliminating concerns about manipulation or fraud. The transparency also allows for greater accountability and traceability of energy sources.
The decentralized nature of these platforms also empowers consumers to gain greater insight into their energy consumption patterns and identify opportunities for optimization and cost savings. This level of transparency promotes informed decision-making and encourages responsible energy management.
Addressing Challenges in Implementing Decentralized Systems
While blockchain offers numerous advantages for decentralized energy systems, challenges remain, including scalability issues, interoperability problems between different energy sources and platforms, and regulatory hurdles. Addressing these issues is critical for widespread adoption and successful integration of blockchain into the energy sector.
Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to these decentralized platforms for all participants, regardless of their location or financial capacity, is a significant consideration for sustainable development. Overcoming these challenges is key to maximizing the benefits of decentralized energy systems.
Incentivizing Participation and Collaboration
Decentralized energy platforms often utilize tokenized incentives to encourage participation and collaboration among energy producers and consumers. These tokens can represent energy units, rights to energy generation, or other forms of value, fostering a collaborative energy ecosystem. This approach can help drive innovation and promote sustainable energy practices.
Incentivizing participation is crucial for driving adoption. By providing economic incentives, these platforms can motivate individuals and communities to generate and trade energy, accelerating the transition to a decentralized energy future. These tokens can also be used to reward individuals for environmentally friendly energy choices.
Security and Regulatory Considerations for Blockchain-Based Platforms
Ensuring the security of blockchain-based energy platforms is crucial to maintain the integrity of transactions and prevent malicious activities. Robust security measures are essential to protect the platform from cyberattacks and data breaches. This includes implementing advanced encryption techniques and employing secure protocols for communication and data exchange.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape for blockchain-based energy platforms is still evolving, posing challenges in legal compliance. Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to address issues such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and consumer protection. This is critical for the responsible and sustainable growth of these systems.
Security and Transparency in Energy Transactions
Ensuring Trust and Integrity
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in fostering trust and integrity in energy transactions by providing a transparent and immutable record of every step in the process. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation. The distributed ledger nature of blockchain ensures that all participants have access to the same information, promoting accountability and reducing disputes, ultimately enhancing the trustworthiness of the entire energy transaction ecosystem.
Promoting Decentralization
Traditional energy markets often rely on centralized entities for managing transactions and distribution. Blockchain, by its decentralized nature, empowers individual energy producers and consumers. This distributed approach reduces reliance on intermediaries, fostering a more equitable and efficient energy ecosystem. This democratization of energy access is a key benefit of blockchain technology, enabling greater participation and control for all stakeholders.
Facilitating Transparency and Traceability
Every energy transaction, from production to consumption, is meticulously recorded on the blockchain. This inherent transparency allows all parties to track the journey of energy, from its source to its final destination. This traceability not only enhances accountability but also provides valuable insights into energy consumption patterns and potential inefficiencies. Such transparency and traceability can also aid in regulatory compliance and environmental monitoring.
Improving Energy Efficiency and Reliability
Smart contracts, a key component of blockchain technology, can automate energy transactions and streamline processes. This automation reduces manual intervention, minimizing errors and inefficiencies. By enhancing the speed and accuracy of transactions, blockchain can contribute to more efficient energy distribution networks. Improved reliability is also a key benefit, as the immutability of the blockchain ensures that transactions are tamper-proof and secure.
Securing Data and Preventing Fraud
Blockchain's cryptographic security features provide a robust defense against unauthorized access and manipulation. This cryptographic security ensures the integrity and confidentiality of data associated with energy transactions. The decentralized nature of the blockchain further strengthens security by distributing the data across multiple nodes, making it significantly more resilient to cyberattacks and fraud. This robust security framework is vital for maintaining the integrity of the energy market.
Enhancing Regulatory Compliance
The transparency and traceability offered by blockchain make it easier for regulators to monitor and enforce compliance in the energy sector. The immutable record of transactions provides a verifiable audit trail, allowing for efficient compliance checks and reducing the risk of non-compliance. This enhanced regulatory compliance can create a more trustworthy and predictable energy market. Furthermore, it can help governments track and manage energy consumption data for policy and environmental impact assessments.
Promoting Sustainability and Environmental Awareness
By improving efficiency and transparency, blockchain can contribute to a more sustainable energy future. The ability to track energy sources and consumption patterns can help identify areas for improvement and promote responsible energy use. This enhanced visibility can also support the development of renewable energy sources by facilitating the integration of decentralized energy production into the grid. Ultimately, blockchain can help accelerate the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious energy system.