Power to X (P2X) Applications: Converting Green Hydrogen into Synthetic Fuels and Chemicals
Harnessing Renewable Energy for Green Hydrogen
The production of green hydrogen marks a transformative shift toward sustainable energy solutions. Instead of relying on finite fossil fuels, this method taps into the boundless energy of sunlight and wind to split water molecules. Electrolysis, the core technology behind this process, stands as a beacon of hope for industries seeking cleaner alternatives to traditional energy sources. Unlike conventional hydrogen production, which emits significant carbon dioxide, this approach aligns with global decarbonization goals.
As solar and wind energy become more accessible, the potential for scaling green hydrogen production grows exponentially. Researchers are tirelessly working to refine electrolysis techniques, aiming to boost efficiency while reducing costs. These improvements could soon make green hydrogen a practical replacement for fossil fuels in multiple sectors.
Electrolysis Technologies: Key Players in Green Hydrogen
Different electrolysis methods each bring unique advantages to green hydrogen production. Alkaline electrolysis, for instance, offers reliability and affordability, though it may lag in efficiency. Proton exchange membrane (PEM) systems excel in responsiveness and performance, making them ideal for pairing with variable renewable energy sources. Meanwhile, solid oxide electrolysis shows promise with its high-temperature operation and potential efficiency gains, despite facing technical hurdles.
Selecting the right technology depends on specific needs, such as energy availability and desired output. Continued innovation in this field is vital to lowering costs and enhancing performance, paving the way for broader adoption of green hydrogen solutions.
Sustainable Hydrogen Storage and Transportation
Producing hydrogen is just the beginning; storing and moving it efficiently presents its own set of challenges. Due to hydrogen's lightweight nature and high energy content, specialized storage methods like cryogenic tanks or high-pressure systems are essential. Similarly, transporting hydrogen—whether through pipelines or specialized carriers—requires careful planning to ensure safety and efficiency at scale.
Building a robust infrastructure for hydrogen storage and distribution is critical to unlocking its full potential. Without it, the benefits of green hydrogen may remain limited to niche applications rather than reaching industries worldwide.
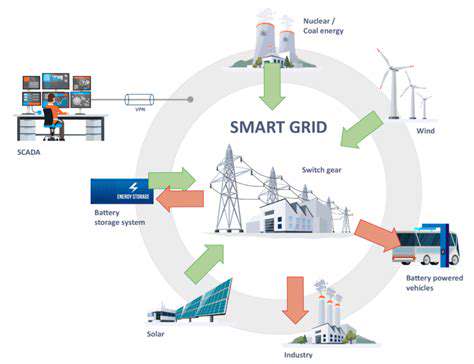
Green Hydrogen's Role in Power-to-X Applications
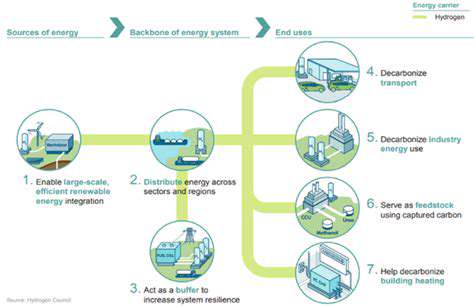
In Power-to-X (P2X) systems, green hydrogen acts as a versatile building block for sustainable fuels and chemicals. It can be transformed into synthetic fuels, ammonia, or methanol, offering carbon-neutral alternatives for transportation, industry, and heating. This adaptability positions green hydrogen as a cornerstone of future energy systems, capable of replacing fossil fuels across multiple sectors.
Beyond energy storage, green hydrogen enables the creation of an entire ecosystem of clean products. From powering vehicles to manufacturing materials, its applications are vast and transformative.
Economic and Societal Benefits of Green Hydrogen
The rise of green hydrogen promises far-reaching economic and social advantages. New jobs will emerge in manufacturing, infrastructure development, and technology innovation, driving economic growth. At the same time, reduced reliance on fossil fuels will lead to cleaner air and better public health outcomes.
Embracing green hydrogen isn't just an environmental imperative—it's an opportunity to build a healthier, more prosperous world. By investing in this technology, societies can reduce emissions, spur innovation, and create sustainable livelihoods for future generations.
Addressing the Challenges of P2X Implementation
Understanding the Fundamental Concepts of P2X
P2X, or peer-to-exchange, revolutionizes value transfer by cutting out middlemen. This decentralized model slashes costs and broadens access, empowering individuals and businesses alike. By enabling direct exchanges, P2X systems streamline transactions while fostering greater efficiency and transparency.
Identifying Key Barriers to P2X Adoption
Despite its promise, P2X adoption faces obstacles, including the need for secure, scalable infrastructure. Trust is paramount, and without foolproof systems, fraud risks could undermine progress. Equally challenging is the absence of universal standards, which complicates integration across platforms and regions.
The Role of Technology in Overcoming P2X Challenges
Blockchain and smart contracts are game-changers for P2X, offering secure, automated transaction frameworks. User-friendly interfaces will be critical to democratizing access and ensuring widespread adoption. As these technologies mature, they’ll help bridge gaps between innovation and practicality.
Addressing Security Concerns in P2X Systems
Security can't be an afterthought in P2X networks. Robust encryption and authentication protocols are non-negotiable. Regular audits and proactive measures will safeguard user assets and maintain system integrity over time.
The Importance of Interoperability in P2X
For P2X to thrive, different platforms must communicate seamlessly. Interoperability ensures users aren’t locked into single ecosystems, fostering flexibility and broader participation. This connectivity will be key to building a cohesive, decentralized economy.
The Impact of Regulation on P2X Development
Clear, balanced regulations can accelerate P2X growth by instilling confidence and stability. Without thoughtful oversight, uncertainty may stifle innovation and deter investment. Policymakers must strike a delicate balance between fostering progress and protecting stakeholders.
The Future Outlook for P2X Innovation
The trajectory of P2X is bright, with blockchain advancements and expanding use cases driving momentum. As these systems evolve, they’ll democratize access to financial tools and redefine global exchange networks. Success hinges on overcoming current limitations while nurturing an ecosystem conducive to innovation.
The Future of P2X: A Sustainable Energy Revolution
Harnessing Renewable Energy for a Sustainable Future
Power-to-X technologies are redefining energy systems by converting renewables into storable fuels. This breakthrough tackles the intermittency of solar and wind power, ensuring reliable energy supplies. With P2X, industries once reliant on fossil fuels can transition to cleaner alternatives, slashing emissions in the process.
From synthetic fuels to green chemicals, P2X unlocks diverse applications. Its ability to store and transport energy flexibly makes it indispensable for decarbonizing challenging sectors like aviation and heavy industry.
Beyond the Hype: Real-World P2X Applications
Pilot projects are proving P2X’s viability, from sustainable jet fuel to renewable heating solutions. However, scaling these initiatives demands solutions for cost, infrastructure, and efficiency. The path forward requires collaboration between innovators, investors, and policymakers.
The Economic Implications of P2X
Transitioning to P2X demands significant investment but promises substantial returns. New industries will emerge, creating jobs and stimulating economic activity. Yet, success depends on supportive policies and continued technological breakthroughs to ensure competitiveness.
Technological Advancements Driving P2X
Breakthroughs in electrolysis, catalysts, and system design are making P2X more efficient and affordable. These innovations are critical to achieving commercial viability and widespread adoption. Ongoing research will further refine these technologies, unlocking new possibilities.
Overcoming the Challenges: Infrastructure and Policy
A robust infrastructure—from storage facilities to transport networks—is essential for P2X to flourish. Policymakers must incentivize investment and streamline regulations to accelerate deployment. By fostering collaboration and innovation, governments can pave the way for a sustainable energy future.