Energy Storage for EV Charging Infrastructure: Boosting Charging Speed
Energy Storage: A Fundamental Necessity
Storing energy has evolved from a theoretical idea to an indispensable part of our sustainable energy infrastructure. Capturing power from renewable sources such as solar panels and wind turbines solves the problem of inconsistent energy generation, which is particularly valuable in areas with unpredictable weather where energy output can change dramatically.
Diverse Energy Storage Solutions
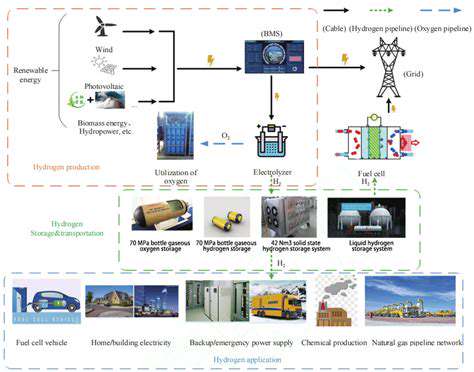
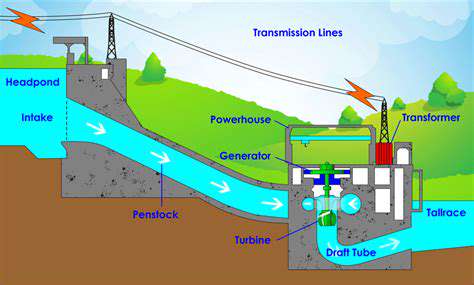
Engineers are developing multiple approaches to energy storage, each with unique benefits and limitations. While lithium-ion batteries dominate portable electronics, they're also crucial for large-scale energy storage due to their efficient energy retention and quick recharge times. Alternative methods like pumped hydroelectric storage use gravity and water, while compressed air systems store power by pressurizing air in underground caverns.
Benefits of Modern Storage Technology
Contemporary energy storage solutions provide advantages beyond simple power preservation. They play a vital role in balancing energy grids by absorbing variations between supply and demand. This stabilizing effect prevents power interruptions and ensures consistent electricity delivery. Additionally, these systems make renewable energy sources more practical by smoothing out their natural variability.
Enabling Renewable Energy Adoption
Energy storage dramatically improves the practicality of solar and wind power systems. Since these green energy sources produce power unpredictably, storage units act as buffers to maintain steady electricity flow. This breakthrough technology is accelerating the global shift toward renewable energy solutions by making them more dependable for everyday use.
Economic Impact of Storage Solutions
The financial aspects of energy storage present numerous opportunities. Funding for storage technology research and implementation creates employment and stimulates growth in related industries. These investments address current needs while building a foundation for future energy sustainability. Storage systems are becoming more affordable, expanding their potential applications across different sectors.
Innovations in Storage Technology
Continuous progress in battery design, material science, and energy systems is revolutionizing storage capabilities. Scientists are experimenting with novel battery compositions to improve energy capacity and longevity while lowering manufacturing expenses. These developments are crucial for applying storage technology to electric vehicles, smart buildings, and manufacturing processes.
Future Potential and Obstacles
The outlook for energy storage is promising, pointing toward a future with stable, sustainable power. Remaining challenges include creating more economical and eco-friendly storage options. Manufacturing scalability and the environmental impact of storage materials require careful attention. Addressing these issues will help achieve truly sustainable energy systems.
Emerging Developments in EV Charging Storage
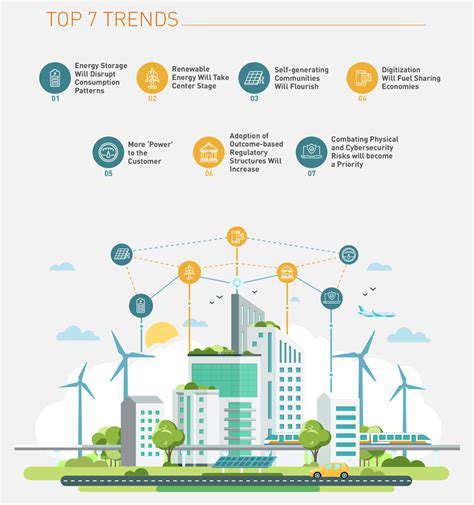
Cutting-Edge Technologies Transforming the Sector
The swift progress in artificial intelligence and automated learning systems is transforming energy management. These innovations enable precise energy optimization and reduced ecological footprint. Intelligent systems can process extensive data to forecast energy needs, improve grid operations, and schedule maintenance automatically, resulting in enhanced efficiency and dependability.
Improvements in renewable technology, particularly solar and wind systems, continue to influence energy storage applications. Enhanced solar cell manufacturing paired with creative storage methods is making renewable power more consistent and competitive with conventional energy sources.
Sustainability Initiatives and Regulatory Frameworks
National governments and corporations are prioritizing eco-friendly energy strategies and establishing regulations that support clean energy adoption. This environmental focus is essential for addressing climate issues and securing long-term energy stability. Carbon capture and storage methods will be particularly important for minimizing emissions from current power generation facilities.
Global cooperation will significantly contribute to sharing expertise in sustainable energy practices. Collaborative international efforts to exchange technological progress and policy strategies will speed up the worldwide adoption of cleaner energy alternatives.
Economic and Community Effects
Shifting to sustainable energy systems will create substantial economic and societal changes. The renewable energy sector will generate new employment opportunities, stimulating local economies that previously depended on fossil fuels. However, workers in traditional energy industries may require retraining programs to transition to new roles.
Ensuring fair distribution of the energy transition's benefits and costs is paramount. Implementation of inclusive policies will guarantee that the move toward sustainable energy benefits all community members equitably.
International Relations and Energy Security
Global political dynamics, including resource limitations and international tensions, significantly affect energy technology development. Competition for natural resources might fuel energy innovation but could also create market volatility and strain international partnerships. Multilateral agreements are necessary to ensure all nations have fair access to energy resources.
The constantly changing global energy environment requires flexible, forward-thinking strategies. Navigating the complex interplay of international relations will be key to managing future energy challenges and opportunities.