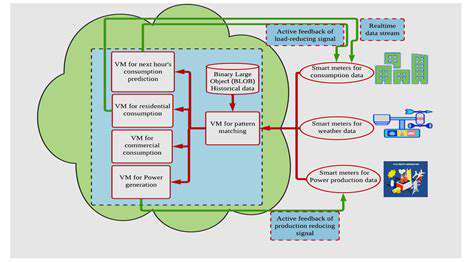
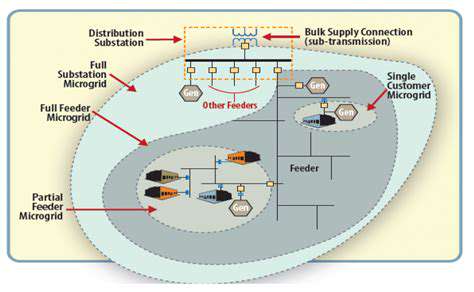
Designing Effective Renewable Energy Policies: Lessons Learned Globally
Promoting Public Awareness and Engagement
Raising Public Understanding of Renewable Energy
Educating communities about sustainable energy solutions is fundamental for implementing effective environmental policies. Successful awareness campaigns should highlight renewable energy's ecological benefits, economic potential, and climate change mitigation capabilities. Rather than relying solely on statistics, these initiatives should emphasize tangible examples of how clean energy positively impacts local neighborhoods.
Encouraging Public Participation in Renewable Energy Initiatives
Community involvement drives renewable energy adoption. Creating avenues for public input on projects like neighborhood solar programs or regional wind farms fosters personal investment in sustainability efforts. When residents participate in decision-making, they become more likely to support policies promoting renewable energy transitions.
Highlighting the Economic Benefits of Renewable Energy
Clean energy development generates substantial economic growth through job creation in production and installation sectors, plus new business opportunities. Awareness campaigns should effectively communicate these financial advantages to demonstrate that environmental responsibility aligns with economic prosperity. Showcasing successful local renewable energy implementations helps illustrate these benefits concretely.
Addressing Public Concerns and Misconceptions
Dispelling common misunderstandings about renewable technologies requires transparent communication. Addressing questions about expenses, performance consistency, and ecological effects through factual information and real-world examples builds public confidence in sustainable energy solutions.
Promoting Renewable Energy Education in Schools and Communities
Incorporating energy education into academic programs and public workshops cultivates early understanding of sustainability principles. Interactive learning experiences like facility tours and hands-on demonstrations engage participants more effectively than traditional lectures, nurturing future advocates for renewable energy policies.
Facilitating Public Access to Renewable Energy Information
Making reliable energy information readily available through intuitive digital platforms, community events, and media partnerships empowers citizens to make informed decisions about sustainability initiatives. Clear, accessible resources are essential for building public support.
Encouraging Citizen Advocacy for Renewable Energy Policies
Effective public engagement should translate into active policy support. Motivating community members to contact government representatives, attend public meetings, and join environmental organizations creates the political momentum needed for meaningful renewable energy legislation.
International Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing
Global Collaboration for Sustainable Development
Multinational partnerships are essential for addressing worldwide issues like environmental crises, economic inequality, and public health challenges. Combining international resources and expertise accelerates progress toward sustainability objectives. Diverse national perspectives enrich solution development when governments, nonprofits, and businesses collaborate effectively.
Knowledge Sharing and Best Practices
Cross-border cooperation enables valuable exchanges of successful strategies across sectors including medical care, learning systems, and urban planning. This information sharing reduces redundant efforts and accelerates innovation implementation. Adapting proven approaches to local conditions ensures solutions remain relevant and effective in different cultural contexts.
Addressing Transnational Challenges
Global issues like health emergencies, financial instability, and ecological damage require coordinated international responses. Only through cooperative action can nations develop comprehensive solutions for borderless problems. Joint resource allocation and strategy development are necessary to address root causes effectively.
Economic Interdependence and Trade
International partnerships foster beneficial economic relationships through fair trade agreements. Open commerce policies generate growth opportunities for participating countries at all development levels. Multilateral institutions help maintain equitable trading environments that particularly benefit emerging economies.
Strengthening International Institutions
Robust global organizations provide essential platforms for diplomatic engagement and standard-setting. These bodies play critical roles in maintaining worldwide stability and conflict resolution. They establish frameworks for peaceful dispute settlement and cooperative problem-solving.
Cultural Exchange and Understanding
International interactions promote mutual appreciation of diverse traditions and perspectives. Cross-cultural exposure cultivates empathy and respect across societies. These exchanges enrich global understanding and create stronger connections between people worldwide.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Global research collaboration accelerates scientific and technological breakthroughs. Pooling international expertise leads to pioneering solutions for complex challenges. The free flow of ideas between nations drives progress in critical fields like healthcare, infrastructure, and digital technology.