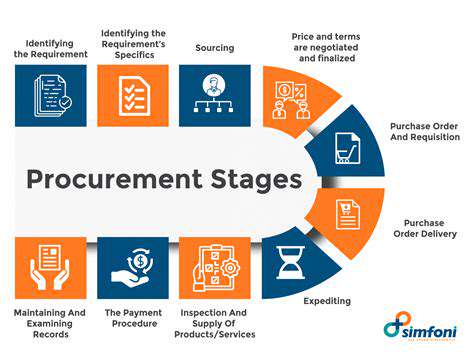
Decentralization of Energy Generation for Remote Areas
Harnessing Solar Power
Solar power stands out as one of the most accessible clean energy sources available today. By converting sunlight directly into usable electricity through photovoltaic (PV) systems, households and businesses can significantly reduce their dependence on traditional power grids. This shift toward localized energy production proves especially valuable in remote regions where grid connectivity remains unreliable or nonexistent. Recent breakthroughs in solar technology, including more efficient panels and lower production costs, continue to make this renewable source increasingly practical for widespread adoption.
Energy storage solutions like advanced battery systems play a critical role in maximizing solar potential. These storage units capture surplus energy generated during sunny periods, making it available for use during nighttime or cloudy days. This capability helps balance supply and demand, creating a more consistent and dependable energy supply for off-grid applications.
Unlocking the Potential of Wind Power
Wind energy represents another pillar of decentralized power generation, with turbines capable of producing substantial electricity across diverse landscapes. From coastal areas with consistent breezes to inland regions with occasional strong winds, this technology adapts well to various geographical conditions. Smaller-scale wind turbines have become particularly valuable for rural communities seeking energy independence without relying on extensive transmission infrastructure.
The development of compact, efficient wind turbine designs has opened new possibilities for localized energy production. By generating power closer to where it's needed, these systems minimize energy loss during transmission while providing reliable electricity to areas traditionally underserved by centralized grids.
Exploring Emerging Renewable Technologies
Beyond the familiar solar and wind options, several innovative technologies show promise for decentralized energy systems. Geothermal installations tap into the Earth's natural heat to deliver consistent baseload power in geologically suitable locations. Meanwhile, concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirror arrays to focus sunlight, generating both electricity and thermal energy in sun-rich regions.
Biomass conversion offers another pathway, particularly in agricultural areas where organic waste materials can be transformed into usable energy. The key to successful implementation lies in matching specific technologies with local resources and conditions, creating customized solutions that maximize efficiency and sustainability for each unique situation.
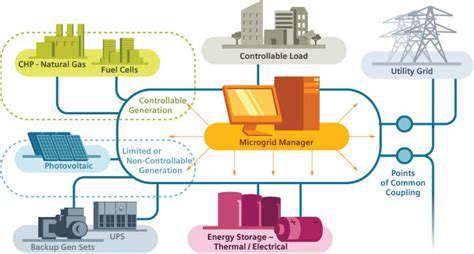
Integrating Renewables into Microgrids
Microgrid technology represents the backbone of modern decentralized energy systems. These self-contained networks combine various renewable sources with smart storage and distribution capabilities. During grid outages or emergencies, microgrids can operate independently, ensuring continuous power for critical services while demonstrating remarkable resilience. Their modular design allows communities to start small and expand their renewable capacity over time as needs and resources dictate.
Addressing Challenges and Opportunities
While the transition to decentralized renewable energy presents some obstacles, none appear insurmountable with proper planning and investment. The variable nature of solar and wind generation requires sophisticated energy management systems and storage solutions. Infrastructure development must also keep pace with technological advancements to ensure efficient energy distribution at local levels.
Policy frameworks and financial incentives will prove crucial in accelerating adoption of these technologies. Governments and private investors alike recognize the triple benefit of decentralized renewables: economic growth through new industries, job creation in installation and maintenance, and significant progress toward environmental sustainability goals. With coordinated effort across sectors, the vision of energy-independent communities powered by clean, local sources moves closer to reality every day.