Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): A Deep Dive for Businesses
Thorough comprehension of these structural components enables both parties to identify potential risks and opportunities, ensuring the agreement supports their respective operational and financial objectives. The contract must clearly delineate responsibilities regarding energy delivery, quality standards, and performance metrics.
Evaluating Financial Implications
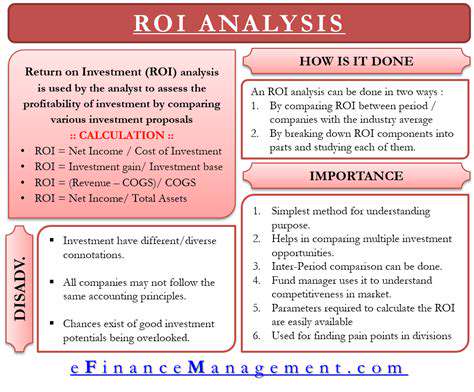
Financial assessment represents perhaps the most critical phase of PPA evaluation. Organizations must conduct detailed comparative analyses between projected PPA costs and conventional energy procurement options. This evaluation should encompass both immediate financial commitments and long-term expenditure projections, accounting for potential market fluctuations and contract escalation clauses.
Comprehensive financial modeling must extend throughout the entire contract term, incorporating sensitivity analyses for various market scenarios. The analysis should evaluate not just direct energy costs but also ancillary expenses like infrastructure upgrades or connection fees that might be required.
Assessing the Technical Feasibility
Technical evaluation requires careful examination of the generator's operational capabilities and reliability history. Buyers should review historical performance data, maintenance records, and capacity utilization rates to assess the provider's ability to meet contractual commitments.
Equally important is evaluating the buyer's infrastructure readiness to receive and utilize the contracted power. This assessment should identify any necessary system upgrades, interconnection requirements, or operational adjustments needed to integrate the new energy source effectively.
Analyzing Regulatory Environment
The legal and regulatory landscape significantly impacts PPA viability and structure. Organizations must stay current with evolving energy policies, environmental regulations, and incentive programs at all government levels. These factors can substantially influence project economics and operational requirements.
Anticipating potential regulatory changes helps mitigate future compliance risks and ensures the agreement remains viable throughout its term. The analysis should include review of renewable energy credits, carbon pricing mechanisms, and any applicable tax incentives.
Considering Operational and Maintenance Requirements
Clear delineation of operational responsibilities prevents disputes and ensures reliable energy delivery. The agreement must specify maintenance obligations, performance monitoring protocols, and response procedures for service interruptions.
Operational provisions should address routine maintenance schedules, emergency repair protocols, and performance benchmarking. Well-defined service level agreements help maintain consistent energy supply quality and availability throughout the contract period.
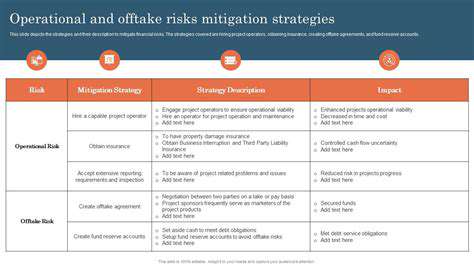
Identifying Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Risk assessment should encompass multiple dimensions including market volatility, technological obsolescence, regulatory changes, and force majeure events. Each identified risk requires corresponding mitigation strategies incorporated into the contract terms.
Effective risk management plans include provisions for periodic contract reviews, adjustment mechanisms for material changes, and clear dispute resolution processes. These safeguards help protect both parties' interests while maintaining agreement stability.
Structuring and Implementing a Successful PPA
Understanding the Core Principles of PPA
The foundation of effective PPA implementation begins with comprehensive understanding of its fundamental components. These long-term energy contracts require alignment between buyer requirements and seller capabilities across technical, financial, and operational dimensions.
Key agreement elements like pricing structures, energy volume commitments, and quality specifications must be carefully crafted to support the strategic objectives of both organizations. Detailed attention to these components facilitates accurate financial forecasting and operational planning throughout the multi-year contract duration.
Identifying Suitable PPA Candidates
The selection process involves rigorous analysis of energy consumption patterns, load profiles, and future growth projections. Organizations should evaluate multiple renewable energy sources and contract structures to identify optimal solutions matching their specific requirements.
Thorough assessment of current energy procurement costs compared to PPA alternatives helps quantify potential savings and validate the business case. This analysis should consider both direct cost comparisons and indirect benefits like sustainability achievements and energy security improvements.
Developing a Comprehensive PPA Strategy
Strategic planning for PPAs requires multi-disciplinary evaluation incorporating financial, technical, legal and sustainability perspectives. The strategy should address key considerations like contract duration preferences, risk allocation preferences, and desired sustainability outcomes.
Market analysis should examine current and projected energy price trends, regulatory developments, and technology advancements that might impact agreement viability. This comprehensive approach ensures the PPA aligns with broader organizational objectives beyond simple cost savings.
Negotiating and Finalizing the PPA Terms
Contract negotiations demand specialized expertise across multiple domains. Teams should include legal counsel familiar with energy contracts, financial analysts, and technical experts who can evaluate operational implications.
Critical negotiation points typically include pricing structures, performance guarantees, penalty provisions, and change management protocols. Well-drafted contracts clearly articulate responsibilities, performance expectations, and remedies for various scenarios that might arise during the agreement term.
Managing the PPA Throughout its Lifecycle
Effective contract administration ensures continued value realization from PPAs. Organizations should establish robust monitoring systems to track energy delivery, quality metrics, and financial performance against contractual commitments.
Regular performance reviews and relationship management activities help address operational challenges proactively. These practices maintain alignment between contractual obligations and evolving business requirements throughout the extended agreement period.
Addressing Potential Challenges and Risks
Proactive risk management involves anticipating potential disruptions and establishing mitigation protocols. Common challenges include technology performance issues, market price fluctuations, and regulatory changes that might impact contract economics.
Effective agreements incorporate flexible adjustment mechanisms, clear dispute resolution processes, and periodic review provisions. These features help maintain agreement viability despite changing circumstances over long contract durations.
Evaluating the Financial and Environmental Impacts
Comprehensive benefit assessment should quantify both monetary savings and sustainability achievements. Financial analysis must extend beyond simple cost comparisons to include factors like avoided risk, price stability value, and potential revenue from renewable energy credits.
Environmental impact evaluation should measure carbon reduction achievements and contribution to broader sustainability goals. This dual focus on financial and ecological benefits demonstrates the full value proposition of renewable energy PPAs.