Managing Risk in Corporate Renewable PPAs
Introduction to Corporate Renewable Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Understanding Corporate PPAs
Corporate Renewable Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) represent innovative contracts forged between businesses and renewable energy producers. These arrangements specify conditions under which companies procure clean electricity from designated projects—such as solar arrays or wind farms—for predetermined durations. This strategic move toward sustainable energy sources simultaneously diminishes corporate carbon footprints and can yield favorable economic outcomes, contingent upon contract specifics.
Grasping the subtle complexities within these contracts proves vital for organizations seeking to integrate renewables while managing associated uncertainties. A meticulous examination of financial frameworks—including pricing structures and extended obligations—becomes imperative to verify congruence with overarching corporate goals.
Key Benefits of Corporate PPAs
Apart from obvious ecological merits, corporate PPAs deliver multiple strategic advantages. These include diminished exposure to unpredictable fossil fuel markets—potentially resulting in sustained energy cost reductions—along with strengthened brand perception among sustainability-focused stakeholders. Businesses can showcase environmental stewardship, attracting investment from entities prioritizing ethical operations.
This enhanced corporate image profoundly affects investor confidence and consumer allegiance. Furthermore, PPAs serve as protective measures against impending energy price surges while guaranteeing consistent power availability.
Assessing Financial Implications
Evaluating corporate PPAs demands rigorous financial scrutiny. This involves examining long-term expenditure commitments, analyzing fixed versus variable pricing structures, and contrasting these with existing energy expenses. Comprehensive forecasting becomes necessary to determine the agreement's complete fiscal impact throughout its duration.
Organizations must meticulously assess cash flow consequences and budgetary effects. Securing favorable payment conditions and comprehending potential surcharges or sanctions proves critical for ensuring the PPA's economic feasibility.
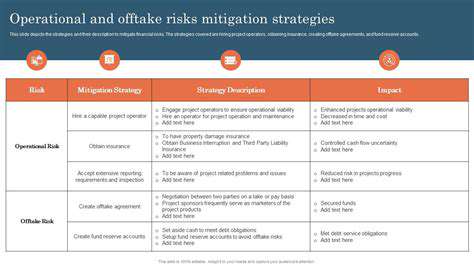
Managing Contractual Risks
All Power Purchase Agreements—whether conventional or renewable—involve inherent contractual hazards. Scrutinizing legal terminology—particularly provisions concerning unforeseeable circumstances, performance assurances, and conflict resolution protocols—becomes essential. Thorough comprehension of contractual stipulations remains fundamental for reducing possible operational interruptions or financial exposures.
Ensuring Operational Efficiency
Successful corporate PPA execution necessitates sturdy operational systems to guarantee seamless energy distribution and administration. This includes creating transparent communication pathways with energy suppliers, formulating internal protocols for consumption tracking, and implementing accurate measurement and reporting mechanisms. Efficient operational oversight becomes pivotal for optimizing benefits while curtailing potential service disturbances.
Comprehensive vetting of the energy provider's capability to fulfill contractual duties remains equally important to preclude future conflicts or power delivery issues.
Identifying Key Risk Categories in Corporate PPAs
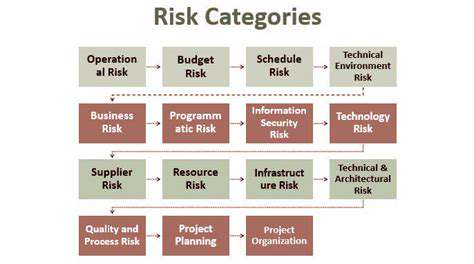
Identifying External Threats
External threats constitute risks emerging from outside corporate boundaries, encompassing diverse potential perils. These external factors can substantially impair operational effectiveness and fiscal health. Recognizing the characteristics and probable consequences of such threats proves crucial for formulating robust risk management approaches. Detecting these hazards requires exhaustive examination of external conditions, accounting for economic variations, political uncertainty, technological developments, and environmental catastrophes.
Competitive maneuvers, legislative modifications, and logistical interruptions all represent external threats warranting careful deliberation. Proactive identification and evaluation of these dangers remains vital for preserving competitive advantage and ensuring organizational resilience.
Assessing Financial Vulnerabilities
Financial weaknesses involve risks pertaining to organizational fiscal soundness, including capital management, leverage ratios, and earnings stability. Monetary instability can trigger operational breakdowns and potential bankruptcy. Detailed inspection of financial records, industry patterns, and economic predictions becomes necessary to detect and appraise possible fiscal vulnerabilities.
Evaluating financial frailties demands thorough analysis of multiple monetary indicators, including solvency measures, leverage statistics, and profit margins. This assessment should further consider corporate adaptability to shifting market dynamics and financial unpredictability.
Evaluating Operational Disruptions
Operational interruptions involve risks directly affecting daily business functions, influencing manufacturing, service provision, and general productivity. Such disturbances may originate from machinery malfunctions, logistical challenges, or environmental calamities. Strategic preparation and preventative actions become critical for minimizing disruption impacts.
Comprehending probable origins and ramifications of operational breakdowns proves essential for risk reduction and continuity assurance. Creating emergency protocols and establishing resilient restoration systems represent crucial steps in effective risk governance.
Analyzing Reputation Risks
Reputation hazards relate to incidents or decisions potentially harming organizational public perception and brand equity. Adverse media coverage, product withdrawals, and ethical dilemmas all constitute possible reputation threats. Safeguarding and improving corporate reputation stands as fundamental for enduring prosperity. Complete risk evaluation should incorporate analysis of public image, stakeholder anticipations, and possible reputational dangers.
Tracking digital platforms, news sources, and public discussions remains imperative for identifying and responding to developing reputation issues. Maintaining prepared crisis response procedures proves essential for handling negative publicity competently.
Addressing Legal and Compliance Risks
Legal and regulatory risks arise from potential breaches of statutes, rules, and moral guidelines. These hazards may result in substantial fines, litigation, and image deterioration. Conforming to legal and regulatory mandates remains indispensable for sustaining secure business operations. An effective compliance framework—incorporating periodic legal assessments and staff training—becomes crucial for mitigating these perils.
Early detection of potential legal and compliance problems can avert significant financial and reputational harm. Routine examinations and internal checks further ensure continuous adherence to legal requirements.