Grid Scale Energy Storage: Ensuring Power Reliability
Grid-scale batteries are transforming how electricity is managed and distributed. These massive energy storage systems provide a vital answer to the inconsistency issues faced by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. By capturing surplus energy during peak production times, they guarantee a steady and dependable power supply around the clock, regardless of weather conditions. This balancing act between supply and demand is indispensable for weaving renewables into our current power grid.
The underlying technology is advancing at a breakneck pace. Breakthroughs in battery chemistry, materials science, and control mechanisms are driving higher energy density, extended lifespans, and superior operational efficiency. Such progress is pivotal in making large-scale energy storage both economically feasible and practical for tomorrow's energy landscape.
Addressing Intermittency and Enhancing Grid Stability
Among their many advantages, grid-scale batteries excel at mitigating the unpredictable nature of renewable energy. Solar and wind outputs vary with weather patterns, complicating power supply management. These batteries serve as a cushion, soaking up excess energy during high production and discharging it when demand spikes, ensuring consumers receive uninterrupted electricity.
Their stabilizing effect is critical for grid reliability. Without adequate storage, renewable energy fluctuations could destabilize the grid, potentially triggering blackouts or equipment damage. Grid-scale batteries act as a safeguard, fortifying our energy infrastructure against such risks.
Economic and Environmental Advantages
The benefits extend beyond technology. By diminishing reliance on fossil fuel plants during peak hours, grid-scale batteries substantially cut greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This translates to a cleaner, healthier environment for future generations.
Additionally, they promise long-term cost savings. Reducing dependence on expensive peaking plants and optimizing renewable energy use leads to a more efficient and economical power system. The combination of financial savings and environmental benefits positions grid-scale storage as a cornerstone of sustainable energy.
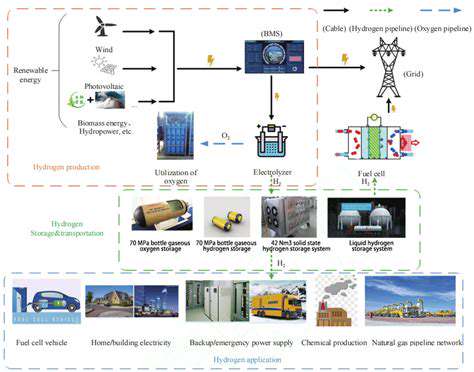
Beyond Batteries: Exploring Diverse Storage Technologies
Beyond Traditional Lithium-ion: Solid-State Batteries
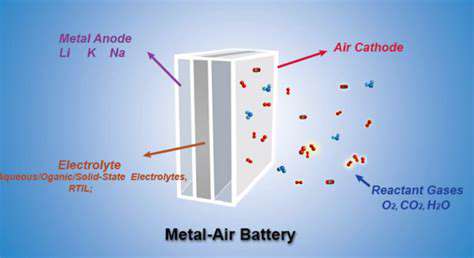
Solid-state batteries represent a groundbreaking alternative to lithium-ion technology. By employing solid electrolytes instead of flammable liquids, they offer enhanced safety and potentially greater energy density and longevity. Though challenges in scalability and cost remain, ongoing research highlights their promise for future grid applications.
A key benefit is their superior energy density, which could lead to more compact and lightweight storage systems—a crucial factor for space-constrained grid installations.
Flow Batteries: A Steady Stream of Energy
Flow batteries take a unique approach, storing active materials in external tanks and circulating them through cells as needed. This design allows effortless scaling by simply enlarging tank capacity, making them ideal for grid use. Their modularity and durability further enhance their appeal for flexible energy solutions.
Pumped Hydro Storage: Harnessing Gravity's Power
As a proven large-scale solution, pumped hydro uses gravity to store energy by moving water between reservoirs. Its high efficiency makes it a reliable option, though substantial infrastructure requirements can pose challenges.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): Capturing Air's Potential
CAES stores energy by compressing air in underground spaces, later using it to power turbines. While efficient for large-scale use, the construction of storage facilities demands significant investment and time.
Thermal Energy Storage: Capturing Heat and Cold
Thermal systems store energy as heat or cold in materials like molten salts, excelling in temperature-sensitive applications. Though not direct electricity producers, they optimize grid efficiency by managing demand.
Capacitive Energy Storage: A Rapid Response Option
Ultracapacitors deliver quick power bursts, ideal for stabilizing grid fluctuations. While their energy density is lower than other technologies, their speed makes them invaluable for specific applications.
The Future of Energy Storage: A Sustainable Path
Harnessing Renewable Energy Sources
As renewables like solar and wind dominate, reliable storage becomes non-negotiable. These intermittent sources demand systems that can absorb and release energy seamlessly, ensuring grid stability. Smoothing out supply-demand mismatches is essential for a decentralized, sustainable energy network.
Advanced Battery Technologies
Innovations are overcoming lithium-ion limitations, with solid-state batteries leading the charge. Their potential for higher efficiency, durability, and safety could redefine storage standards.
Grid-Scale Integration and Management
Sophisticated systems are required to monitor and optimize storage deployment, using advanced algorithms to maintain grid harmony.
Economic Viability and Cost Reduction
Falling technology costs and supportive policies are accelerating adoption. As scale increases, storage will become even more accessible.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sustainable material sourcing and recycling must advance to minimize ecological footprints, ensuring storage solutions align with environmental goals.
Technological Innovation and Research
Continued R&D in materials and designs will unlock new possibilities, from advanced thermal storage to next-gen hydro solutions.
Public Policy and Infrastructure Development
Governments must foster growth through incentives and standards, collaborating with industry to build a resilient energy future.