Energy Storage Basics: Why It's Crucial for Renewables
Beyond the Traditional Grid: The Rise of Decentralized Energy Storage
Decentralized energy storage systems are rapidly emerging as a critical component of a more resilient and sustainable energy future. These systems, often located closer to the point of consumption, move away from the centralized grid model, offering a plethora of benefits for both individual consumers and the broader energy infrastructure. This shift towards distributed energy storage is driven by the need for greater grid stability and enhanced energy independence, potentially leading to significant cost savings and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
The ability to store energy locally allows for a more reliable and responsive energy supply. This localized energy storage can help communities and businesses weather outages and power fluctuations, and potentially even provide backup power during emergencies. This is particularly important in areas with unreliable or aging grid infrastructure.
The Benefits of Localized Energy Storage
Decentralized energy storage systems offer a variety of benefits, including enhanced grid stability, reduced reliance on centralized power sources, and increased energy independence for consumers. These systems can help to balance energy supply and demand, smoothing out fluctuations and reducing the strain on the overall grid. This can lead to a more efficient use of available energy resources, potentially lowering costs for both consumers and utilities.
Moreover, localized storage solutions often improve resilience. In the event of a grid outage, decentralized systems can provide backup power, ensuring essential services and minimizing disruptions to daily life. This increased resilience is crucial for communities that experience frequent power outages or face geographical challenges to grid connectivity.
Technological Advancements Driving the Shift
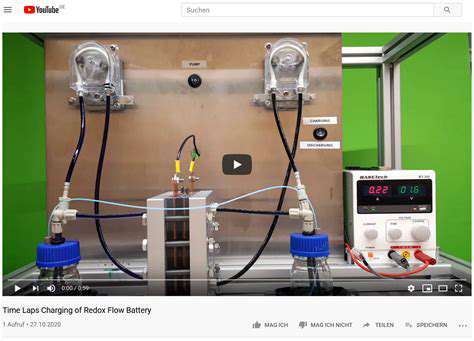
Significant advancements in battery technology, particularly in lithium-ion batteries, are driving the growth of decentralized energy storage. These advancements are improving battery life, energy density, and safety, making them a more viable and attractive option for residential and commercial use. Furthermore, the development of innovative energy storage solutions, such as pumped hydro and thermal storage, is broadening the range of possibilities for decentralized energy storage.
Economic Incentives and Policy Support
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in encouraging the adoption of decentralized energy storage. Incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, can make these systems more affordable for consumers and businesses, thereby stimulating market growth. Furthermore, supportive policies can accelerate the integration of these technologies into the existing energy infrastructure, facilitating the transition to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
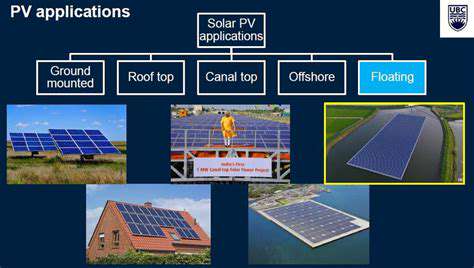
Decentralized energy storage systems are particularly well-suited for integration with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind. By storing excess energy generated from these intermittent sources, these systems help to ensure a consistent and reliable energy supply, regardless of weather conditions or fluctuations in solar irradiance or wind speed. This integration is essential for maximizing the utilization of renewable energy and minimizing the reliance on fossil fuels.
Addressing Challenges and Concerns
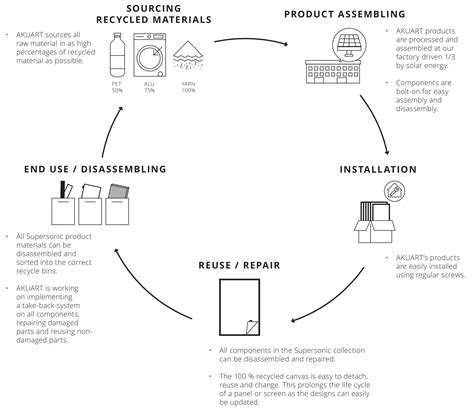
Despite the numerous benefits, there are challenges associated with decentralized energy storage. One significant concern is the potential environmental impact of battery production and disposal. Careful consideration of these factors is needed to ensure responsible manufacturing and recycling practices are implemented. Addressing issues around material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management is critical for the long-term sustainability of these technologies.
The Future of Energy: A Decentralized Approach
The future of energy storage is undoubtedly leaning towards decentralized models. As technology continues to evolve, and supportive policies are enacted, the integration of these systems will become increasingly seamless and cost-effective. This shift will not only enhance grid resilience and sustainability but also empower consumers and communities with greater control over their energy needs. The decentralized approach promises a future where energy is more accessible, reliable, and sustainable.