The Future of Energy: Decentralization of Energy Generation: A Paradigm Shift
The Rise of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Decentralization as a Paradigm Shift
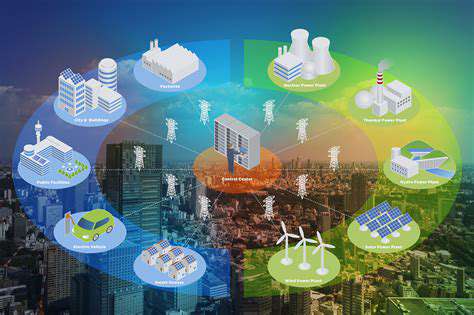
The traditional energy model, with centralized power plants supplying electricity to vast grids, is undergoing a profound transformation. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) are emerging as a crucial component of this shift, fundamentally changing the way we produce, distribute, and consume energy. This decentralization moves power generation closer to the point of consumption, fostering a more resilient and responsive energy system.
This paradigm shift is driven by a confluence of factors, including Technological advancements, environmental concerns, and a growing demand for greater energy independence. The potential for local energy generation and control is creating new opportunities for both consumers and utilities, enabling a more dynamic and sustainable energy future.
Technological Advancements Driving DER Adoption
Technological innovations are significantly accelerating the adoption of DERs. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, energy storage systems, and smart inverters are becoming increasingly affordable and efficient. This progress is driving down the cost of generating electricity locally, making DERs a more economically attractive option for many consumers.
Furthermore, advancements in smart grid technologies are enabling seamless integration of DERs into existing power grids. This integration allows for the efficient management and balancing of fluctuating energy production from distributed sources, enhancing grid stability and reliability.
Economic Benefits of Integrating DERs
The integration of DERs offers substantial economic benefits. Consumers can potentially reduce their energy bills by generating a portion of their own electricity. This self-sufficiency translates into greater energy independence and financial savings over time. Businesses can also benefit from reduced energy costs, potentially improving their operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the development of local energy markets facilitated by DERs creates new economic opportunities for entrepreneurs and investors. This includes businesses involved in the design, installation, and maintenance of DER systems, as well as those providing related services such as energy storage and management.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The increasing use of DERs plays a vital role in achieving environmental sustainability goals. By reducing reliance on centralized power plants, DERs contribute to minimizing carbon emissions and promoting a cleaner energy future. The transition to distributed renewable energy sources like solar and wind significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation.
Moreover, local energy generation fosters reduced transmission losses, which further contributes to a more sustainable energy system. This shift towards decentralized energy production aligns perfectly with the growing global commitment to combat climate change and achieve net-zero emissions targets.
The Role of Policy and Regulation in Supporting DERs
Government policies and regulations are crucial for fostering the growth and integration of DERs into the energy sector. Supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs, net metering programs, and tax incentives, can encourage investments in DER technologies and incentivize their deployment. Clear regulatory frameworks that address grid integration challenges are essential to ensure a smooth transition to a decentralized energy system.
Furthermore, policies that promote energy efficiency and demand response programs can optimize the performance of DERs within the energy system. This collaboration between policymakers and the private sector is essential for realizing the full potential of distributed energy resources and achieving a sustainable energy future.
The Environmental and Economic Impacts
Decentralized Energy and Environmental Impacts
Decentralized energy systems, characterized by smaller, localized power generation units, offer a potent approach to mitigating environmental damage. By reducing reliance on large, centralized power plants, these systems lessen the environmental footprint associated with transportation of energy over long distances. This localized generation also significantly decreases transmission losses, leading to more efficient energy use and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, decentralized systems can potentially integrate renewable energy sources more effectively, accelerating the transition towards a sustainable energy future.
The reduced reliance on fossil fuels in decentralized systems directly translates to lower air and water pollution. This cleaner energy production method directly impacts public health, resulting in fewer respiratory illnesses and other environmental health problems. The environmental benefits extend beyond air and water quality, impacting ecosystems and biodiversity positively.
Economic Impacts of Decentralization
Decentralization offers significant economic advantages, fostering local job creation and economic development. The spread of smaller energy generation units across communities can stimulate local economies, creating opportunities for maintenance, repair, and construction jobs. This localized economic activity can boost local businesses and infrastructure, leading to sustainable growth and reduced regional disparities.
Moreover, decentralized energy systems can potentially lower energy costs for consumers. By reducing transmission losses and promoting energy efficiency, decentralized systems can contribute to more affordable energy prices for households and businesses. Furthermore, the shift to localized control of energy production can enhance energy security and resilience, reducing vulnerability to disruptions in the centralized energy supply.
Technological Advancements in Decentralized Energy
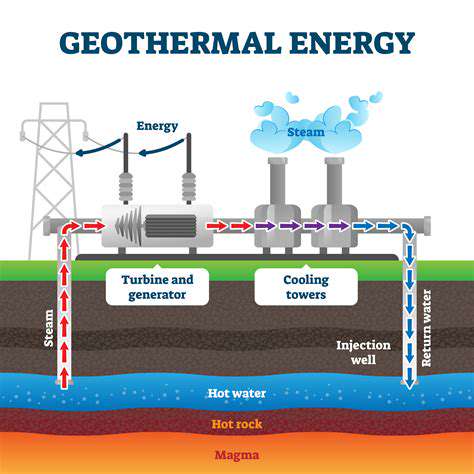
Technological advancements are crucial for realizing the full potential of decentralized energy systems. Innovations in energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries and pumped hydro storage, are essential for managing fluctuating renewable energy sources. Smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure are vital for efficient management of decentralized energy networks. These advancements enable seamless integration of renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and maximizing energy efficiency.
Community Engagement and Public Acceptance
Successful implementation of decentralized energy systems hinges on community engagement and public acceptance. Transparent communication about the benefits and challenges of decentralized energy is essential. Public participation in planning and decision-making processes can foster trust and support for these initiatives. Community-owned energy projects can empower citizens and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for the energy future.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Support
Appropriate regulatory frameworks and supportive policies are critical for facilitating the transition to decentralized energy systems. Policies that incentivize renewable energy adoption, streamline permitting processes for smaller-scale energy projects, and promote energy efficiency measures are essential for encouraging widespread adoption. Furthermore, policies that address the potential challenges associated with interconnecting decentralized systems to existing grids are crucial for a smooth transition.
Addressing Grid Integration Challenges
Integrating decentralized energy systems into existing electricity grids presents significant challenges. The fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources requires advanced grid management strategies to maintain grid stability and reliability. Smart grid technologies and advanced energy storage solutions can help address these challenges. Overcoming these technical and logistical hurdles is essential for the seamless integration of decentralized energy into the existing infrastructure.
Sustainability and Long-Term Vision
A sustainable energy future hinges on the widespread adoption of decentralized energy systems. This transition towards a decentralized model fosters a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting local economic development. Long-term planning and investment in research and development are critical for ensuring the success and sustainability of decentralized energy systems for generations to come.
Technological Advancements Fueling the Transition

Revolutionizing Communication
Technological advancements have dramatically altered how we communicate, fostering unprecedented connectivity and information sharing. The rise of instant messaging platforms and social media has fundamentally reshaped interpersonal interactions, allowing individuals to connect across geographical boundaries in real-time. This seamless communication has profoundly impacted various aspects of our lives, from personal relationships to professional collaborations.
This rapid evolution of communication tools has also ushered in new challenges, demanding careful consideration of privacy, security, and the potential for misinformation. Navigating this complex landscape requires a nuanced understanding of the ethical implications associated with these powerful technologies.
Transforming Healthcare Delivery
Technological innovations are revolutionizing healthcare delivery, empowering medical professionals with advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options. From sophisticated imaging techniques to personalized medicine approaches, technology is enabling more accurate diagnoses and more effective treatments. These advancements are leading to improved patient outcomes and a more proactive approach to healthcare management.
The integration of telemedicine platforms has expanded access to care, particularly for those in rural or underserved areas. Remote monitoring devices and wearable technology are also contributing to preventative healthcare, empowering individuals to actively manage their health.
Enhancing Educational Opportunities
Technology is undeniably transforming education, enriching learning experiences and providing unparalleled access to information. Interactive online learning platforms and digital resources are expanding educational opportunities to a global scale.
Students can now engage with educational content in flexible and personalized ways, adapting learning approaches to individual needs. This personalized learning experience fosters deeper understanding and encourages a more active role in the learning process. Educators can also leverage technology to create engaging and interactive learning environments, fostering creativity and critical thinking skills.
Revolutionizing Industrial Processes
Automation and robotics are reshaping industrial processes, streamlining operations and boosting productivity. These advancements are driving efficiency gains across various sectors, from manufacturing to logistics. The integration of sophisticated machinery and automated systems is enabling greater precision and accuracy in production, leading to higher quality outputs.
Technological advancements in industrial processes are not only boosting efficiency but are also contributing to a safer and healthier work environment. Improved safety protocols and reduced manual labor are leading to fewer accidents and a more comfortable work experience for employees.
Boosting Agricultural Productivity
Technological advancements are significantly enhancing agricultural productivity, addressing global food security challenges. Precision farming techniques, guided by data analytics and satellite imagery, enable farmers to optimize resource utilization and maximize crop yields.
These advancements are crucial for meeting the increasing global demand for food while minimizing environmental impact. Sustainable agricultural practices, facilitated by technology, are crucial for ensuring food security in the face of a growing population.
Improving Transportation Infrastructure
Technological innovations are significantly enhancing transportation infrastructure, improving efficiency and safety. Smart transportation systems, incorporating real-time data and intelligent traffic management, are streamlining traffic flow and minimizing congestion.
Advanced navigation systems and autonomous vehicle technology are further transforming the transportation landscape, promising safer and more efficient travel experiences. These advancements are not only improving mobility but also contributing to a more sustainable future through reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Improving Financial Services
Technological advancements are streamlining financial services, providing greater accessibility and efficiency. Online banking, mobile payments, and digital investment platforms are transforming how individuals and businesses manage their finances.
These advancements are not only enhancing convenience but also increasing financial inclusion. Access to financial services is expanding, empowering individuals and fostering economic growth. However, the increased reliance on digital platforms necessitates robust security measures to mitigate potential risks and fraud.