Renewable Energy Beyond Electricity: Heat and Fuel
The Future of Renewable Energy: A Multifaceted Solution

Harnessing Solar Power for a Sustainable Future
The sun's boundless energy is set to become a cornerstone of renewable energy solutions. Its widespread availability and decreasing costs position solar power as a compelling substitute for traditional fossil fuels, paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape. Modern solar panels, now more efficient and affordable, are increasingly viable for both homes and businesses. Additionally, breakthroughs in energy storage are addressing the variability of sunlight, making solar energy more dependable than ever.
Incorporating solar power into current grid systems demands meticulous planning regarding infrastructure and storage. Fortunately, continuous innovations in these fields are showing great promise, suggesting that these hurdles can be overcome, ushering in an era dominated by solar energy.
Wind Power: A Powerful Force for Change
Wind energy, another vital renewable resource, captures the kinetic force of wind to produce electricity. Wind turbines, frequently grouped in expansive wind farms, convert wind into electrical power, offering a clean and steady alternative to conventional fossil fuel plants. Advances in turbine technology and materials are consistently boosting efficiency and lowering expenses, enhancing the economic and environmental appeal of wind energy.
The strategic placement of wind farms is essential for maximizing energy output while minimizing ecological disruption. By carefully selecting locations, we can ensure wind power is harnessed responsibly and effectively.
Hydropower: Tapping into the Power of Water
Hydropower, which utilizes the energy of moving water, plays a significant role in renewable energy. Hydroelectric dams capture the power of rivers to generate electricity, delivering a stable and continuous energy supply. However, large-scale dam projects can disrupt local ecosystems and alter natural water courses, raising environmental concerns.
Adopting sustainable hydropower practices that prioritize ecological preservation and biodiversity is critical for the enduring success of this energy source.
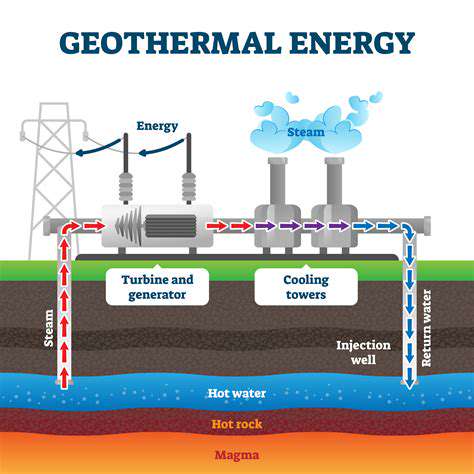
Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Earth's Internal Heat
Geothermal energy, sourced from the Earth's internal heat, represents a promising renewable option. Its reliability and consistency make it an excellent supplement to other renewable sources, ensuring a steady energy flow. Although suitable geothermal sites are geographically limited, technological progress is expanding access to this resource, making it a viable future energy solution.
Innovations like enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are unlocking potential in previously inaccessible areas, broadening the scope and impact of geothermal energy.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Biomass energy converts organic materials, such as crop residues and wood, into usable energy. These materials can be processed into biofuels for transportation or burned directly to produce electricity. Sustainable biomass practices are vital to prevent overharvesting and deforestation, ensuring this resource remains renewable.
Evaluating the environmental effects of biomass production, including emissions and land use changes, is essential for its sustainable adoption.
Ocean Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Seas
Ocean energy, derived from tides, waves, and currents, is an emerging field with immense potential. These untapped marine resources could provide vast amounts of clean energy. However, technological and environmental challenges must be resolved before large-scale implementation becomes feasible.
Continued research and development are key to overcoming these obstacles and realizing the full potential of ocean energy.
Integrating Renewable Energy Systems
Achieving a sustainable energy future requires a cohesive strategy that combines various renewable sources. Coordinating different technologies and storage solutions is essential for creating a resilient and efficient energy grid. Smart grids and advanced management systems are instrumental in this process, optimizing energy distribution and usage.
Supportive policies, investments in innovation, and public education are fundamental to accelerating the shift toward renewable energy.