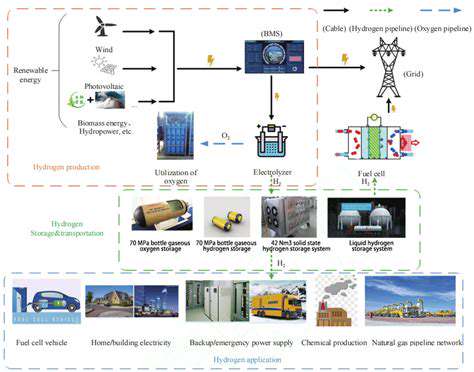
Renewable Energy and Energy Independence
Harnessing Solar Power
The sun delivers more energy to Earth in one hour than humanity consumes annually, making solar technologies indispensable for sustainable development. Contemporary photovoltaic systems achieve conversion efficiencies unimaginable a decade ago, while concentrated solar plants demonstrate remarkable scalability. Storage solutions like advanced batteries and molten salt systems are overcoming traditional limitations, enabling solar to provide consistent baseload power.
Distributed solar installations empower communities through localized generation, reducing strain on transmission networks and improving system resilience. When strategically deployed across underutilized spaces—from rooftops to brownfields—solar infrastructure can meet significant energy demand without competing with agricultural land. The environmental advantages are clear, with lifecycle emissions dramatically lower than conventional alternatives.
Tapping into Wind Energy
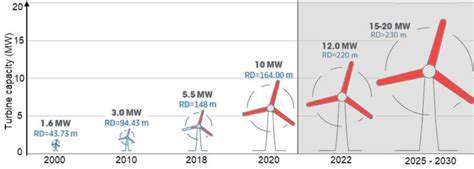
Modern wind turbines represent engineering marvels, with some models exceeding 250 meters in height and 15 MW in capacity. These technological leaps have driven down levelized costs, making wind competitive with legacy generation. Offshore developments particularly stand out, accessing stronger and more consistent wind resources while minimizing land use conflicts.
Innovative blade designs and predictive maintenance systems continue pushing performance boundaries, while floating turbine prototypes unlock deep-water potential. Grid operators now employ sophisticated forecasting tools to manage wind's variable output, demonstrating how system integration challenges can yield to innovation. The sector's rapid maturation suggests even greater contributions in the coming decade.
Exploring Hydropower Potential
Water power remains the largest renewable electricity source globally, offering reliable generation with extensive storage capacity. Modern facilities incorporate fish-friendly turbines and improved sediment management, addressing historical environmental concerns. Pumped storage hydropower provides crucial grid flexibility, acting as massive batteries that can respond to demand fluctuations within minutes.
Smaller-scale hydro projects minimize ecological disruption while still delivering meaningful output. Run-of-river systems maintain natural water flows, and innovative in-stream technologies harness currents without dams. When properly designed, these solutions can balance energy production with ecosystem preservation.
The Versatility of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal systems leverage the Earth's internal heat with remarkable consistency, unaffected by weather or daylight cycles. Enhanced geothermal techniques are expanding viable locations beyond traditional volcanic regions, potentially unlocking terawatts of continuous power. Direct-use applications for heating and industrial processes further broaden geothermal's role in decarbonization.
Geothermal heat pumps demonstrate exceptional efficiency for climate control, delivering three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. These systems could dramatically reduce building emissions if widely adopted. While exploration costs remain a barrier, technological innovations in drilling and reservoir management continue improving the economics.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation Potential
Economic Benefits of Renewable Energy
The renewable transition stimulates economic activity across multiple dimensions. Supply chain development for components like solar inverters and wind nacelles creates manufacturing opportunities, while installation and maintenance services generate local employment. Unlike fossil fuel expenditures that largely leave regional economies, renewable investments circulate more capital domestically.
Price stability represents another significant advantage, as renewable generators face minimal fuel cost volatility. This predictability benefits everything from household budgets to industrial competitiveness. The democratization of energy production through distributed systems enables broader participation in energy markets, creating new revenue streams for communities and individuals.
Job Creation Potential in the Renewable Energy Sector
Renewable industries already employ millions worldwide, with growth projections outpacing most other sectors. These jobs span the skills spectrum—from construction laborers assembling solar racks to PhD researchers developing novel battery chemistries. The sector's diversity ensures opportunities for workers transitioning from declining industries, particularly when supported by retraining initiatives.
Ancillary services including legal, financial, and consulting specialties will expand alongside technical roles. Smart grid technologies and energy management systems require specialized expertise, fostering innovation ecosystems around universities and research centers. This virtuous cycle of investment and innovation promises sustained employment growth for decades.
Workforce development programs must prioritize accessibility, ensuring equitable participation across demographic groups. Apprenticeship models that combine classroom instruction with hands-on experience can efficiently prepare workers for in-demand positions. Policymakers should coordinate with educators and industry to align training with evolving technological requirements.
Effective system design prioritizes user autonomy through intuitive navigation structures. When platforms integrate clear informational architecture and predictable interactions, users operate with greater confidence. Strategic user guidance and transparent system feedback prevent frustration, allowing full utilization of available features. This user-centered philosophy directly correlates with improved engagement metrics and satisfaction outcomes.