The Just Transition: Supporting Workers and Communities in Fossil Fuel Phase Out
The Urgency of a Just Transition
The Growing Need for Change
Climate change has shifted from a theoretical concern to a daily reality across the globe, requiring swift and determined responses. The critical importance of moving toward sustainability cannot be overstated, as hesitation will only intensify existing problems. This transformation calls for a complete restructuring of our economic and social frameworks, replacing fossil fuel dependence with renewable alternatives. Postponing this essential shift guarantees more severe environmental damage for coming generations.
Today's energy systems remain deeply connected to carbon-intensive industries. This interconnection creates powerful economic interests that frequently oppose progress. Yet dismissing overwhelming scientific consensus and visible ecological damage is no longer feasible. Prioritizing planetary health and future inhabitants demands that fair transition strategies take center stage.
Addressing the Social Impacts of Change
True transition extends beyond energy sources - it demands equitable outcomes for all involved parties. This includes fossil fuel workers, industry-dependent towns, and marginalized groups. Building a green economy must account for human consequences, offering retraining initiatives, new employment pathways, and social support systems to those affected.
Uprooting livelihoods without proper safeguards risks social instability and financial distress. Thoughtful preparation and execution are vital to frame this shift as an avenue for renewal rather than a threat. Success requires deep understanding of regional circumstances and community-specific requirements.
The Economic Benefits of a Just Transition
Sustainability efforts present remarkable potential for financial expansion and technological breakthroughs. Renewable energy investments and eco-friendly practices can generate employment, attract capital, and stimulate growth in developing sectors. This evolution unlocks substantial economic possibilities while driving industrial innovation.
Funding renewable infrastructure, energy-saving upgrades, and sustainable transit networks can boost economic activity while establishing new job markets. Moreover, decreasing fossil fuel dependence will ultimately reduce energy expenses and enhance security for all consumers. This transformation represents both an environmental necessity and a strategic economic blueprint.
Identifying Vulnerable Sectors and Communities
Identifying Key Sectors for Transition
Recognizing which industries and positions face the highest transition risks proves fundamental. This requires examining employment patterns, technological developments, and changing global markets. Thorough investigation into sector-specific attributes - including necessary skills, worker geographic distribution, and retraining requirements - enables effective support mechanisms. Such analysis permits customized solutions that help workers navigate economic changes successfully.
Understanding Community Vulnerability
Assessing community resilience demands evaluation of geographic, economic, and resource accessibility factors. Locations dependent on singular industries like mining endure disproportionate transition impacts. Comprehending these communities' social and cultural contexts proves vital for creating appropriate assistance programs.
Analyzing the Impact of Automation
Technological progress continues reshaping employment landscapes. Identifying automation-prone roles allows for targeted intervention strategies. Examining automation adoption rates and projected job losses informs proactive approaches to mitigate technological disruption effects.
Assessing Existing Disparities
Successful transitions must confront current inequalities. Marginalized groups often encounter greater obstacles when accessing transition resources. Acknowledging these differences permits creation of specialized assistance initiatives.
Evaluating Policy Effectiveness
Government actions significantly influence transition outcomes. Effective measures should address worker and community needs comprehensively. Analyzing policy impacts helps refine approaches for optimal results.
Investment in Green Technologies and Skills Development

Investing in a Sustainable Future
Global sustainability efforts require substantial commitments to green innovation. These investments represent our best opportunity for climate stabilization and environmental preservation. The spectrum includes renewable energy systems, efficient construction materials, and eco-friendly transportation options.
Renewable Energy Advancements
Solar, wind, and other renewable sources continue gaining efficiency and affordability. Expanding renewable infrastructure guarantees cleaner energy solutions long-term. Supportive government policies accelerate technology adoption significantly.
Energy Conservation Strategies
Enhanced efficiency measures across buildings, industries, and transport networks minimize energy waste dramatically. Efficiency technologies deliver both environmental benefits and financial savings. Continued research promises further improvements.
Sustainable Transportation Options
As major emissions contributors, transport systems require green overhauls. Electric vehicle investments and alternative fuel development reduce pollution while decreasing fossil fuel reliance. Expanded public transit options provide additional environmental gains.
Agricultural Sustainability
Eco-conscious farming methods protect ecosystems while ensuring food supplies. Precision agriculture and organic techniques conserve resources effectively. Sustainable food systems minimize waste throughout production chains.
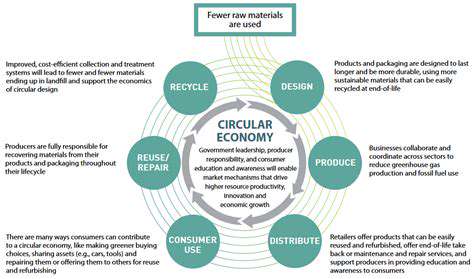
Circular Economy Implementation
Resource-efficient economic models reduce material waste substantially. Recycling infrastructure and product redesign maximize resource utilization. These approaches decrease dependence on raw material extraction.
Community Engagement and Empowerment
Community-Centered Transition Approaches
Local involvement remains essential for equitable transitions, ensuring affected populations guide the process. Active listening to community concerns about economic changes fosters collaborative solution development.
Workforce Skill Enhancement
Transition success depends on preparing workers for emerging industries. Comprehensive training covering renewable technologies and sustainability sectors builds necessary competencies. This investment demonstrates commitment to workforce stability during economic shifts.
Business Support Systems
Sustaining existing enterprises while encouraging sustainable startups requires multifaceted assistance. Financial access, technical guidance, and mentorship programs stimulate innovation and job creation in transitioning economies.
Equitable Resource Distribution
Fair transitions demand equal access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Addressing current disparities prevents worsening inequalities during economic restructuring periods.
International Cooperation and Policy Frameworks
Global Transition Agreements
International collaboration provides critical foundations for balanced transitions. Existing climate accords establish parameters for managing change while protecting vulnerable groups. Global knowledge sharing enhances policy effectiveness.
Comprehensive Policy Development
Effective transition strategies incorporate worker retraining, financial assistance, and community support mechanisms. Customized solutions accounting for local conditions ensure policy relevance and success.
Transition Financing Solutions
Substantial funding requirements necessitate innovative financial instruments and international support structures. Condition-based funding encourages sustainable practices and labor protections globally.
Stakeholder Collaboration Models
Successful transitions rely on cooperation between governments, businesses, and community representatives. Transparent communication builds consensus around shared transition objectives.