Offshore Wind Farm Engineering and Construction Challenges: Innovative Solutions
Innovative Foundation Design and Installation Techniques
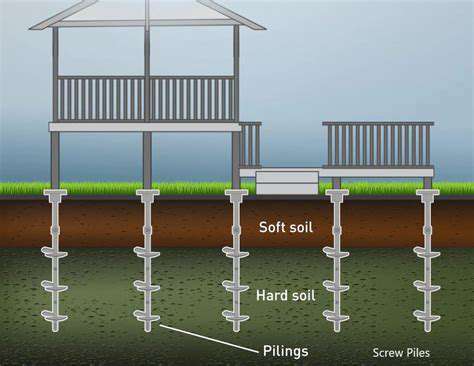
Innovative Foundation Design Considerations
Modern foundation design approaches play a pivotal role in guaranteeing building stability and durability, especially in difficult soil conditions. Engineers now employ cutting-edge methods including soil enhancement procedures and custom materials to tackle specific ground characteristics and location-based challenges. Meticulous planning and engineering are absolutely necessary to avoid expensive future repairs or catastrophic structural damage.
Critical evaluation of elements like soil load-bearing potential, water table depth, and earthquake risks must be prioritized during foundation planning. Professionals utilize comprehensive simulation and examination processes to properly evaluate these variables and customize the foundation accordingly. This typically requires detailed subsurface investigations to fully grasp the complexities of the underground environment.
Soil Analysis and Computer Simulations
Detailed soil examination is fundamental for comprehending how the ground will behave beneath the planned structure. This process includes rigorous lab tests to establish soil characteristics like density, elasticity, and water absorption. Precise computer modeling of how structures interact with soil is crucial for maintaining building safety and steadiness.
Advanced computational methods, including finite element analysis, are frequently employed to predict foundation performance under various weight distributions. This enables engineers to assess sinking patterns, pressure points, and shape changes in both the ground and foundation components. Such information is invaluable for making well-informed engineering choices.
Soil Enhancement Methods
At locations with poor soil quality, ground improvement techniques can substantially boost foundation performance. These methods might include soil reinforcement, densification, and the application of synthetic ground materials. These approaches can remarkably increase the soil's weight-bearing ability and decrease the likelihood of structural settling.
Advanced Materials and Building Techniques
Incorporating modern materials like ultra-strong concrete and innovative steel reinforcements can enhance a foundation's weight capacity and lifespan. These materials also support more eco-friendly building practices. Contemporary construction approaches, including prefabricated elements and modular systems, can streamline foundation engineering and assembly. These methods may shorten project timelines while improving accuracy.
Eco-Friendly Design Principles
Environmentally conscious practices are becoming increasingly vital in foundation engineering. Reducing the ecological footprint of construction activities, such as limiting waste production and responsibly managing water usage, is critically important. Incorporating recycled components into foundation plans can further promote sustainable construction. This requires thoughtful evaluation of the project's lasting environmental consequences, including effects on nearby natural habitats.

Addressing Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
Environmental Impact Evaluation
A key component of offshore wind energy projects is the detailed environmental impact evaluation (EIE). This procedure thoroughly examines potential wind farm effects on multiple marine environment aspects, including aquatic organisms, ecosystems, and ocean cleanliness. Comprehensive EIE research must account for possible interruptions to animal migration paths, feeding behaviors, and reproduction areas, plus the risk of sound and vibration disturbances affecting sea mammals and fish populations. Serious attention must be paid to potential ecological consequences to guarantee minimal environmental disruption and proper implementation of corrective measures.
Sustainable Material Choices and Production
Environmentally responsible material selection is fundamental for offshore wind turbine construction. Designers should emphasize using reprocessed and sustainable materials when feasible, thereby decreasing the ecological impact of manufacturing. This involves analyzing the complete lifespan assessment of various materials, from initial extraction to final disposal. Selecting materials optimized for saltwater corrosion resistance while limiting use of environmentally problematic substances represents a crucial element of sustainable production methods.
Reducing Construction Footprint
Minimizing ecological disturbance during offshore wind farm assembly is paramount. Approaches should incorporate prudent location selection to protect sensitive zones and limiting employment of hazardous substances during installation. Building techniques should be deliberately chosen to reduce seabed disruption and possible ocean floor damage. Sophisticated equipment like underwater drones can help decrease ecological effects on marine habitats during construction phases.
Environmental Protection and Oversight
Effective protection and surveillance plans are vital for reducing long-term wind farm environmental consequences. These plans should incorporate specific procedures to track marine ecosystem health surrounding the installation. Consistent monitoring of ocean purity, aquatic organism numbers, and potential sound pollution levels is essential for spotting negative impacts and taking immediate corrective steps. Comprehensive information gathering and examination are necessary to verify the project's environmental achievements.
Public Involvement and Partnership
Including local populations and working with interested parties is essential for successful offshore wind project execution. Clear, honest communication about potential project effects and mitigation approaches is crucial for establishing credibility and resolving concerns. This means engaging fishing communities, environmental organizations, and other local representatives in development discussions. Cooperation with marine scientists and ecological specialists helps ensure project harmony with regional ecosystems and enhances environmental outcomes.