Advanced Energy Storage for Corporate Resilience and Cost Savings
At the heart of any successful energy independence strategy lies cutting-edge energy storage technology. These systems let businesses stockpile surplus power generated from renewable sources, creating a reliable backup during peak demand or grid failures. This dual benefit not only decreases dependence on public utilities but also makes it practical to incorporate variable renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines into daily operations.
Financial Benefits and Streamlined Operations
Energy autonomy through modern storage solutions offers significant economic advantages. Companies insulate themselves from volatile energy prices while optimizing their power usage. The strategic deployment of stored energy minimizes operational disruptions and boosts output efficiency, leading to measurable cost savings and improved profitability metrics.
Environmental Stewardship and Brand Enhancement
The move toward energy independence naturally supports corporate sustainability goals. When businesses adopt renewable energy and sophisticated storage methods, they send a powerful message about their environmental commitment. This ethical positioning strengthens brand reputation, appeals to eco-conscious stakeholders, and can even influence investment decisions. The intangible benefits of this approach often prove as valuable as the direct financial returns.
Breakthroughs in Storage Technology
The energy storage sector continues to evolve at a rapid pace, bringing down costs while improving performance. Lithium-ion battery innovations have dramatically increased storage capacity and durability, while alternative solutions like pumped hydro and thermal storage provide flexible options for different business needs. These technological leaps are making independent energy systems increasingly practical for commercial applications.
Navigating Policies and Incentives
Government energy policies and financial incentives play a crucial role in adoption rates. Savvy businesses stay informed about tax credits, subsidies, and regulatory changes that can make or break the economics of energy storage projects. Proactive engagement with these policy frameworks can significantly accelerate implementation timelines and improve return on investment calculations.

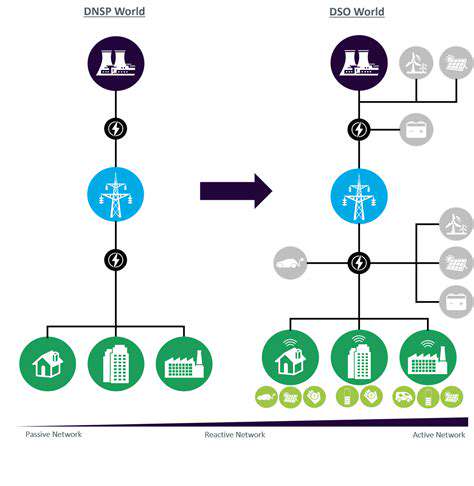
Strategic Integration for Optimal Results
Blueprint for Successful Implementation
The journey toward energy autonomy begins with meticulous planning. Each company must define its unique objectives - whether reducing grid dependence, stabilizing energy costs, or increasing renewable usage. This planning phase requires careful analysis of current infrastructure, power consumption trends, and applicable regulations to ensure the chosen solution fits both technically and financially.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
With options ranging from lithium-ion batteries to compressed air systems, selecting the appropriate technology demands careful consideration. Decision-makers must weigh factors like storage capacity, operational efficiency, environmental impact, and total cost of ownership against their specific operational requirements. This technology matching process is critical for achieving long-term success.
Operational Excellence and Maintenance
Effective system integration requires clear protocols for energy management, including charging cycles, discharge strategies, and performance monitoring. Establishing rigorous maintenance routines ensures system reliability and extends equipment lifespan. Companies must invest in proper training to develop in-house expertise for managing these sophisticated systems.
Financial Planning and Justification
A comprehensive financial analysis forms the foundation for any energy storage initiative. Projections should account for reduced utility expenses, potential revenue from excess power sales, and all associated operational costs. This evaluation must also consider future energy price scenarios and anticipated technological improvements to ensure the investment remains sound over time.
Building Consensus and Ensuring Compliance
Successful projects require buy-in from all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and community members. Clear communication about project benefits helps build support. Simultaneously, strict adherence to all relevant regulations and permitting requirements prevents costly delays or legal complications during implementation.
The Path Forward: Embracing a Sustainable Future

Committing to Sustainable Operations
Sustainable business practices represent more than environmental responsibility - they embody a strategic approach to long-term viability. The shift toward sustainability requires rethinking traditional resource management models and operational paradigms. Prioritizing renewable energy, minimizing waste, and promoting efficient consumption patterns creates value while protecting ecosystems. This transformation benefits both current operations and future generations.
Real progress demands collaboration across all sectors of society. When businesses, governments, and individuals unite behind sustainable principles, we create more resilient communities and preserve natural resources for the future.
Leveraging Technological Innovation
Breakthrough technologies serve as powerful enablers for sustainability goals. From smart energy grids to advanced recycling systems, innovation drives efficiency improvements and environmental protection. Continued investment in research and development yields solutions that make sustainable practices more accessible and cost-effective.
Emerging technologies also empower consumers to participate in sustainability efforts. Smart home systems, for instance, allow households to optimize energy use and reduce waste, demonstrating how technological solutions can scale sustainable behaviors across society.
The Policy Framework for Change
Effective regulations and incentives create the necessary conditions for widespread adoption of sustainable practices. Well-designed policies encourage businesses to innovate while ensuring environmental protections remain strong. Governments must establish clear standards for emissions, energy efficiency, and resource conservation while providing support for organizations transitioning to greener operations.
Policy frameworks should evolve alongside technological and market developments, maintaining relevance in a changing world. Regular reviews and adjustments ensure regulations continue driving meaningful progress toward sustainability targets.
Educating and Engaging Communities
Lasting change requires broad public understanding and participation. Comprehensive education programs help individuals recognize their role in sustainability efforts and make informed choices. Community-based initiatives demonstrate practical applications of sustainable principles while fostering local engagement.
Schools and universities increasingly incorporate sustainability into their curricula, preparing future leaders to prioritize environmental considerations in all aspects of business and civic life. This educational foundation supports long-term cultural shifts toward sustainability.
The Business Case for Sustainability
Beyond environmental benefits, sustainable practices offer compelling economic advantages. The transition to green technologies creates new industries, employment opportunities, and revenue streams while reducing long-term operational risks. Companies embracing sustainability often see improved efficiency, stronger customer relationships, and enhanced resilience against regulatory changes.
Forward-thinking organizations recognize that sustainable operations align profitability with planetary health. This alignment creates value for shareholders while contributing to broader societal goals, proving that responsible business practices can drive both financial success and positive environmental impact.