Solar Energy for Off Grid Communities
Overcoming the Challenges of Implementing Solar in Off-Grid Areas
Overcoming Implementation Barriers
Implementing new systems or processes often faces hurdles that can derail even the best-laid plans. These barriers can stem from various sources, including inadequate resources, resistance to change from stakeholders, and a lack of clear communication. Addressing these challenges head-on is crucial for successful implementation. Understanding the potential obstacles and proactively developing strategies to mitigate them is essential for project success.
A key aspect of overcoming implementation barriers is thorough planning. This involves meticulous research and analysis to identify potential roadblocks. Effective communication channels and strategies are vital, ensuring all stakeholders are informed and involved. Developing a robust implementation plan with clear timelines and responsibilities is also critical.
Resource Allocation and Management
Sufficient resources, including financial backing, personnel, and technology, are essential for successful implementation. A realistic assessment of the required resources is crucial. Underestimating the necessary resources can lead to delays, cost overruns, and ultimately, project failure. Careful budgeting and resource allocation are key elements for project success.
Effective management of allocated resources is equally important. This involves monitoring progress, identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks, and adapting to unforeseen circumstances. A strong project management framework, coupled with skilled personnel, is critical for efficient resource utilization.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Successful implementation hinges on the active participation and buy-in from all stakeholders. Understanding their needs, concerns, and perspectives is crucial. Building strong relationships with key stakeholders will foster a collaborative environment and reduce resistance to change. Open and transparent communication is paramount throughout the entire implementation process.
Effective communication strategies should be implemented from the outset and adapted to the needs of different stakeholders. Clear and concise communication of project goals, timelines, and progress updates is critical. Regular feedback sessions with stakeholders will be crucial to identifying and addressing any concerns early on.
Adaptability and Flexibility
The implementation process is rarely linear. Unforeseen circumstances, unexpected challenges, or shifts in the project's scope can occur. Developing an adaptable approach is crucial to navigate these changes. Flexibility and adaptability are essential for staying on track and achieving project goals.
Having contingency plans in place for potential challenges can help mitigate the impact of unexpected events. Regular reviews of the implementation process and adjustments to strategies as needed will be crucial for successful outcomes. A commitment to continuous learning and improvement is important to refine the implementation process throughout.
Financial Incentives and Support for Solar Energy Adoption
Government Incentives for Solar Panel Installations
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of transitioning to renewable energy sources, and solar energy is a key component of this shift. To encourage widespread adoption of solar panels, many jurisdictions offer financial incentives. These incentives can take various forms, including tax credits, rebates, and grants. Such initiatives significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with installing solar systems, making them more accessible to homeowners and businesses alike. This makes it a more attractive investment compared to traditional energy sources.
Specific details of these incentives often vary by location. Understanding the available incentives in a given area is crucial for homeowners and businesses considering solar panel installations. Researching local government programs and regulations is essential for maximizing the benefits of these financial supports.
Federal Tax Credits and Rebates
Federal tax credits and rebates play a vital role in promoting solar energy adoption. These are often substantial financial incentives that can substantially reduce the overall cost of a solar installation. The specifics of these credits and rebates, including eligibility requirements and maximum amounts, are subject to changes in legislation, so it is essential to consult the latest government resources for up-to-date details. Staying informed about these changes is important for maximizing any potential savings.
The availability and value of these incentives can influence the decision-making process for individuals and businesses considering a solar energy transition. This can be a crucial factor in the overall feasibility and cost-effectiveness of the project.
State and Local Incentives
Many states and local governments also implement their own financial incentives to support solar energy adoption. These incentives can complement federal programs and offer additional reductions in the cost of solar installations. The programs vary widely across different regions, reflecting local priorities and economic conditions. Understanding and utilizing these state-level incentives is critical for homeowners and businesses to fully leverage the financial support available.
State incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and even grants, all designed to encourage solar energy adoption within their respective jurisdictions. The specific details of these incentives are important to understand and research based on the location of the solar installation project.
Financing Options for Solar Installations
Beyond direct government incentives, several financing options are available to facilitate solar energy adoption. These options can help spread the cost of the installation over time, making it more manageable for individuals and businesses. Loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) are common financing structures that can significantly ease the financial burden of transitioning to solar power. These options offer flexibility and can be tailored to individual financial situations and needs.
Support Programs for Low-Income Households
Recognizing that solar energy adoption might present a greater financial challenge for lower-income households, dedicated support programs are emerging. These programs often offer tailored financial assistance, installation subsidies, or reduced-cost financing options for qualified individuals and families. Such programs are crucial in making solar energy more accessible to everyone, regardless of economic status, and promote equitable access to renewable energy.
Often, these programs work in conjunction with local government incentives to provide a comprehensive support system. This can help ensure that low-income households can still benefit from the advantages of solar energy adoption.
Community Solar Programs
Community solar programs offer an alternative approach to solar energy adoption, especially for individuals who may not have sufficient space or resources to install their own systems. These programs allow participants to invest in a shared solar array, thereby gaining a share of the generated clean energy without the need for a personal solar installation. This is a powerful strategy that allows for greater community participation in renewable energy projects.
These programs provide access to solar energy benefits without requiring substantial upfront investment or installation effort, making it accessible to a wider range of people and promoting broader adoption of solar energy.
Benefits beyond Financial Incentives
While financial incentives are crucial for driving solar energy adoption, the benefits extend far beyond the immediate cost savings. Solar energy systems offer environmental advantages, contributing to a reduction in carbon emissions and a cleaner environment. This aligns with broader societal goals and promotes sustainability. This can create a positive impact on the environment and community.
Longer-term energy independence and price stability are additional benefits of adopting solar energy, making it a potentially lucrative investment in the long run. These benefits enhance the attractiveness of solar installations beyond purely financial considerations.
The Future of Solar Energy in Empowering Off-Grid Communities
Harnessing Sunlight for Remote Villages
Solar energy is rapidly emerging as a crucial solution for empowering off-grid communities, particularly those situated in remote areas with limited access to traditional electricity grids. These communities often face significant challenges in accessing essential services and opportunities, hindering their overall development. Harnessing the power of the sun offers a sustainable and reliable alternative, providing a pathway to improved livelihoods, education, and healthcare.
The potential of solar energy to transform lives in off-grid communities is undeniable. By providing a clean and renewable energy source, solar solutions can power homes, schools, clinics, and small businesses, creating a more vibrant and self-sufficient environment. This independence from reliance on external grids also fosters resilience in the face of natural disasters and other disruptions.
Technological Advancements in Solar Panel Efficiency
Significant strides in solar panel technology are driving down costs and increasing efficiency. Innovations in materials science, manufacturing processes, and design are leading to more affordable and powerful solar panels that can effectively capture and convert sunlight into usable electricity. This translates to a more cost-effective and accessible solution for off-grid communities.
Furthermore, advancements in energy storage solutions, such as improved batteries and energy storage systems, are crucial for leveraging the intermittent nature of solar energy. These improvements ensure that solar energy can be utilized consistently throughout the day and night, addressing the challenges posed by fluctuating sunlight levels.
Addressing Infrastructure and Grid Integration
Implementing solar energy solutions in off-grid communities requires careful consideration of local infrastructure. Challenges such as building reliable electrical distribution networks, connecting homes and businesses to the solar system, and ensuring the proper maintenance of these systems need to be proactively addressed. This includes training local technicians and establishing community-based maintenance programs.
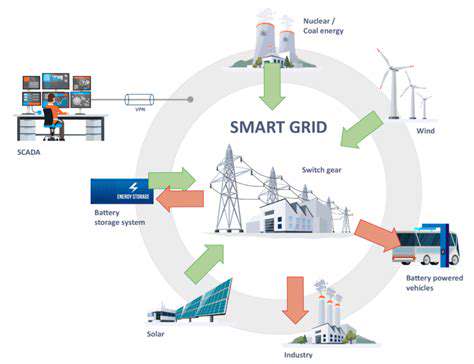
The integration of solar energy with existing grids, where possible, can further enhance the reliability and sustainability of the system. Smart grid technologies can optimize energy distribution and ensure that solar energy is effectively integrated into the wider energy infrastructure. This integration can also create economic opportunities for local communities.
Community Engagement and Education
Successful implementation of solar energy projects in off-grid communities hinges on active community engagement. Educating residents about the benefits of solar energy, its practical application, and the importance of maintenance is paramount. This includes workshops, training programs, and community-based projects that empower local individuals to participate in the design, implementation, and maintenance of solar systems.
Financial Sustainability and Investment
Securing sustainable funding for solar projects in off-grid communities is crucial for long-term success. Innovative financing mechanisms, such as community-based microfinancing, and government subsidies can play a key role in making solar energy accessible and affordable for these populations. Attracting private investment and developing sustainable business models are also important components in ensuring the financial viability of these projects.
Partnerships between international organizations, NGOs, local businesses, and governments are vital for developing and implementing effective solar energy programs. These partnerships should focus on leveraging expertise, resources, and financial support to create a supportive ecosystem for the development of sustainable solutions.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
Solar energy offers a significant environmental advantage over traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. Its clean and renewable nature helps to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the negative impacts of pollution on the environment. This is particularly crucial for off-grid communities, where the environmental consequences of traditional energy sources can be more pronounced.
Promoting solar energy fosters a more sustainable energy future, ensuring long-term environmental well-being for off-grid communities and beyond. This includes incorporating environmentally sound practices in the manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of solar systems to minimize environmental impact.