Renewable Energy in Developing Economies: Business Models for Access
Decentralized networks are revolutionizing how we manage energy and technology. These distributed systems offer superior security, transparency, and resilience compared to traditional centralized models. Growing demand for local control over energy resources is accelerating this transformation.
Beyond Traditional Centralization
While centralized systems offer efficiency, their vulnerability to single-point failures creates unacceptable risks. Decentralization distributes these risks while enhancing overall system stability.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Modern decentralized systems use advanced cryptography to ensure data integrity. This combination of security and transparency proves especially valuable for applications requiring trust verification, like energy trading and supply chain tracking.
Improved Resilience and Fault Tolerance
The distributed architecture of these systems provides built-in redundancy. Local failures don't disrupt the entire network, creating unprecedented reliability for critical infrastructure.
Potential Applications Across Industries
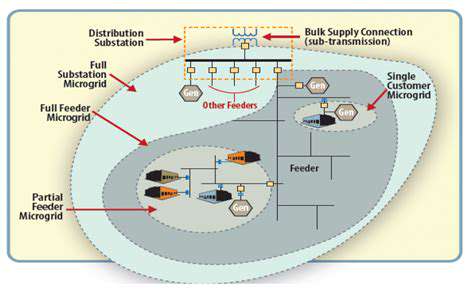
From microgrids to carbon credit markets, decentralized solutions are transforming multiple sectors. These innovations promise to redefine our relationship with energy systems and digital infrastructure. The potential efficiency gains could dramatically lower costs while improving service.
Challenges and Considerations
Scalability issues and user adoption barriers remain significant hurdles. Solving these challenges will determine how quickly decentralized systems can reach their full potential. Simplifying interfaces and improving interoperability are particularly crucial.
The Future of Decentralization
Ongoing technological advances promise to expand decentralized solutions across industries. This evolution will fundamentally reshape how communities generate, store, and distribute renewable energy.
Exploring Innovative Financing Mechanisms for Renewable Energy Projects

Innovative Approaches to Funding
Creative financing solutions are unlocking new possibilities for clean energy development. These alternatives to traditional bank loans are particularly valuable for startups and community projects that struggle to secure conventional funding. Specialized financing tools can address unique challenges in different regions and sectors.
Leveraging Technology for Efficiency
Digital platforms and blockchain are streamlining renewable energy financing. These technologies reduce transaction costs while increasing transparency, making funding more accessible for smaller projects.
Crowdfunding as a Funding Source
Community-based funding allows renewable energy projects to bypass traditional gatekeepers. This approach builds local support while accelerating project timelines through direct community investment.
Impact Investing and Social Enterprise Financing
Investors increasingly seek projects delivering environmental benefits alongside financial returns. This trend is channeling capital toward renewable energy initiatives that create measurable social impact.
Sustainable Financing Strategies
ESG-focused investing is redirecting capital toward renewable energy projects with strong sustainability credentials. This shift recognizes that responsible investments often outperform traditional options over the long term.
Government Initiatives and Public-Private Partnerships
Strategic government support can de-risk renewable energy investments. Well-designed partnerships combine public resources with private sector innovation to accelerate the energy transition. Policy incentives remain crucial for attracting investment.
Analyzing the Risks and Rewards
While alternative financing offers exciting potential, thorough due diligence remains essential. Understanding each model's unique risks helps maximize success rates for renewable energy projects.
Bridging the Digital Divide for Energy Access Management
Addressing the Gap in Infrastructure
The digital divide creates major obstacles for energy management in developing regions. Without reliable connectivity, implementing smart renewable energy solutions becomes extraordinarily difficult. This infrastructure deficit prevents effective monitoring of energy systems, hindering efficiency improvements.
Empowering Communities Through Digital Literacy
Teaching digital skills enables communities to actively participate in energy management. Practical training should cover monitoring energy use, troubleshooting, and making data-driven decisions about local energy systems.
Developing Sustainable Data Management Systems
Effective energy management requires robust data systems tailored to local needs. These solutions must balance accessibility with security while providing actionable insights for optimizing renewable energy deployment.