Renewable Energy and Grid Modernization
The Economic and Societal Benefits of a Modernized Grid
Improved Reliability and Resilience
A modernized grid, incorporating advanced technologies and smart grid components, significantly enhances the reliability and resilience of the electricity supply. This translates to fewer power outages, reduced downtime for critical infrastructure, and improved service continuity during extreme weather events or other disruptions. Modern grid infrastructure, with its enhanced monitoring and control capabilities, can more effectively anticipate and respond to potential problems, minimizing the impact on consumers and businesses.
This improved resilience isn't just about minimizing inconvenience; it's crucial for maintaining the functionality of hospitals, data centers, and other essential services. A reliable power supply is fundamental to modern life, and a modernized grid plays a critical role in ensuring that reliability.
Enhanced Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
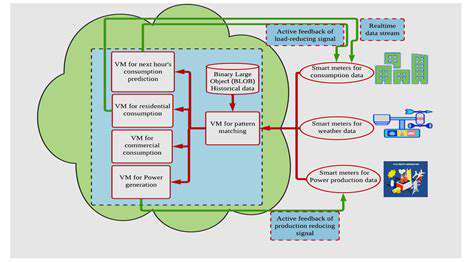
One of the most significant benefits of a modernized grid is its ability to seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the existing electricity system. Traditional grids often struggle with the intermittent nature of these sources, but a smart grid can manage fluctuating energy production by dynamically adjusting energy distribution and storage. This integration fosters a more sustainable energy future, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Furthermore, the ability to effectively integrate distributed energy resources, like rooftop solar panels, is crucial for a modern grid. This not only increases energy independence for consumers but also creates new avenues for local energy generation and management. This integration can lead to a more decentralized and resilient energy system.
Reduced Operational Costs and Increased Efficiency
Modernizing the grid leads to substantial cost savings for utilities and consumers alike. By optimizing energy distribution and reducing transmission losses, a modernized grid can significantly reduce operational costs. Smart grid technologies, such as automated metering infrastructure and advanced analytics, enable more efficient energy management, allowing for better forecasting and improved grid performance. This efficiency translates to lower energy bills for consumers and reduced costs for utilities, leading to a more sustainable and economical energy system.
The streamlined processes and improved data analysis capabilities inherent in a modernized grid contribute to reduced maintenance costs and increased operational efficiency. Predictive maintenance based on real-time data can prevent equipment failures before they occur, further reducing expenses associated with grid upkeep.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
The modernization of the electricity grid is not just about technological advancements; it's a catalyst for economic growth and job creation. Investment in new infrastructure and technologies creates employment opportunities in manufacturing, construction, and maintenance. The development and deployment of smart grid technologies foster innovation and attract further investment in the renewable energy sector, creating a virtuous cycle of economic activity. This ripple effect extends beyond the energy sector, impacting related industries and stimulating overall economic growth.
The development and implementation of new grid technologies also fosters a skilled workforce, creating opportunities for training and education in emerging fields. This investment in human capital is essential for the long-term sustainability and success of the modernized energy infrastructure.