Building Trust and Public Support for a Renewable Energy Future
Promoting Education and Awareness about the Benefits of Renewable Energy
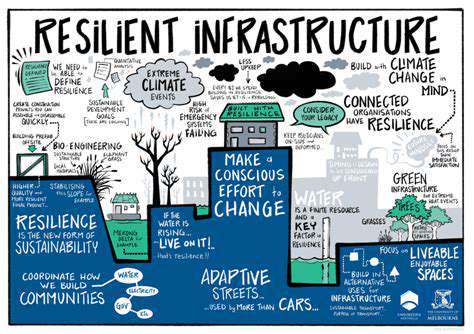
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Fossil Fuels
The reliance on fossil fuels for energy production has had a profound and detrimental effect on our environment. Burning fossil fuels releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and causing a cascade of environmental problems. This includes rising sea levels, more frequent and intense extreme weather events, disruptions to ecosystems, and the endangerment of countless species. Understanding the severity of this impact is crucial to motivating the shift towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
The Advantages of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, in contrast to fossil fuels, are replenished naturally and do not contribute to the depletion of finite resources. Examples include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. These sources offer significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing pollution. Furthermore, they promote energy independence and reduce reliance on volatile global energy markets.
The Economic Benefits of Transitioning to Renewable Energy
The transition to renewable energy sources presents a significant economic opportunity. Investing in renewable energy technologies creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research. This creates a sustainable economic model, fostering innovation and reducing our dependence on fossil fuel imports. Moreover, the long-term cost savings associated with renewable energy can significantly benefit both individuals and businesses.
Education and Awareness Campaigns for a Sustainable Future
Raising public awareness about the benefits of renewable energy is critical for driving the necessary change. Educational campaigns can effectively communicate the environmental, economic, and social advantages of transitioning to a sustainable energy system. This includes emphasizing the positive impact on public health, the creation of new job opportunities, and the overall improvement of our planet's future.
Policy Support and Incentives to Encourage Renewable Energy Adoption
Government policies play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to renewable energy. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and favorable regulations can encourage investment in renewable energy projects and technologies. Furthermore, supportive policies can create a predictable and attractive market for renewable energy, driving innovation and accelerating the adoption of cleaner energy sources.
Community Engagement and Collaboration for Renewable Energy Initiatives
Successful adoption of renewable energy requires collaborative efforts across communities. Community engagement can involve local initiatives for installing solar panels, developing wind farms, or creating local energy cooperatives. These initiatives foster a sense of shared responsibility and promote the development of sustainable energy solutions tailored to specific community needs. Ultimately, this collaborative approach empowers individuals and communities to play an active role in shaping a greener energy future.
Implementing Effective Policies and Incentives to Drive Public Adoption
Understanding the Crucial Role of Incentives
Effective policies for promoting public adoption of emerging technologies like building technologies require a deep understanding of the motivations and needs of the target audience. Incentives play a critical role in driving adoption by making the technology more accessible and attractive. These incentives can range from financial subsidies to streamlined regulatory processes. Understanding how different types of incentives resonate with various user groups is crucial for maximizing their impact and ensuring broad public support for the implementation of these technologies. A well-designed incentive program should consider factors such as affordability, accessibility, and long-term sustainability to encourage widespread adoption and ensure that the benefits are felt throughout the community.
Incentives can be monetary, such as tax breaks or rebates for consumers who adopt the new technologies, or non-monetary, like simplified permitting processes, educational resources, or community support networks. The most effective incentive programs are often those that address the specific needs and concerns of various user segments, providing tailored support that directly addresses their unique challenges. This approach ensures that incentives reach those most likely to benefit and encourages more widespread participation. By carefully considering the needs and motivations of the public, policymakers can design incentive programs that are both effective and sustainable, fostering a positive feedback loop for the long-term success of the building technology initiatives.
Streamlining Policy Frameworks for Enhanced Adoption
Building trust and confidence in new technologies is paramount for public adoption. Clear and concise policies that outline the benefits, functionalities, and safety measures associated with a building technology are essential for fostering this trust. Transparent regulatory frameworks that address potential risks and concerns head-on are crucial for building public confidence and encouraging widespread adoption. This transparency allows individuals to understand the implications of adopting the new technologies and make informed decisions.
Policies should also consider the potential impacts on existing infrastructure and processes. A phased approach to implementation, allowing for gradual integration and adaptation, can minimize disruption and maximize public acceptance. Furthermore, ongoing communication and feedback mechanisms are vital for ensuring that policies remain responsive to public needs and concerns. This ensures that the policies are adaptable to evolving circumstances and that the technology's implementation aligns with the needs of the community.
Creating a Supportive Ecosystem for Technological Advancement
Promoting public adoption of building technologies requires more than just incentives and policies. A supportive ecosystem that fosters innovation, collaboration, and knowledge sharing is essential for long-term success. This includes initiatives that encourage research and development, facilitate partnerships between industry players and government agencies, and provide training and education opportunities for the workforce.
Engaging community leaders and stakeholders in the design and implementation process is crucial for ensuring buy-in and support. Public forums, workshops, and community events can provide platforms for open dialogue and address concerns proactively. This engagement builds trust and fosters a sense of ownership in the project, ultimately contributing to a smoother and more successful implementation process. Finally, continuous monitoring and evaluation are critical for measuring the effectiveness of policies and incentives, allowing for adjustments and improvements based on real-world data and feedback. This iterative approach ensures that the initiatives remain relevant, effective, and adaptable to the evolving needs of the community.
This supportive ecosystem fosters a culture of innovation and collaboration, making it easier for individuals and businesses to adopt the new technologies. It also creates a sense of shared responsibility and ownership, ensuring that the benefits of the new technologies are widely distributed and that the community as a whole benefits from the technological advancements.