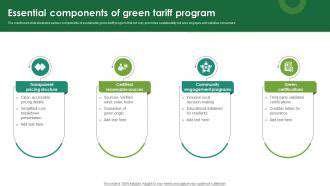
Investment in Research for Advanced Renewable Energy Grid Solutions
The Economic and Environmental Benefits of Advanced Grids
Improving Energy Efficiency
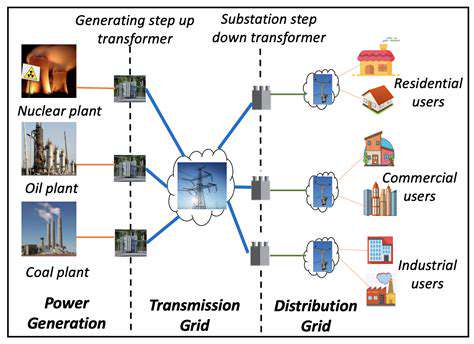
Advanced grids, with their enhanced capabilities for monitoring and control, offer significant opportunities to improve energy efficiency across the entire electricity supply chain. Smart meters, integrated into these grids, provide real-time data on energy consumption, enabling consumers to identify and reduce their usage patterns. This granular level of information allows for personalized energy management strategies, promoting responsible consumption habits and minimizing wasted energy. Furthermore, advanced grids can optimize energy distribution, minimizing transmission losses and improving overall system efficiency, leading to substantial savings in energy costs for both consumers and utilities.
The ability to predict and respond to fluctuations in energy demand is another key benefit. Advanced grid technologies can anticipate peak demand periods, allowing utilities to deploy resources proactively, preventing blackouts and ensuring reliable power supply. This proactive management of energy flow contributes to a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure, reducing the need for expensive and environmentally damaging backup solutions.
Reducing Environmental Impact
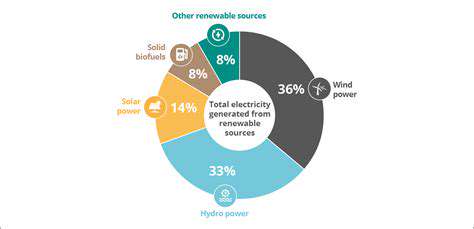
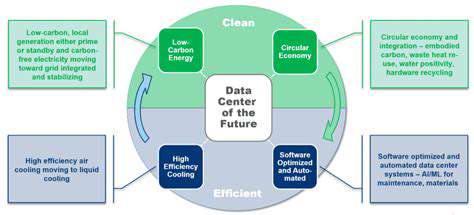
By optimizing energy distribution and reducing transmission losses, advanced grids contribute significantly to minimizing the environmental footprint of electricity generation and consumption. Reduced transmission losses mean less reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the ability to integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid becomes more efficient and reliable with advanced grid technologies. This integration allows for a smoother transition towards a cleaner energy future, reducing our dependence on polluting energy sources and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Advanced grids also support the development of more sustainable energy practices by enabling the integration of distributed energy resources. These resources, such as rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, can be effectively managed and integrated into the grid, fostering a decentralized energy system. This approach promotes energy independence and reduces reliance on centralized power plants, further decreasing emissions and environmental impact.
Boosting Economic Growth
The implementation of advanced grids fosters economic growth by creating new jobs and stimulating innovation in various sectors. The development and deployment of smart grid technologies require skilled professionals, creating job opportunities in engineering, maintenance, and data analysis. This investment in human capital, in turn, strengthens the local economy and promotes technological advancement. Furthermore, the improved reliability and efficiency of advanced grids attract businesses and investment, leading to economic growth and development in regions with strong grid infrastructure.
The reduced energy costs and improved grid resilience, brought about by advanced grids, create a more favorable investment climate for businesses. This, coupled with the potential for new energy-related industries and technologies, fosters economic growth and enhances the overall competitiveness of the region or nation. The integration of renewable energy sources, facilitated by advanced grids, also creates opportunities for the development of new industries and markets related to green technologies and sustainable energy practices.