Peer to Peer Energy Trading: Enabling Decentralization of Energy Generation
Decentralized Platforms and the Future of Energy
Decentralized energy trading platforms represent a significant shift in the energy landscape, moving away from traditional centralized models. These platforms leverage blockchain technology and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks to facilitate direct energy transactions between consumers and producers. This disintermediation reduces reliance on centralized energy companies, potentially lowering costs and increasing transparency in the energy market, fostering a more equitable and efficient system for all participants. The future of energy trading is undeniably intertwined with the evolution of these decentralized platforms.
The benefits extend beyond economic considerations. Decentralization also fosters greater resilience in the energy grid. By distributing energy generation and consumption, the system becomes less vulnerable to single points of failure, like large-scale power plant outages. This enhanced resilience is crucial in today's increasingly unpredictable world and is a major driver of interest in these innovative platforms.
Enhancing Efficiency and Transparency Through Blockchain
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in the efficiency and transparency of decentralized energy trading platforms. Its immutability ensures secure and verifiable transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and significantly reducing transaction costs. This cryptographic ledger provides a transparent record of all energy transactions, fostering trust and accountability among participants. The elimination of intermediaries also allows for greater control over energy data and enables participants to make informed decisions based on accurate and readily accessible information.
The Role of Peer-to-Peer Networks in Energy Trading
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks are fundamental to decentralized energy trading platforms. These networks connect energy producers and consumers directly, bypassing traditional energy companies. This direct connection streamlines the trading process, allowing for faster and more efficient transactions. Furthermore, P2P networks enable the sharing of renewable energy resources, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This direct interaction between producers and consumers is a key element in the overall design of these revolutionary energy platforms.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Scalability
Despite their potential, decentralized energy trading platforms face challenges, particularly in terms of scalability and interoperability. The current infrastructure may not be equipped to handle the volume of transactions expected as these platforms gain wider adoption. Ensuring seamless integration with existing energy grids and overcoming regulatory hurdles are also crucial steps in the development and widespread implementation of these platforms. Addressing these challenges will be critical to realizing the full potential of decentralized energy trading and its impact on the future of energy.
Beyond Solar: Diverse Energy Sources and the P2P Model
Harnessing the Power of Wind and Hydro
Wind power, derived from harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind, offers a clean and renewable alternative to fossil fuels. Modern wind turbines, ranging from small residential installations to massive offshore arrays, are becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective. This sustainable energy source plays a crucial role in diversifying energy portfolios and reducing reliance on volatile fossil fuel markets. Furthermore, advancements in wind turbine technology are constantly improving efficiency and reducing operational costs, making wind power an increasingly attractive option for both individual consumers and large-scale energy producers.
Hydropower, leveraging the potential energy of flowing water, is another significant renewable resource. Dams and other water-based infrastructure can generate substantial amounts of electricity. The consistent nature of water flow, unlike solar or wind, often contributes to a more reliable energy supply. However, the environmental impact of large-scale hydropower projects must be carefully considered, including potential effects on aquatic ecosystems and local communities.
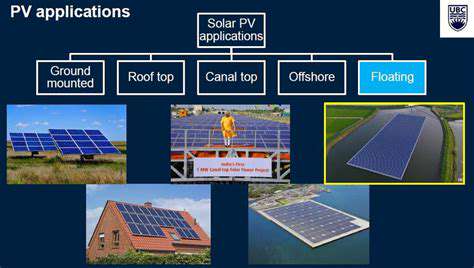
The Rise of Solar and its Potential
Solar energy, utilizing photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity, is experiencing rapid growth. The decreasing cost of solar panels and advancements in energy storage solutions are making solar power increasingly accessible and practical for both residential and commercial applications. This technology offers a significant opportunity to reduce reliance on centralized power grids and promote energy independence.
Moreover, the integration of solar energy with other renewable sources, such as wind, can create a more resilient and balanced energy system. The intermittent nature of solar power, however, necessitates robust energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies to ensure reliable energy supply.
Geothermal Energy: Tapping Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy, harnessing the heat from the Earth's interior, provides a constant and reliable energy source. Geothermal power plants utilize steam or hot water from deep within the Earth to generate electricity. While geographically limited, geothermal resources provide a significant opportunity for sustainable energy production in areas with suitable geological conditions.
Biomass Energy: Renewing from Organic Matter
Biomass energy, utilizing organic matter like agricultural waste, wood chips, and municipal solid waste, offers another renewable alternative. This energy source can be used to generate electricity or produce heat. Careful consideration of the environmental impact of biomass energy, including potential greenhouse gas emissions from unsustainable sources and deforestation, is crucial.
Tidal and Wave Energy: Harnessing Ocean Power
Tidal and wave energy, harnessing the power of ocean currents and waves, are emerging technologies with significant potential. Tidal energy can be generated using barrages or other structures that capture the energy of tides, while wave energy converters capture the kinetic energy of waves. Despite the promising potential, these technologies still face challenges in terms of cost-effectiveness and large-scale deployment.
P2P Energy Trading: A Decentralized Approach
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) energy trading platforms offer a decentralized approach to energy distribution and consumption. These platforms connect individuals and businesses, enabling them to directly buy and sell excess energy generated from renewable sources. P2P models foster a more distributed energy system, potentially reducing reliance on centralized power grids and promoting greater energy independence.
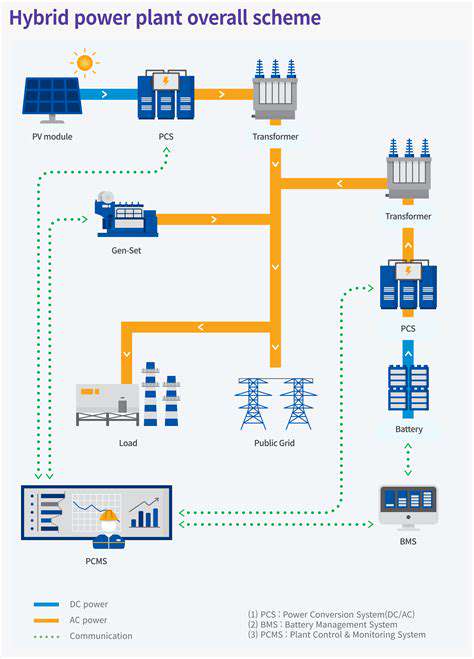
Energy Storage Solutions: Bridging the Gap
Energy storage solutions are critical for ensuring the reliability of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, which are intermittent. Technologies like batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage are crucial in bridging the gap between energy generation and consumption. The continuous advancement of energy storage technologies is essential for the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources and the successful implementation of P2P energy trading models.
Noise pollution, encompassing various sounds from different sources, significantly impacts the acoustic environment, affecting both human health and the well-being of wildlife. The consistent exposure to excessive noise can lead to adverse health consequences, ranging from stress and hearing loss to cardiovascular issues. Understanding the various acoustic impacts is crucial for developing effective noise mitigation strategies.
Enhancing Grid Stability and Resilience
Improving Grid Reliability with P2P Trading
Peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading introduces a decentralized approach to managing electricity supply and demand, potentially enhancing grid stability and resilience. By empowering consumers and small-scale producers to directly interact and exchange energy, P2P platforms can help balance fluctuations in supply and demand, reducing the strain on the traditional grid infrastructure. This dynamic energy exchange can also contribute to a more distributed and less centralized energy system, improving grid resilience to disruptions like natural disasters or equipment failures. The flexibility and responsiveness of P2P trading can significantly mitigate the impact of these events, ensuring a more reliable and robust power supply for all.
One key aspect of enhanced grid reliability is the ability to respond to unexpected events. P2P trading platforms, with their decentralized nature, can facilitate rapid adjustments to energy flow. If a localized grid disturbance occurs, for example, the platform can quickly identify and connect available energy sources with areas experiencing shortages, minimizing disruptions and preventing cascading failures. This inherent flexibility, absent in traditional centralized models, is crucial for maintaining grid stability in the face of unpredictable circumstances. Moreover, the increased participation of diverse energy providers through P2P trading could lead to a more diverse and resilient energy mix.
Decentralized Control and Enhanced Grid Resilience
The decentralized nature of P2P energy trading offers a significant advantage in terms of grid resilience. By distributing control over energy resources, the system becomes less vulnerable to single points of failure. A centralized grid system, with its reliance on large-scale power plants and transmission lines, faces heightened risks if one component malfunctions. P2P trading, however, creates a network effect, where many smaller entities actively participate in managing energy flows. This dispersal of control significantly reduces the impact of localized failures, making the grid more adaptable and robust to various disruptions. It enables more rapid recovery and minimizes the potential for widespread outages.
Furthermore, P2P platforms can facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid more effectively. Distributed generation, such as rooftop solar panels and small wind turbines, can contribute significantly to the overall energy mix through P2P trading. This decentralized energy production reduces reliance on centralized power plants and enhances the grid's ability to absorb intermittent renewable energy sources. The platform's ability to track and manage these diverse energy sources in real-time ensures grid stability, especially during periods of high solar or wind output. These benefits combined contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.