How Decentralization of Energy Generation is Reshaping Grids
The Impact on Grid Infrastructure
Impact on Grid Stability
Modern energy systems face unprecedented challenges as decentralized generation becomes more prevalent. Unlike traditional power plants, renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines produce variable output that can destabilize grid operations. Maintaining consistent voltage and frequency now requires complex monitoring systems and adaptive control mechanisms. Utilities must invest heavily in these technologies to compensate for the inherent unpredictability of distributed generation.
Legacy grid infrastructure was engineered for centralized, predictable power flows. The proliferation of residential solar installations and neighborhood microgrids demands entirely new management approaches. Engineers are developing innovative algorithms that can process real-time data from thousands of points across the network, making instantaneous adjustments to maintain equilibrium throughout the system.
Distributed Energy Resource Management
Coordinating thousands of small-scale generation sources presents both technical and logistical hurdles. Sophisticated networking solutions enable continuous communication between home solar arrays, battery systems, and utility control centers. These systems must optimize each component's performance while ensuring seamless integration with the broader energy ecosystem.
Grid Modernization Requirements
Existing power networks require substantial upgrades to handle bidirectional energy flows from distributed sources. Utilities are deploying advanced sensors and automated switches throughout their systems. These smart grid technologies provide the visibility and control needed to manage increasingly complex power distribution patterns.
Energy Storage Solutions
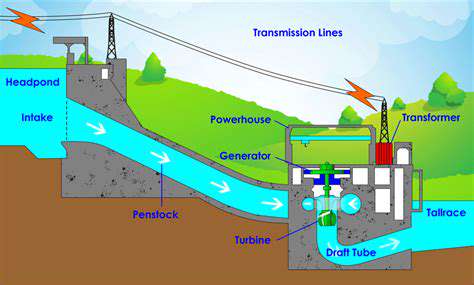
The intermittent nature of renewable generation creates pressing needs for energy storage. Battery banks, pumped hydro facilities, and thermal storage systems help smooth out supply fluctuations. Developing affordable, large-scale storage remains one of the most critical challenges in the transition to decentralized energy.
Consumer Engagement and Demand Response
Modern grids increasingly rely on consumer participation through demand response programs. Homeowners can help balance the system by adjusting usage during peak periods, often receiving financial incentives. This collaborative approach reduces strain on infrastructure while empowering energy consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities
Decentralized Energy Systems: A Shift in Power Dynamics
The energy landscape is undergoing a radical transformation as generation shifts from massive power plants to distributed networks. This decentralization movement creates both technical hurdles and exciting possibilities for sustainable development.
Overcoming Infrastructure Limitations
Aging grid infrastructure often lacks the capacity to accommodate distributed generation. Significant investments in transmission upgrades and smart technologies will be essential to support this transition. Utilities must carefully phase these improvements to maintain reliability during the transformation.
Addressing Grid Stability and Reliability
Maintaining consistent power quality becomes increasingly complex with numerous intermittent sources. Advanced monitoring systems and predictive analytics help operators anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions before they affect customers.
Economic Viability and Investment Incentives
The financial equation for decentralized energy requires careful consideration. While renewable technologies have become more affordable, upfront costs remain substantial. Policy mechanisms like production tax credits and streamlined permitting can accelerate adoption.
Integrating Diverse Technologies and Resources
Successful integration of various generation and storage technologies demands standardized communication protocols. This interoperability ensures different systems can work together seamlessly within the evolving energy ecosystem.
Social and Community Involvement
Local energy projects foster community engagement and economic development. Neighborhood solar cooperatives and municipal microgrids empower residents while creating local jobs and investment opportunities.
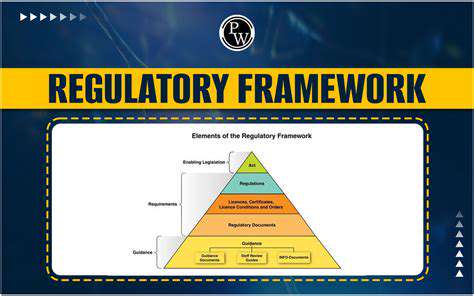
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Changes
Outdated regulations often hinder decentralized energy development. Modernized policies should address interconnection standards, fair compensation for distributed generation, and streamlined project approvals to support this transition.