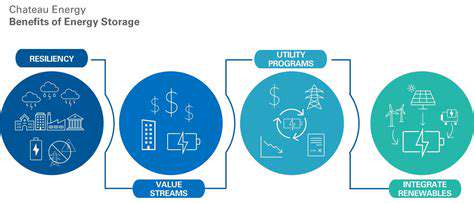
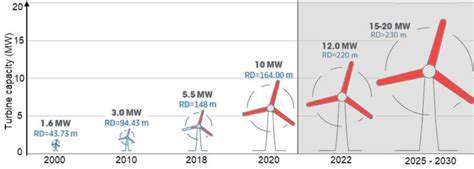
Understanding Renewable Energy Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Legal Aspects
Crucial clauses related to energy delivery detail the specific type of renewable energy (e.g., solar, wind), the quantity and quality of energy to be delivered, and the delivery schedule. These clauses must precisely define the energy output specifications and any potential deviations from the agreed-upon parameters. Accurately specifying the measurement methodology for energy delivery is essential to avoid disputes later on, ensuring both parties are on the same page regarding the quantity and quality of energy exchanged.
Payment Terms and Mechanisms
Payment terms are fundamental to any PPA. This section outlines the payment schedule, the payment method (e.g., fixed price, index-based), and the currency used. Clear stipulations on late payment penalties, payment frequency, and acceptable payment instruments are vital. The inclusion of a detailed payment schedule helps avoid disputes and ensures that the generator receives timely compensation for the energy generated, while the offtaker can budget accordingly.
Force Majeure and Risk Allocation
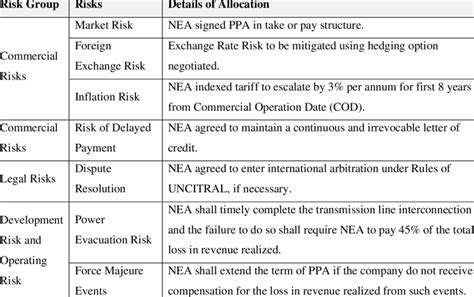
The force majeure clause addresses unforeseen events or circumstances beyond the control of either party, such as natural disasters or governmental actions. This clause defines which events are considered force majeure, and how they impact the performance obligations of the parties. Furthermore, the PPA must clearly delineate the allocation of risks associated with weather patterns, equipment failures, and other potential disruptions in the renewable energy generation process. Proper risk allocation is essential to avoid unexpected financial burdens for either party.
Dispute Resolution and Governing Law
A robust dispute resolution clause outlines the procedures for resolving disagreements that may arise between the parties. This clause should specify the preferred method of resolution, such as mediation, arbitration, or litigation, and the governing jurisdiction. Clearly defining the process for conflict resolution is crucial to ensure a smooth and timely resolution in the event of disputes. This clause protects both parties by outlining a structured approach to resolving disagreements.
Termination and Exit Strategies
A comprehensive PPA should include clauses that cover potential termination events and exit strategies. These clauses define the circumstances under which either party can terminate the agreement and the procedures involved. This section also details the obligations of each party upon termination, including the return of assets, and the mechanism for settling outstanding obligations. The existence of well-defined termination clauses provides a clear path for managing unexpected circumstances or changes in market conditions, ensuring a smooth transition when necessary.
Solar-assisted thermal desorption (SATD) represents an innovative approach for treating polluted substances effectively. This technique employs solar power to heat materials, enabling the removal of volatile organic compounds and other contaminants. As it depends entirely on renewable energy, this process offers an environmentally responsible alternative to conventional methods. Using solar energy for this purpose substantially reduces operational expenses compared to traditional thermal desorption techniques that typically demand significant energy inputs.
Regulatory Compliance and Permitting Processes
Understanding Regulatory Hurdles
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for successful renewable energy projects. Different jurisdictions have varying requirements, and understanding these nuances is essential for project viability. This includes local, state, and potentially federal regulations regarding zoning, environmental impact assessments, permitting timelines, and interconnection agreements with the grid. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to significant delays, cost overruns, and even project termination. Thorough due diligence and consultation with legal and regulatory experts are vital throughout the project lifecycle.
Permitting processes often involve multiple stages and agencies. From initial application submissions to final approvals, understanding the specific requirements for each stage is critical. This includes comprehending the documentation needed, potential challenges, and the typical timelines associated with each approval step. Knowing the specific procedures for your chosen renewable energy technology (e.g., solar, wind, geothermal) is also essential, as these often have unique permitting requirements.
Securing Necessary Permits and Approvals
Securing the necessary permits and approvals is a critical step in establishing a renewable energy project. This encompasses everything from environmental impact assessments to site-specific permits, and involves navigating complex procedures and potentially contentious stakeholder relationships. Detailed and accurate project proposals are key to demonstrating compliance with regulations and garnering support from local communities.
A critical aspect of securing permits is demonstrating the project's environmental compatibility. This involves thorough environmental impact assessments, adherence to environmental regulations, and mitigation strategies to address potential negative impacts. Effective communication with local environmental agencies and stakeholders is crucial for building trust and facilitating a smooth permitting process.
The timeline for permit acquisition can vary significantly depending on the project's scale and complexity. Projects involving large-scale deployments or controversial technologies often face extended review periods. Understanding these potential delays and having a robust contingency plan are important for project success.
Furthermore, the permits themselves often have specific conditions and stipulations that need to be rigorously followed throughout the project's development and operation. Failure to adhere to these conditions can result in costly fines, project delays, or even project termination. Close monitoring and adherence to all permit conditions are critical.
Effective collaboration with regulatory agencies and stakeholders is crucial throughout the permitting process. Clear communication, proactive engagement, and a commitment to transparency are essential for achieving timely and successful approvals.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms and Enforcement

Dispute Resolution Methods
Disputes are an inevitable part of any business or personal interaction. A well-defined dispute resolution mechanism is crucial for navigating disagreements effectively and minimizing potential damage. Choosing the right method is paramount to achieving a fair and efficient resolution. Understanding the nuances of various dispute resolution approaches is essential to ensure parties' rights are protected and the conflict is resolved in a timely manner. Diverse approaches exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, and selecting the appropriate one is vital for a successful outcome.
These mechanisms often involve a range of options, from informal negotiations to formal arbitration or litigation. Each option presents unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting the cost, duration, and level of control each party has over the process. Understanding these factors allows parties to make informed decisions aligned with their specific needs and goals. Knowing the applicable laws and regulations surrounding the dispute is also crucial for selecting the correct mechanism, as this can significantly influence the process's outcome.
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) methods offer a viable alternative to traditional litigation, providing parties with greater control over the process and often leading to more efficient and cost-effective resolutions. These methods generally aim to resolve disagreements outside of court, fostering collaborative problem-solving and potentially preserving relationships. ADR methods encompass various approaches, including mediation, negotiation, and arbitration, each with specific procedures and characteristics.
Mediation, for example, involves a neutral third party facilitating communication and negotiation between disputing parties. The mediator helps identify common ground and explore potential solutions. Negotiation, another ADR technique, allows parties to directly engage in discussions to reach a mutually acceptable agreement. These techniques often involve a degree of flexibility and responsiveness to the specific circumstances of the dispute, leading to a tailored outcome compared to the rigid structure of litigation.
Arbitration, another form of ADR, employs a neutral third party, the arbitrator, to hear evidence and arguments from both sides. The arbitrator then renders a binding decision, which is often legally enforceable. This process can be significantly faster and less expensive than traditional court proceedings, providing an attractive option for parties seeking a more streamlined dispute resolution process. The choice between ADR methods depends on the specific circumstances of the case, the desired outcome, and the preferences of the involved parties.
Formal Legal Proceedings
Formal legal proceedings, such as litigation, represent the traditional approach to dispute resolution. While often perceived as adversarial, litigation provides a structured framework for resolving complex disputes through the courts. This approach involves the presentation of evidence, legal arguments, and testimonies before a judge or jury. The process can be lengthy and costly, potentially impacting the relationships between the involved parties.
The involvement of legal professionals, such as lawyers, is critical in navigating the complexities of litigation. The litigation process adheres strictly to established legal procedures and rules of evidence, ensuring a fair and consistent resolution based on applicable laws. However, this structure often prioritizes the legal framework over the nuanced needs and desires of the parties involved. A thorough understanding of the legal principles governing the dispute is essential to ensure that the case is properly presented.