Understanding Corporate Renewable Procurement Models
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Securing Renewable Energy at a Fixed Price

Understanding Power Purchase Agreements
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are legally binding contracts that outline the terms of a power purchase between two parties: a power seller and a power buyer. These agreements detail the quantity and quality of electricity to be delivered, the duration of the agreement, and the payment terms. Understanding the intricacies of a PPA is crucial for both parties to ensure a mutually beneficial and sustainable energy arrangement. This framework is essential for managing energy needs and costs effectively. A well-structured PPA safeguards both the buyer's energy requirements and the seller's financial stability.
Essentially, a PPA acts as a long-term agreement for the supply of electricity. It removes the uncertainty associated with fluctuating energy prices and provides a predictable cost structure for the buyer. This predictability can be particularly valuable for businesses and institutions with significant energy consumption needs.
Types of Power Purchase Agreements
There are various types of PPAs, each tailored to specific needs and circumstances. One common type is a fixed-price PPA, where the electricity price remains constant throughout the agreement's duration. This offers price stability but might not reflect fluctuating market conditions. Another example is a variable-price PPA, which adjusts the electricity price based on prevailing market rates. This type offers greater flexibility but also exposes the buyer to potential price volatility.
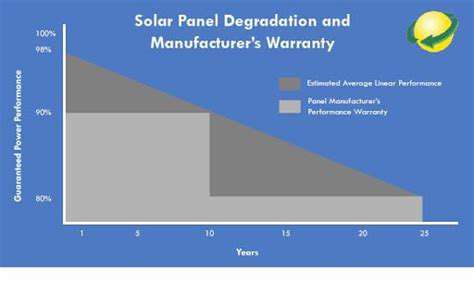
Beyond these fundamental types, other PPAs might include provisions for renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. These agreements can play a significant role in promoting sustainable energy adoption and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Renewable energy PPAs are gaining increasing popularity as environmental concerns rise. The incentives and policies supporting renewable energy are also driving the growth of this specific PPA type.
Key Considerations in a PPA
Several crucial factors must be considered when negotiating a PPA. These include the duration of the agreement, the pricing structure, the quantity of electricity to be delivered, and the quality standards. Careful consideration of these factors is vital to ensure the agreement aligns with the needs and objectives of both parties. Each party must meticulously analyze the potential financial implications of a PPA before committing to the agreement.
Another important element is the risk management associated with the PPA. This involves assessing potential risks such as changes in energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory changes. A robust risk assessment is critical to mitigate potential losses and ensure the long-term viability of the agreement for both the seller and the buyer. This is essential to avoid future disputes and financial complications.
Benefits and Drawbacks of PPAs
Power Purchase Agreements offer several significant benefits, including predictable energy costs and a streamlined approach to energy procurement. This predictability can be particularly crucial for businesses looking to manage their operational expenses. PPAs can also facilitate access to renewable energy sources, aligning with sustainability goals. This alignment can be a significant advantage for companies prioritizing environmental responsibility.
However, PPAs also present some drawbacks. These include the potential for higher initial costs associated with contract negotiation. Moreover, there's a degree of inflexibility in adjusting energy needs, and the financial commitment extends over the agreement's term. Careful consideration of these potential drawbacks is essential during the evaluation process.
Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPA): A Decentralized Approach
Understanding the Fundamentals of VPPA
Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPA) represent a novel approach to procuring renewable energy, moving away from traditional utility-based models. They essentially allow organizations to contract for renewable energy generation without owning or operating the facilities themselves. This decentralized structure fosters collaboration between renewable energy producers and consumers, creating a more dynamic and potentially more efficient energy market. Understanding the core principles of VPPA is crucial to grasping its implications for the future of energy.
VPPA agreements establish a contractual obligation for renewable energy generation, typically over a specified period. This agreement outlines the amount of renewable energy to be supplied, the price, and the delivery schedule. Understanding the contractual terms is paramount for both the energy producer and the consumer, assuring clarity and minimizing future disputes.
Decentralization and Collaboration
One of the most significant aspects of VPPA is its decentralized nature. Instead of relying on a centralized utility, the agreements facilitate direct interaction between renewable energy producers and consumers. This direct engagement fosters collaboration and empowers communities to participate more actively in shaping their energy future. This decentralized structure could potentially lead to more innovative energy solutions.
This collaborative approach often involves community solar projects or other distributed renewable energy sources. The ability to connect directly with smaller-scale producers, often located in local communities, can enhance local economic benefits and encourage the growth of renewable energy infrastructure.
Economic Benefits and Incentives
VPPA agreements can offer several compelling economic benefits. For consumers, they often provide access to lower energy costs, especially in regions with abundant renewable energy resources. Moreover, by directly supporting renewable energy projects, consumers can align their consumption with their environmental values. These projects can generate significant economic growth for local communities, with the potential to create new jobs and stimulate investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
Various government incentives and subsidies can further enhance the economic attractiveness of VPPA. These incentives often aim to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources and support the transition to a more sustainable energy system. Understanding these incentives is crucial for maximizing the economic benefits of VPPA participation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
VPPA agreements play a critical role in promoting environmental sustainability. By supporting renewable energy generation, they directly reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. This environmentally conscious approach aligns with global efforts to transition to a more sustainable energy future.
VPPA's decentralized structure enables a more targeted approach to renewable energy development, concentrating resources in areas with the greatest potential for renewable energy generation. The environmental benefits of this focused approach can be significant, leading to a more sustainable energy mix.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The development and implementation of VPPA are closely intertwined with technological advancements in renewable energy generation and energy storage. Technological improvements in solar and wind power, as well as energy storage solutions, are constantly expanding the possibilities of VPPA agreements. These advancements can lead to more cost-effective and efficient renewable energy procurement.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advantages of VPPA, there are also potential challenges to consider. One key challenge involves the complexities of negotiating and administering these agreements, requiring specialized expertise and legal frameworks to ensure transparency and fairness. Furthermore, the fluctuating nature of renewable energy generation necessitates robust energy management systems to ensure reliable energy supply.
Another consideration is the potential for market volatility and fluctuating energy prices. Long-term agreements need to be carefully structured to mitigate the risks associated with price fluctuations. Understanding these challenges and developing effective strategies to overcome them are essential for widespread adoption of VPPA.