The Role of Blockchain in Corporate Renewable Sourcing
The globalized marketplace has brought unprecedented opportunities for businesses, but it has also created complex and often opaque supply chains. Consumers are increasingly demanding greater transparency, understanding the environmental and social impacts of the products they purchase. This growing awareness necessitates a shift towards more transparent practices, not just to satisfy consumer expectations, but also to mitigate risks and enhance brand reputation. Companies that prioritize transparency often see positive impacts on their bottom line and stakeholder relationships.
Transparency in supply chains is no longer a luxury, but a critical component of sustainable and ethical business operations. It involves a commitment to openness and accountability throughout the entire production process, from sourcing raw materials to the final product delivery. This commitment extends to disclosing information regarding working conditions, environmental standards, and ethical sourcing practices.
Benefits of Enhanced Transparency
Enhanced transparency offers a multitude of benefits, both for businesses and consumers. For businesses, it fosters trust and loyalty among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and employees. It also allows for more effective risk management, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of potential issues. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of reputational damage and financial losses.
Transparency facilitates informed decision-making for consumers. Knowing where their products come from, how they are made, and the conditions under which they are produced empowers consumers to align their purchasing choices with their values. This, in turn, drives demand for ethically sourced and sustainably produced goods.
Challenges in Achieving Transparency
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing a truly transparent supply chain presents significant challenges. One major hurdle is the complexity of the supply chain itself, involving numerous actors and locations. Gathering and verifying information from each step of the process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Developing robust systems for data collection, analysis, and communication is essential but often requires substantial investment.
Furthermore, concerns about intellectual property and competitive advantage may hinder complete transparency. Some companies may be hesitant to share sensitive information, fearing that it could be exploited by competitors. Overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative approach, fostering trust and open communication between stakeholders.
Technological Solutions for Transparency
Fortunately, technological advancements are providing innovative solutions to address the challenges of supply chain transparency. Blockchain technology, for example, can provide a secure and transparent record of every stage of a product's journey. This allows for real-time tracking of materials and information, minimizing the risk of fraud and counterfeiting. Leveraging technology in this way enhances the traceability and accountability of the entire supply chain.
Other technologies, such as data analytics and artificial intelligence, can further enhance supply chain visibility. These tools can identify patterns and anomalies, enabling businesses to proactively address potential risks and improve operational efficiency. Ultimately, adopting these innovative technologies can significantly streamline the process of achieving greater transparency.
The Future of Transparent Supply Chains
The future of supply chains is undeniably intertwined with transparency. As consumer expectations continue to evolve, businesses will need to adapt and embrace transparency as a core value. This will involve not only implementing technological solutions, but also fostering a culture of openness and accountability throughout the entire organization. Furthermore, collaborative efforts between businesses, governments, and NGOs will be crucial in shaping standards and best practices for transparency.
The shift towards transparency is not just about meeting consumer demands; it's about building a more sustainable and equitable global marketplace. By embracing transparency, businesses can strengthen their reputation, enhance their bottom line, and contribute to a more responsible and sustainable future.
Blockchain's Key Advantages for Renewable Sourcing
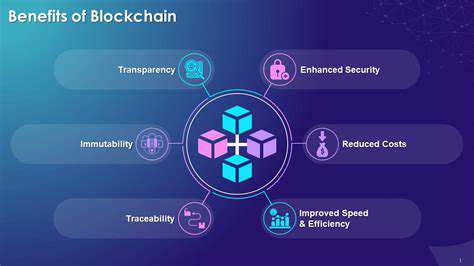
Decentralization
Blockchain's decentralized nature is a significant advantage, removing the need for intermediaries like banks or governments. This eliminates single points of failure, making the system more resilient and resistant to censorship. Transactions are validated by a distributed network of participants, fostering transparency and trust among all parties involved. This distributed ledger technology ensures that data integrity is maintained and that all participants have access to the same information, promoting a more trustworthy and efficient system.
The decentralized structure of blockchain also enhances security. Since no single entity controls the network, it's much harder for malicious actors to compromise the entire system. This inherent resistance to manipulation is a powerful differentiator, particularly in sensitive industries like finance and healthcare.
Transparency and Immutability
Blockchain's inherent transparency is a key advantage. All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, accessible to all participants. This transparency fosters trust and accountability, as every transaction is auditable. This openness in the system also helps to reduce fraud and corruption.
Furthermore, blockchain records are immutable. Once a transaction is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the data. This immutability is crucial for applications requiring high levels of data security and reliability. This permanent record of transactions eliminates the potential for disputes and increases trust among all involved parties.
Security and Trust
Blockchain's cryptographic security measures provide a robust foundation for secure transactions. Cryptographic hashing and digital signatures ensure the authenticity and integrity of data. This approach significantly reduces the risk of fraudulent activities and data breaches.
The immutability of blockchain records further enhances security. Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, eliminating the possibility of tampering. This inherent trust is built into the system and fosters greater confidence in the reliability of transactions. This is particularly important in applications where data integrity and security are paramount.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Blockchain's automation capabilities can streamline processes and reduce the need for manual intervention. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions, automate transactions, minimizing human error and reducing operational costs.
By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can also significantly reduce transaction costs. Direct peer-to-peer transactions on the blockchain often bypass the fees charged by traditional financial institutions, leading to substantial savings for users. This efficiency and cost-effectiveness are key drivers for adoption in various sectors, from supply chain management to financial services.
Streamlining Verification and Certification Processes
Improving Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain's inherent transparency and immutability significantly enhance the traceability of products and services throughout the entire supply chain. This feature allows for the verification of every step, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. By recording every transaction on a shared, encrypted ledger, businesses gain a clear audit trail, enabling them to identify potential issues and maintain high standards of quality and authenticity. This level of detail and security is invaluable in industries facing challenges like counterfeiting and provenance disputes.
Automating Verification Procedures
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written into the blockchain, automate many verification procedures. This automation reduces the need for manual intervention, significantly speeding up the process and minimizing human error. By pre-programming the conditions for verification, businesses can ensure consistent and reliable results, eliminating bottlenecks and improving overall efficiency. This automation also fosters greater trust and confidence in the verification system.
Enhancing Security and Integrity
Blockchain's cryptographic security measures protect against data manipulation and tampering, ensuring the integrity of verification data. This is crucial in preventing fraud and ensuring that the certifications and verifications are genuine and trustworthy. The decentralized nature of blockchain further strengthens this security, as no single entity controls the data, making it resistant to unauthorized access and modification.
Reducing Costs and Time
By automating verification processes and minimizing manual intervention, blockchain technology can substantially reduce operational costs. The elimination of redundant paperwork, manual checks, and potential errors leads to significant cost savings. Furthermore, the streamlined process speeds up the verification and certification cycle, reducing lead times and enabling faster turnaround times for businesses. This efficiency translates into a more competitive advantage in the market.
Facilitating Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration
Blockchain's decentralized nature enables seamless collaboration among multiple stakeholders involved in verification and certification. Shared access to the immutable ledger allows all participants to view and verify information, fostering transparency and trust. This collaborative environment promotes greater accountability and reduces disputes, as all parties have access to a unified, verifiable record.
Improving Regulatory Compliance
In many industries, regulatory compliance is a significant concern. Blockchain can help businesses meet these regulatory requirements by providing a secure and auditable record of compliance activities. This enables organizations to demonstrate adherence to regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and ensuring smooth operations. The transparency and traceability provided by blockchain also aid in regulatory audits, providing a clear picture of all activities related to verification and certification.
Building Trust and Credibility
The inherent trust and transparency of blockchain technology build trust and credibility among stakeholders. The immutable nature of the ledger eliminates the potential for disputes and encourages greater confidence in the verification and certification processes. This trust is critical for establishing strong business relationships and fostering a positive reputation within the industry. It allows businesses to build more robust supply chains with reliable partners.
Accurate assessment of subsurface conditions is paramount for the successful design and construction of offshore wind farms. This involves a comprehensive investigation of the seabed, including its stratigraphy, soil properties, and geological history. Detailed site characterization needs to account for the potential variability of the seabed, which can significantly impact foundation design and construction methodologies. This process often includes advanced geophysical surveys, such as seismic reflection and refraction methods, to map the subsurface layers and identify potential geological hazards. Furthermore, direct sampling and in-situ testing are crucial to determine the mechanical properties of the soils, enabling the creation of accurate geotechnical models.
Improving Supply Chain Collaboration and Efficiency
Leveraging Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to supply chain management by providing a shared, immutable ledger of transactions. This shared view of the entire supply chain, from raw materials to final product delivery, fosters greater transparency and accountability among all stakeholders. Businesses can track products and materials with unprecedented detail, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies more readily. This transparency extends to verifying product authenticity, ensuring ethical sourcing, and complying with regulations, ultimately building trust and confidence throughout the supply chain.
By eliminating the need for intermediaries and complex verification processes, blockchain streamlines information sharing. This streamlined approach reduces errors and delays, leading to significant cost savings and improved overall efficiency. The ability to instantly access real-time data on product movement and status allows for proactive adjustments to mitigate risks and optimize logistics.
Streamlining Communication and Collaboration
Traditional supply chains often rely on disparate systems and communication channels, leading to delays and miscommunication. Blockchain provides a centralized platform for all stakeholders to access and share information securely and efficiently. This collaborative environment enables real-time updates on order status, shipment tracking, and inventory levels, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
This unified communication channel fosters better coordination and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Improved communication leads to faster response times to issues, reduced lead times, and ultimately, enhanced customer satisfaction. The ability to track and trace goods throughout the supply chain also enables faster resolution of disputes and greater accountability.
Automating Processes and Reducing Errors
Blockchain's inherent security and immutability features automate various processes within a supply chain, reducing the risk of human error and fraud. Automated documentation and verification processes minimize delays and ensure data integrity, streamlining the entire supply chain operation. This automation also helps in reducing administrative overhead and freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives.
Improving Traceability and Product Authenticity
Blockchain's inherent nature as a distributed ledger makes it ideal for tracking products throughout their lifecycle. This detailed traceability enables businesses to verify the origin of materials, manufacturing processes, and distribution points, ensuring product authenticity and ethical sourcing. This transparency builds consumer trust and allows for swift responses to product recalls or quality issues. By embedding unique identifiers on each product, companies can trace its journey from its origin to the consumer, offering customers the ability to verify the product's history and legitimacy.
Enhancing Security and Preventing Fraud
The decentralized and encrypted nature of blockchain significantly enhances the security of supply chain data. This security reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud, bolstering confidence among all participants. Blockchain's immutable ledger ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, which prevents tampering and ensures accurate records. This enhanced security fosters greater trust and transparency, critical for long-term collaboration and efficient supply chain operations. It also allows for the tracking of goods and materials in real-time, making it difficult for counterfeit products to enter the supply chain.
Ensuring Sustainability and Reducing Environmental Impact
Blockchain's Potential for Sustainable Supply Chains
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to enhance transparency and traceability throughout supply chains, which is crucial for sustainability initiatives. By recording every transaction and movement of goods on a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain provides an auditable record of the entire journey of a product. This detailed history allows businesses to identify and address environmental impacts at various stages, from sourcing raw materials to final product delivery. For instance, understanding the origin and production methods of agricultural products allows companies to promote sustainable farming practices and reduce reliance on environmentally damaging processes. This improved visibility also empowers consumers with greater knowledge about the products they purchase, fostering a more conscious and sustainable consumerism.
The ability to track and verify the environmental credentials of products, such as carbon footprints or water usage, is a key advantage of blockchain. This data can be integrated into the supply chain management system, enabling companies to make informed decisions about sourcing and production methods to minimize environmental harm. By making this data easily accessible to all stakeholders, blockchain fosters collaboration and shared responsibility in achieving sustainable practices throughout the entire value chain. This can lead to significant improvements in resource management, waste reduction, and ultimately, a healthier planet.
Promoting Ethical Labor Practices and Reducing Waste
Beyond environmental concerns, blockchain can also play a vital role in promoting ethical labor practices. By recording worker information, compensation, and working conditions throughout the supply chain, blockchain provides a transparent and auditable record of labor standards. This transparency can deter unethical practices like forced labor or exploitation and empower workers to have a greater say in their working conditions. This improved accountability can help ensure that companies adhere to fair labor standards and contribute to a more just and equitable global economy.
Furthermore, blockchain's ability to track products from origin to consumer can help reduce waste along the supply chain. By providing real-time visibility into product movement and demand, companies can optimize inventory management, minimize overproduction, and better predict future needs. This reduced waste translates into lower environmental impact and significant cost savings for businesses. The ability to trace goods and identify potential issues early on also helps prevent spoilage and product recalls, further enhancing efficiency and sustainability within the supply chain.
Beyond these benefits, the enhanced traceability afforded by blockchain can help establish product authenticity and reduce counterfeiting. This is particularly important in sectors like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, where counterfeits can pose significant risks to consumers and the environment. By creating a secure and tamper-proof record of each product's journey, blockchain can enhance consumer confidence and protect the integrity of the supply chain.
Blockchain technology has the potential to dramatically impact our understanding of sustainability and the ethical practices within supply chains. By fostering transparency, accountability, and efficiency, blockchain can play a critical role in creating more sustainable and responsible business operations.