Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and Renewable Energy Linkages
The rise of personalized recommendations is fundamentally changing how we consume entertainment. No longer are we limited to the suggestions of a friend or a fleeting algorithm. Modern platforms are leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated machine learning to curate experiences tailored to individual preferences. This personalized approach goes beyond simply suggesting movies or music; it's about understanding and anticipating the specific needs and desires of each user. This shift is driving a new level of engagement and satisfaction for consumers.

The Future of SAF and Renewable Energy: A Synergistic Partnership
Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) and the Renewable Energy Landscape
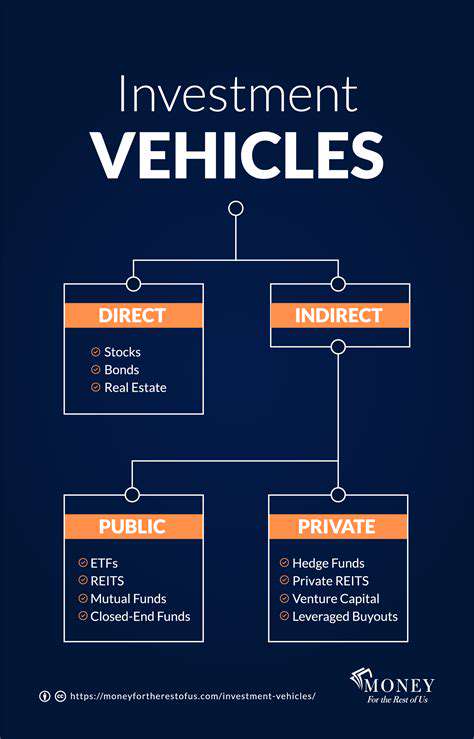
The future of aviation hinges on a crucial partnership between Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) and renewable energy sources. SAF production relies heavily on feedstocks derived from biomass, agricultural waste, and even captured carbon emissions. These feedstocks are often cultivated or processed using renewable energy, creating a symbiotic relationship where the production of SAF becomes intrinsically linked to the growth and development of the renewable energy sector. This interconnectedness promises a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for air travel.
The development and deployment of SAF are not only essential for decarbonizing aviation but also offer significant opportunities for economic growth and job creation in rural communities. This is possible through the establishment of new processing facilities and the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure, leading to a wider, more inclusive impact on society.
The Role of Biomass in SAF Production
Biomass, including agricultural residues, dedicated energy crops, and forestry byproducts, plays a pivotal role in SAF production. Converting these organic materials into usable fuels requires specialized processing techniques, and the efficiency of these processes directly impacts the overall sustainability and cost-effectiveness of SAF. Innovative technologies are crucial for maximizing the yield and minimizing environmental impact throughout the entire value chain.
Renewable Energy Integration in SAF Production Processes
The production of SAF is not simply about sourcing feedstocks; it also significantly involves the use of renewable energy. From the initial cultivation of biomass to the processing and refining stages, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of SAF production. Integrating these renewable energy sources into the supply chain is crucial for achieving true sustainability in the aviation sector.
Challenges and Opportunities for Scalable SAF Production
While the potential of SAF is immense, scaling up production to meet the growing demand of the aviation industry presents several challenges. These challenges include the availability of suitable feedstocks, the development of cost-effective processing technologies, and the need for substantial investment in infrastructure. However, these challenges also represent opportunities for innovation and technological advancement. Investing in research and development, coupled with supportive policies, can pave the way for a future where SAF becomes the dominant fuel source for air travel.
The Future of SAF and the Aviation Industry's Transition
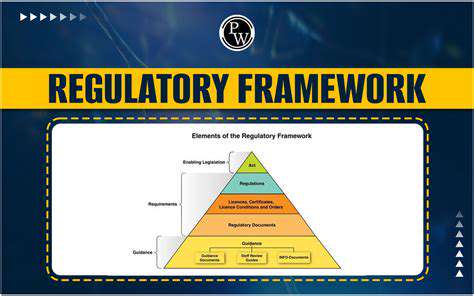
The aviation industry's transition to SAF is not merely a technological shift; it's a fundamental paradigm change. It requires a collaborative effort between governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions. Developing supportive policies, establishing clear regulatory frameworks, and fostering public-private partnerships are vital to accelerate the adoption of SAF. This transition will also necessitate significant investment in infrastructure, creating job opportunities and driving economic growth in the renewable energy sector.