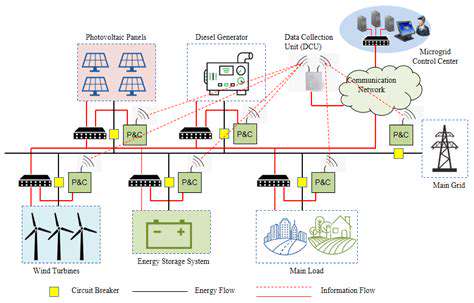
Renewable Energy and Energy Security
Harnessing Solar Power
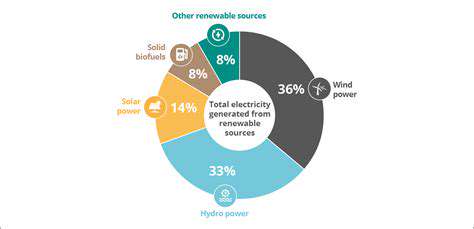
Solar energy, derived from the sun's radiant energy, is a remarkably versatile renewable resource. Its abundance and accessibility make it a compelling option for powering homes, businesses, and even entire communities. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, while concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver, generating heat that can be used to produce steam and drive turbines, ultimately creating electricity. The continuous advancements in solar technology are making it increasingly cost-effective and efficient, further solidifying its position as a pivotal component of the global energy transition.
Various factors influence the effectiveness of solar energy systems, including geographical location, sunlight intensity, and the specific design of the solar panel. Optimizing these elements is crucial to maximizing the energy output and minimizing the environmental footprint of solar installations. Furthermore, energy storage solutions are becoming more prevalent, allowing solar systems to generate electricity even when the sun isn't shining, thus enhancing the reliability and sustainability of this renewable energy source.
Tapping into Wind Power
Wind energy, harnessed through wind turbines, is another significant renewable energy source. Large-scale wind farms, strategically placed in areas with consistent wind patterns, generate substantial amounts of electricity. The technology behind wind turbines has evolved significantly, resulting in more efficient and powerful machines that can capture wind energy more effectively. This has led to a substantial reduction in the cost of wind energy production, making it a more attractive and viable option for many regions.
The environmental impact of wind farms is also a subject of ongoing discussion and research. While they produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, the manufacturing and disposal of turbine components do have an environmental footprint. However, the long-term benefits of wind energy in reducing reliance on fossil fuels often outweigh these considerations. Furthermore, the potential for noise pollution and visual impact must be carefully addressed during the planning and implementation stages of wind farm projects.
Exploring Hydropower Potential
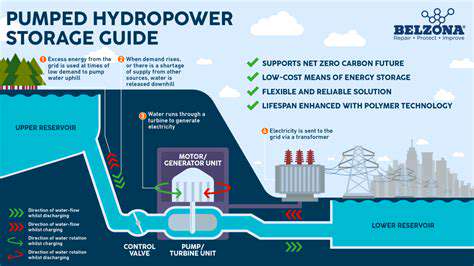
Hydropower, utilizing the energy of flowing water, is a long-established renewable energy source. Hydroelectric dams harness the kinetic energy of rivers and streams to generate electricity. The sheer volume of water available in many regions makes hydropower a powerful and consistent source of clean energy. However, the construction of large-scale hydroelectric dams can have significant environmental consequences, including habitat disruption and the displacement of communities.
Smaller-scale hydropower projects, like micro-hydro systems, offer a more localized and potentially less disruptive approach. They can be effectively implemented in areas with suitable water resources to provide a reliable and sustainable source of energy. Careful environmental assessments are essential to minimize the impact of these projects on local ecosystems and communities.
The Role of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, extracting heat from the Earth's subsurface to generate electricity. This is a remarkably consistent and sustainable source of energy, independent of weather conditions. Geothermal power plants operate continuously, providing a steady supply of electricity to the grid. The technology for harnessing geothermal energy is relatively advanced, allowing for efficient extraction and utilization of this resource.
While geothermal energy offers a compelling alternative to fossil fuels, there are challenges associated with its implementation. The location of suitable geothermal reservoirs can be geographically restricted, and the environmental impact of drilling and extraction must be carefully managed. Despite these challenges, the potential for geothermal energy to play a crucial role in the global energy mix is significant.
The Future of Energy Security: A Sustainable and Resilient Pathway
Renewable Energy and National Security
The future of energy security is inextricably linked to the transition to renewable energy sources. Renewable energy, encompassing solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, offers a pathway to energy independence, reducing reliance on volatile global fossil fuel markets. This independence fosters greater national security by lessening geopolitical vulnerability and enhancing resilience to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. The diversification of energy sources through renewable energy infrastructure strengthens national power and autonomy, creating a more stable and secure energy landscape.
Diversification is not just about replacing fossil fuels; it's about building a robust, resilient energy system. This involves investing in diverse renewable technologies, supporting local energy production, and fostering innovation in energy storage solutions. A robust and diversified energy portfolio strengthens national security by decreasing exposure to global energy price shocks and political instability, enhancing the resilience of critical infrastructure, and promoting economic growth through job creation and technological advancement.
Decarbonization and Climate Resilience
The transition to renewable energy is not merely about energy security; it's a crucial step towards a sustainable and resilient future. Climate change poses a significant threat to national security, impacting infrastructure, agriculture, and public health. Integrating renewable energy sources reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the effects of climate change and bolstering national resilience to extreme weather events.
A focus on renewable energy sources helps to create a more resilient infrastructure against the impacts of climate change. Decreased reliance on fossil fuels diminishes vulnerability to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, and protects critical infrastructure from the rising costs associated with climate adaptation. A transition to renewable energy is essential for safeguarding the future of our nation and its citizens, ensuring a sustainable and resilient pathway for generations to come.
The integration of renewable energy sources into the broader energy infrastructure also fosters climate resilience. This includes strategies like incorporating renewable energy into the design and construction of buildings, improving energy efficiency in transportation, and creating decentralized energy systems.
Economic Opportunities and Technological Advancement
The shift towards renewable energy presents significant economic opportunities. Investing in renewable energy infrastructure creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research. Furthermore, it fosters innovation in technology, leading to advancements in areas like energy storage, smart grids, and energy efficiency. These advancements not only contribute to economic growth but also enhance national competitiveness in the global market.
The development and implementation of renewable energy technologies stimulate economic growth and create new industries. The transition fosters innovation, boosts technological advancement, and creates new market opportunities. This includes opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research, leading to significant job creation and economic diversification.