Small Scale Wind Energy Advancements

Streamlined Workflow
Implementing a more streamlined workflow is crucial for boosting efficiency in any operation. This involves analyzing current processes, identifying bottlenecks, and then implementing solutions to optimize each step. By eliminating redundant tasks and automating repetitive actions, significant time savings can be achieved. This leads to a more productive workforce and ultimately, improved output.
A well-defined and documented workflow ensures that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities. This clarity minimizes confusion and ensures consistent execution, which ultimately reduces errors and improves overall productivity. Clear communication channels are also a key component of streamlining workflows.
Enhanced Technology Integration
Integrating advanced technologies, such as cloud-based platforms and automated systems, can dramatically enhance productivity and efficiency. These modern tools allow for real-time data access, collaboration, and streamlined communication across teams, departments, or even locations. Leveraging these tools can transform the way tasks are handled and completed.
Implementing robust data management systems allows for easy access and analysis of critical information. This enables informed decision-making and ensures that resources are allocated effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing output.
Optimized Resource Allocation
Optimizing resource allocation is a key factor in improving overall performance. This involves strategically assigning personnel, equipment, and materials to the most pressing tasks and projects, ensuring that resources are used effectively. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each team member and assigning tasks accordingly is vital.
A detailed analysis of resource utilization can reveal areas where resources are being wasted or underutilized. Addressing these inefficiencies leads to a more efficient use of available resources, ultimately improving performance.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for achieving optimal performance. Open communication channels facilitate seamless information exchange and allow teams to work together more effectively. This fosters a collaborative environment where ideas are shared, problems are solved collectively, and overall productivity increases.
Implementing collaborative tools and platforms can aid in streamlining communication and collaboration, allowing for real-time updates, shared documents, and project tracking. This transparency and real-time access enhance teamwork and efficiency across the organization.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making is critical for continuous improvement. Analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and other relevant data allows for a deeper understanding of trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach ensures that decisions are based on factual information, leading to more effective strategies and better outcomes.
A comprehensive data analysis process allows for the identification of areas where processes can be streamlined, resources can be allocated more effectively, and overall performance can be maximized.
Training and Development Initiatives
Investing in training and development initiatives for employees is vital for enhancing their skills and knowledge. This investment in human capital directly translates to increased productivity and improved performance. By providing opportunities for professional growth, employees become more confident and capable in their roles.
Regular training sessions and workshops focused on efficiency and productivity tools can equip employees with the necessary skills to perform their tasks more effectively and efficiently. This, in turn, contributes to a more productive and high-performing organization.
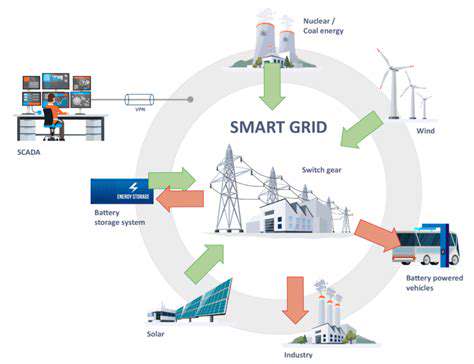
Technological Integration and Connectivity: Smart Grids for Small-Scale Systems
Enhancing Efficiency and Reliability
Smart grids, when implemented on a small scale, offer significant potential for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution systems. By incorporating advanced sensors, communication networks, and automated control systems, small-scale systems can optimize energy flow, predict potential outages, and respond proactively to fluctuations in demand. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and maximizes the use of available resources, thereby increasing the overall reliability of the energy supply.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, becomes more streamlined and effective within a smart grid framework. This allows for a more balanced and sustainable energy mix, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels and promoting environmental stewardship. The ability to better manage and integrate intermittent renewable energy sources is crucial for the long-term viability of small-scale energy systems.
Optimizing Resource Management
Smart grids provide a sophisticated platform for optimizing resource management, particularly important for small-scale systems where resources may be more limited. Real-time data collection and analysis allow for precise monitoring of energy consumption patterns, enabling proactive adjustments to minimize waste and maximize efficiency. This data-driven approach can help identify areas where energy consumption can be reduced, leading to cost savings for users and a more sustainable energy footprint.
Improving Distributed Generation Integration
The integration of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar panels or small-scale wind turbines, is crucial for the future of small-scale energy systems. Smart grids facilitate the seamless integration of these resources by enabling real-time communication and coordination between various energy sources and consumers. This interconnectedness allows for a more balanced energy flow, ensuring that energy is produced and consumed efficiently.
By enabling the effective management of distributed generation, smart grids empower small-scale system owners and users to participate in the energy market, either by selling excess generation or by reducing their consumption during peak demand periods. This creates a more dynamic and decentralized energy landscape.
Facilitating Consumer Engagement and Control
Smart grids empower consumers by providing them with greater control and awareness over their energy consumption. Through advanced metering infrastructure and user-friendly interfaces, consumers can monitor their energy usage in real time, identify patterns of consumption, and make informed decisions to reduce their energy bills. This transparency and control foster a sense of responsibility and engagement with the energy system, ultimately promoting a more sustainable energy culture.
Furthermore, smart grids enable consumers to participate actively in the energy market. Consumers can potentially generate their own energy, share it with the grid, or adjust their consumption based on real-time pricing signals. This increased consumer engagement fosters a more collaborative and sustainable approach to energy management.
Smart building technologies are rapidly transforming the construction and operation of modern facilities. These technologies leverage advancements in automation, data analytics, and connectivity to optimize various aspects of building performance, from energy consumption to occupant comfort. The integration of these technologies fosters a more sustainable and responsive environment. This shift from traditional building practices towards smart solutions promises significant improvements in operational efficiency and sustainability.

Addressing the Challenges: Policy and Infrastructure Support
Policy Incentives for Small-Scale Wind
Government policies play a crucial role in fostering the adoption of small-scale wind energy. Incentives such as tax credits, grants, and rebates can significantly reduce the financial burden for individuals and businesses considering installing small wind turbines. These financial supports act as a catalyst, encouraging investment and accelerating the growth of this renewable energy sector. Furthermore, clear and consistent policy frameworks provide a stable environment for investors and manufacturers, promoting innovation and sustainable development.
Targeted policies can also address specific challenges, such as permitting processes and grid integration issues. Streamlined permitting procedures can reduce the time and cost associated with installing small wind turbines, making the process more accessible and attractive to potential adopters. A well-defined grid integration framework ensures that the generated power can be effectively fed into the existing electricity network, maximizing the benefits of small-scale wind energy.
Infrastructure Development for Small Wind Farms
Supporting infrastructure is essential for the successful deployment of small-scale wind energy systems. This includes the development of efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes for small wind turbines, as well as the creation of robust supply chains for components and materials. Investing in research and development for improved turbine designs, optimized for small-scale applications, is also critical for enhancing performance and reducing costs.
Moreover, the development of specialized infrastructure, such as grid connection points and maintenance facilities, tailored to the specific needs of small wind farms, is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of these systems. These investments will not only improve the reliability of the small-scale wind energy generation but also lower the overall cost of deployment and operation.
Grid Integration and Intermittency Management
Integrating small-scale wind energy into existing electricity grids poses unique challenges due to the intermittent nature of wind power. Developing strategies to manage the fluctuations in power output is critical for maintaining grid stability and reliability. This may involve using energy storage solutions, such as batteries or pumped hydro, to smooth out the variability in wind generation.
Smart grid technologies, which enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flow, are also crucial in addressing these challenges. These technologies can help optimize the integration of small-scale wind energy systems, ensuring that the power generated is effectively utilized and distributed throughout the grid.
Permitting and Zoning Regulations
Simplifying permitting and zoning regulations is essential for accelerating the deployment of small-scale wind energy systems. Often, outdated or overly complex regulations can hinder the development of these projects. Streamlining the permitting process can reduce the time and cost associated with obtaining necessary approvals, thereby making small-scale wind energy more accessible.
Clear zoning regulations that explicitly address the placement and operation of small wind turbines can also contribute to a more predictable and supportive environment for developers. Creating a transparent and efficient framework for permitting and zoning can encourage greater investment in this renewable energy source.
Financial Incentives and Investment Mechanisms
Attracting investment in small-scale wind energy requires a strong financial incentive structure. Government incentives, such as tax credits or grants, can make small wind turbines more financially viable for individuals and businesses. Developing innovative financing mechanisms, such as leasing arrangements or power purchase agreements, can provide additional options for accessing capital and promoting investment.
Furthermore, establishing clear ownership and investment structures for small wind projects, as well as providing a predictable regulatory environment, can increase investor confidence and attract capital towards this promising sector. This will stimulate further growth and development of small-scale wind energy projects across the nation.
Community Engagement and Acceptance
Successfully deploying small-scale wind energy projects requires addressing local community concerns and promoting public acceptance. Transparency, communication, and proactive engagement with communities are crucial for fostering a positive perception of these projects. Community workshops, open forums, and presentations can help educate residents about the benefits of small-scale wind energy, such as job creation, energy independence, and environmental sustainability. These efforts can help mitigate potential opposition and foster a sense of shared ownership.
Educational Programs and Workforce Development
Investing in educational programs and workforce development initiatives is crucial for building a skilled workforce to support the growth of the small-scale wind energy sector. Training programs focusing on the installation, maintenance, and operation of small wind turbines can equip technicians with the necessary expertise to ensure efficient and reliable operation of these systems.
Educational outreach initiatives can also inform the public about the benefits and opportunities associated with small-scale wind energy, fostering a greater understanding and appreciation for this renewable energy source. Providing educational resources and training opportunities will ensure a skilled workforce is available to meet the growing demands of the small-scale wind energy sector.