Decentralization of Energy Generation for Energy Access: Global Initiatives
Distributed Generation: A Paradigm Shift in Power Production
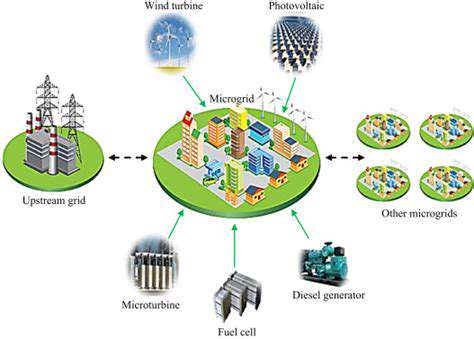
Distributed generation (DG) technologies are rapidly transforming the landscape of power production. This shift involves the decentralization of power generation, moving away from large, centralized power plants towards smaller, dispersed generation units. This paradigm shift offers a multitude of benefits, including increased grid reliability and reduced transmission losses.
The increased resilience of the power grid is a key advantage of DG. By distributing generation, the system becomes more resistant to failures in a single location. If a large power plant experiences an outage, a significant portion of the local grid can remain operational, thanks to the distributed sources.
Types of Distributed Generation Technologies
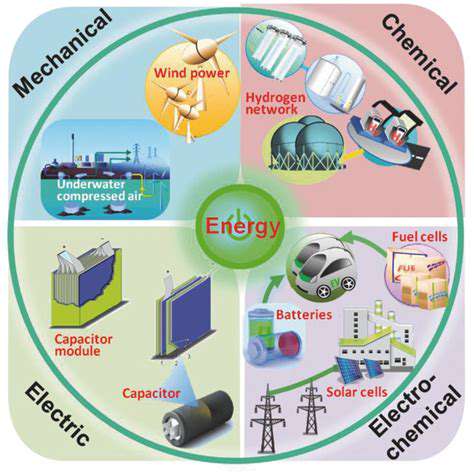
A variety of technologies fall under the umbrella of distributed generation, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Photovoltaic (PV) systems, utilizing solar energy, are a prominent example, converting sunlight directly into electricity. Wind turbines harness the power of wind to generate electricity, offering another clean and renewable energy source.
Other technologies include microturbines, fuel cells, and combined heat and power (CHP) systems. These diverse options cater to different needs and locations, allowing for a tailored approach to energy generation.
Economic Benefits of Distributed Generation
Distributed generation can offer significant economic advantages for consumers and utilities. Reduced transmission losses translate into lower energy costs for consumers, as less energy is lost during transmission from the generation source to the end-user. This efficiency directly impacts the bottom line for both residential and commercial energy users.
Furthermore, distributed generation can enable consumers to reduce their reliance on the utility grid, potentially leading to lower electricity bills and increased energy independence.
Environmental Impact of Distributed Generation
Distributed generation technologies, particularly renewable sources like solar and wind, contribute to a cleaner environment. By reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants, the emission of harmful greenhouse gases is minimized, contributing to a more sustainable energy future. This transition towards cleaner energy sources is vital for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
The reduced environmental impact of DG is a critical factor in its growing adoption, as consumers and policymakers prioritize sustainability.
Grid Integration Challenges
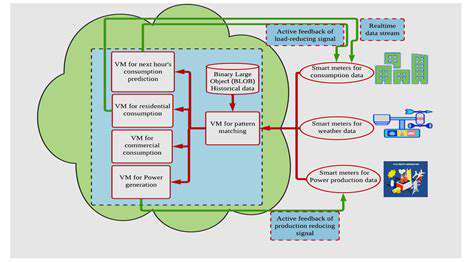
While distributed generation offers numerous benefits, there are challenges in integrating these technologies seamlessly into existing power grids. Intermittency, particularly with renewable sources like solar and wind, requires sophisticated grid management systems to maintain grid stability. The fluctuating nature of these sources needs to be carefully balanced with the consistent demand for electricity.
However, advances in energy storage technologies and smart grid technologies are addressing these challenges and improving the efficiency and reliability of DG integration.
Future Trends in Distributed Generation
The future of distributed generation is poised for continued growth and innovation. The development of more efficient energy storage solutions will be crucial for overcoming the intermittency issues associated with renewable sources. Smart grid technologies will play an increasingly important role in managing the flow of power from distributed sources to the grid, thereby improving grid stability and reliability.
Further advancements in energy storage and smart grid technology will be essential to further realize the full potential of distributed generation. This includes advancements in battery technology, and more sophisticated grid management systems.
The real estate industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven largely by technological advancements. From sophisticated property valuation software to virtual tours and online marketplaces, technology is streamlining processes, enhancing efficiency, and connecting buyers and sellers in unprecedented ways. This digital revolution is fundamentally altering how real estate transactions are conducted, impacting everything from the initial search to the final closing.
Global Initiatives and Policy Support: A Catalyst for Change
International Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Global initiatives play a crucial role in fostering the decentralization of environmental protection efforts. International collaborations allow for the sharing of best practices, technologies, and resources among nations, enabling a more comprehensive and effective approach to environmental challenges. This knowledge exchange is vital for developing countries that often lack the resources or expertise to implement sophisticated environmental programs independently. Successful partnerships can accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices and promote a more equitable distribution of environmental responsibility across the globe.
Furthermore, the exchange of scientific data and research findings is essential. This interconnectedness allows for the identification of global trends and emerging environmental issues, enabling proactive responses and the development of evidence-based policies. International cooperation can also provide a platform for addressing transboundary environmental problems, such as air and water pollution, which require collaborative solutions to be effective.
Policy Frameworks and Legal Instruments
Robust policy frameworks and legal instruments are essential for enabling and accelerating the decentralization of environmental protection. These frameworks should clearly define the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, from national governments to local communities. Effective policies need to be adaptable and responsive to local contexts, recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities presented by different regions and communities. Such policies should also incentivize sustainable practices and provide adequate support for local communities to implement them.
International agreements and conventions play a significant role in establishing common standards and principles for environmental protection. These agreements can provide a foundation for national policies and regulations, promoting consistency and collaboration across borders. However, the effectiveness of these policies hinges on their implementation at a local level. Local governments and communities must be actively involved in the development and enforcement of these policies to ensure their effectiveness and relevance.
Financial Mechanisms and Resource Mobilization
Decentralization of environmental protection requires significant financial investment and resource mobilization. This includes funding for capacity building, technology transfer, and the implementation of local environmental projects. Innovative financial mechanisms, such as grants, loans, and public-private partnerships, can play a vital role in attracting resources and ensuring the sustainability of decentralized initiatives. Effective resource allocation strategies are critical to ensure that funds are directed towards the most pressing environmental challenges in a given region or community.
The development of sustainable financing models is crucial for long-term success. These models must consider the specific needs and priorities of local communities, ensuring that funding is accessible and responsive to local contexts. Transparent and accountable mechanisms for managing and monitoring financial resources are essential to build trust and ensure that investments are used effectively to achieve environmental goals.
Community Engagement and Empowerment
Empowering local communities is paramount to the success of decentralized environmental protection strategies. Local communities possess valuable knowledge and experience regarding their specific environmental challenges and opportunities. Engaging communities in decision-making processes, providing them with the necessary resources and information, and recognizing their traditional practices are critical for effective implementation. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more sustainable and resilient outcomes.