Understanding the Cost of Energy Storage Systems

Geographic Location and Market Conditions
Geographic Variations in Energy Storage Costs
The cost of energy storage systems varies significantly across different geographic regions. Factors such as the availability of raw materials, labor costs, local regulations, and the prevailing energy market conditions all contribute to these variations. For example, regions with abundant solar resources might see a lower cost per kilowatt-hour for battery storage systems due to economies of scale and the lower cost of incorporating renewable energy into the grid. Conversely, regions with limited access to essential materials or high labor costs may experience higher energy storage prices. Understanding these geographic disparities is critical for accurate cost estimations when implementing energy storage solutions.
Furthermore, government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping energy storage costs. Subsidies, tax credits, and regulatory frameworks can influence the affordability and adoption of these technologies in specific regions. Analyzing these local policies is essential for businesses and organizations seeking to deploy energy storage solutions, as they can significantly impact the overall project economics.
Market Conditions and Technological Advancements
Fluctuations in the energy market, including electricity prices, demand, and the availability of financing, directly impact the cost of energy storage. Periods of high electricity prices can incentivize investment in energy storage, leading to potentially lower costs as the market responds to increased demand. Conversely, periods of low electricity prices may result in reduced investment and consequently higher costs for energy storage systems.
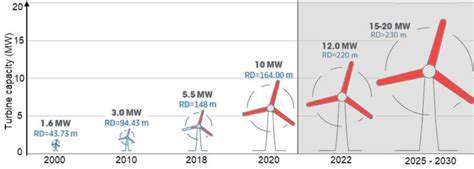
Technological advancements are continuously driving down the cost of energy storage components, particularly battery technology. Innovations in battery chemistry, manufacturing processes, and energy storage system design are leading to significant improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. As these advancements progress, the overall cost of energy storage is expected to decline, making it more accessible for a wider range of applications.
The competitive landscape of the energy storage market also influences pricing. Increased competition among manufacturers and vendors can drive down prices and enhance the availability of various energy storage solutions tailored to diverse needs. This competitive pressure encourages innovation and efficiency improvements, ultimately benefiting consumers and businesses by providing cost-effective options.
Impact of Energy Source and Grid Integration
The type of energy source used to charge energy storage systems plays a vital role in determining the overall cost. For example, integrating renewable energy sources like solar or wind power with energy storage can potentially reduce the reliance on traditional fossil fuel-based power plants, leading to lower operating costs over time. However, the cost of integrating these renewable sources with storage systems must be carefully considered.
The efficiency of grid integration also significantly impacts the cost of energy storage. A well-designed and efficient grid infrastructure can facilitate seamless energy transfer between the storage system and the grid, minimizing losses and improving overall system performance. Conversely, inefficient grid integration can result in higher energy storage costs due to increased transmission and distribution losses. It is crucial to evaluate the grid integration costs when planning energy storage deployment.
The complexity of grid integration and the associated infrastructure requirements can vary greatly depending on the specific region and existing grid infrastructure. Factors like transmission capacity, grid stability, and the need for upgrades or modifications to existing grid systems must be carefully considered during the planning phase, as these factors can significantly impact the overall cost of energy storage projects.