The Role of Distributed Energy Resources in Emergency Response
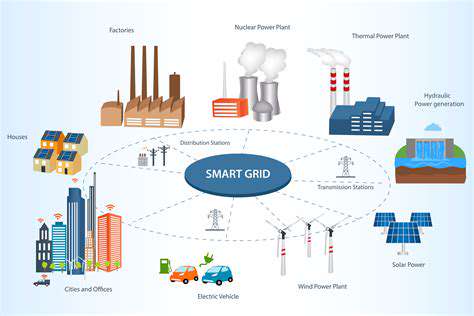
Decentralized Energy Resources (DERs) are rapidly gaining prominence in the energy landscape, marking a significant shift from traditional centralized power generation. This shift is driven by various factors, including the increasing need for resilience and reliability in energy supply, the rise of renewable energy sources, and the growing demand for local energy control and management. DERs offer the potential to revolutionize the energy sector, creating a more distributed and responsive energy system.
The integration of DERs into the grid presents a multifaceted challenge and opportunity. It requires careful consideration of grid stability, energy storage solutions, and effective communication protocols. However, the potential benefits are substantial, including reduced transmission losses, enhanced grid resilience against outages, and greater local control over energy generation and consumption. The integration of DERs is poised to reshape the relationship between energy producers, consumers, and the grid itself.
Technological Advancements Driving DER Adoption
Several technological advancements are facilitating the widespread adoption of DERs. These include innovative energy storage solutions, such as advanced battery technologies and pumped hydro storage, enabling DERs to effectively manage fluctuating energy production from renewable sources. Furthermore, smart grid technologies are crucial in enabling seamless communication and coordination between DERs and the existing power grid, ensuring efficient operation and grid stability. Smart grid technologies are pivotal for managing the dynamic nature of DERs and enabling a smooth transition to a more distributed energy system.
Improvements in inverter technology and communication protocols are also essential for integrating DERs into the grid. These advancements minimize grid stress, reduce transmission losses, and enable more efficient energy management. The synergy between these technologies is crucial for maximizing the benefits of DERs and minimizing the challenges associated with their integration.
Economic and Societal Benefits of DERs
The adoption of DERs offers significant economic and societal benefits. From a consumer perspective, DERs can lead to lower energy bills and greater control over energy consumption. Businesses can also benefit from reduced reliance on centralized power grids and potentially reduced operating costs. Decentralized energy systems can improve energy access in remote areas and underserved communities. This access is especially crucial in areas where traditional grid infrastructure is absent or unreliable.
Furthermore, DERs contribute to a more sustainable energy future by promoting renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This transition not only mitigates the environmental impact of energy production but also enhances energy security by reducing dependence on external energy sources. DERs are a key component in the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Enhanced Grid Reliability and Redundancy
Improving Grid Resilience Through Redundancy
Enhanced grid reliability hinges on robust redundancy mechanisms. Distributed energy resources (DERs) play a crucial role in bolstering this resilience by providing alternative pathways for power delivery. This redundancy mitigates the impact of single points of failure, such as transmission line outages or substation malfunctions, ensuring a more stable and reliable power supply. The distributed nature of DERs, dispersed across various locations, increases the overall system's capacity to withstand disruptions.
By incorporating DERs, the grid becomes less susceptible to cascading failures. If one part of the network experiences a problem, the DERs can often step in to maintain power flow, preventing the disruption from spreading and affecting other areas. This is particularly valuable in areas prone to natural disasters or other events that can disrupt traditional grid infrastructure.
Distributed Generation for Enhanced Grid Stability
Distributed generation, a key component of DERs, introduces localized power generation. This localized generation reduces the reliance on long transmission lines, which are often vulnerable to outages. By producing power closer to the point of consumption, DERs help to stabilize the grid and maintain voltage levels within acceptable ranges. This localized power generation translates to improved grid stability and a more responsive power system.
The introduction of distributed generation from DERs also reduces the strain on existing transmission infrastructure. This is crucial in aging grids, where upgrades to the existing network may be costly and time-consuming. DERs offer a more agile and cost-effective approach to maintaining grid stability in these scenarios.
DERs and Grid Automation for Optimized Performance
The integration of DERs with grid automation technologies creates a more dynamic and responsive power system. Smart grid technologies allow for real-time monitoring and control of DERs, enabling optimal utilization of their power output. This real-time optimization ensures that DERs contribute effectively to grid stability during various operating conditions.
Automated communication between DERs and the grid facilitates rapid responses to changes in demand and supply. This responsiveness is critical for maintaining grid balance and preventing voltage fluctuations. The integration of DERs with advanced grid automation technologies represents a significant step toward a more efficient and resilient power grid.
Enhanced Grid Fault Tolerance through DERs
DERs significantly enhance the grid's fault tolerance by providing localized power sources capable of quickly responding to grid disturbances. When a fault occurs, DERs can often isolate the affected section of the grid, preventing the fault from propagating to other parts of the network. This localized response reduces the scope and duration of outages.
This fault tolerance, enabled by DERs, is crucial for maintaining the reliability and continuity of power supply. The ability to quickly isolate and manage faults significantly minimizes the impact on consumers and industries that depend on a stable power supply. This localized fault management capability is a key advantage of incorporating DERs into the grid.
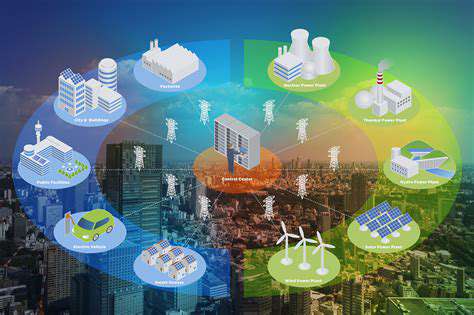
DERs and the Future of Microgrids
The integration of DERs is instrumental in the development of microgrids, which are localized, self-sufficient power systems. These microgrids, often composed of DERs, can operate independently from the main grid during disruptions, ensuring continued power supply for critical loads. This capability is particularly valuable in remote areas or during emergency situations.
Microgrids provide a significant level of resilience and control over power supply. The ability to isolate and manage localized power resources is a crucial step toward building more resilient and sustainable energy systems. DERs are a fundamental component in the future development of microgrids and their associated benefits.
Economic Benefits of Enhanced Grid Reliability
Enhanced grid reliability through the implementation of DERs translates into substantial economic benefits. Reduced downtime for businesses and industries due to power outages translates into significant cost savings. The minimized risk of equipment damage from voltage fluctuations and surges also contributes to cost savings.
Improved grid reliability fosters a more predictable and stable business environment. This, in turn, encourages investments and economic growth. The long-term benefits of incorporating DERs into the grid far outweigh the initial costs, making it a financially sound investment in the future of the energy sector.
Improving Community Self-Sufficiency and Economic Recovery

Cultivating Local Resources
A crucial aspect of enhancing community self-sufficiency involves actively identifying and nurturing local resources. This encompasses everything from readily available agricultural land to skilled artisans and entrepreneurs within the community. By recognizing and leveraging these existing assets, communities can build a strong foundation for economic prosperity and stability. This proactive approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, empowering residents to participate in shaping their future.
Examining local strengths and weaknesses is fundamental to effective resource cultivation. Understanding the unique characteristics of the area, including its climate, soil quality, and available labor pool, provides valuable insights into potential opportunities for growth. A comprehensive assessment allows for the development of targeted strategies that capitalize on local advantages and address any existing limitations.
Developing Sustainable Infrastructure
Robust infrastructure is essential to support a self-sufficient community. This encompasses not only physical infrastructure like roads, water systems, and sanitation facilities but also digital infrastructure, such as reliable internet access. A well-developed infrastructure network facilitates trade, communication, and access to essential services, thereby fostering economic growth and improving overall quality of life for residents.
Investing in sustainable infrastructure ensures the long-term viability of the community. This involves prioritizing environmentally conscious practices, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and implementing water conservation measures. By prioritizing sustainability, communities can ensure the availability of resources for future generations.
Promoting Local Businesses
Supporting local businesses is paramount to community self-sufficiency. This includes offering incentives and resources to encourage entrepreneurship and small business growth. Active promotion of local products and services through marketing and outreach efforts can significantly boost local economies and create job opportunities. Moreover, fostering a supportive environment that fosters innovation and creativity amongst local businesses is vital for sustained economic growth.
Encouraging the development of a diverse range of businesses within the community will provide a wider spectrum of goods and services to residents, while also stimulating competition and innovation, further strengthening the local economy.
Enhancing Educational Opportunities
Investing in education is key to developing a skilled and adaptable workforce. High-quality educational opportunities, from early childhood programs to vocational training, are critical for equipping residents with the necessary knowledge and skills to contribute to the community. By investing in education, communities can foster a skilled and adaptable workforce that can drive innovation and economic growth.
Furthermore, access to higher education opportunities, whether through partnerships with local colleges or distance learning programs, will enhance skill development and broaden career prospects for residents, ultimately strengthening community self-sufficiency.
Fostering Community Cooperation
Strong community bonds are the bedrock of self-sufficiency. Cultivating a sense of shared responsibility and cooperation among residents is crucial. This can be achieved through community events, volunteer initiatives, and collaborative problem-solving efforts. By fostering collaboration, communities can pool resources, share knowledge, and tackle challenges collectively.
Furthermore, encouraging active participation in local governance and decision-making processes empowers residents and reinforces a sense of ownership in the community's future. This fosters a culture of mutual support and shared responsibility vital for long-term success.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agricultural practices are essential for food security and environmental health. Supporting local farmers and promoting the cultivation of diverse crops can create a resilient food system. By focusing on sustainable agriculture, communities can ensure a stable supply of fresh produce and reduce reliance on external food sources.
Diversifying agricultural production to include crops that thrive in the local environment, and implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques, will enhance the sustainability of local food production, contributing to the overall self-sufficiency of the community.