Peer to Peer Energy Trading: Revolutionizing Decentralization of Energy Generation
The rise of DERs has paved the way for a new paradigm in energy trading: peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading. This innovative approach allows individuals and businesses with DERs to directly exchange energy with each other, bypassing traditional utility intermediaries. P2P energy trading platforms facilitate the buying and selling of excess energy generated by one party to another, creating a more dynamic and efficient energy market. This decentralized model promotes energy independence, reduces reliance on centralized power plants, and fosters a more participatory energy system.
One of the key advantages of P2P energy trading is the potential for significant cost savings for consumers. By allowing individuals to sell excess renewable energy, they can reduce their energy bills and potentially earn income. Furthermore, the increased participation of consumers in energy production and consumption can lead to a more sustainable and resilient energy system, promoting energy independence and reducing dependence on fossil fuel-based energy sources. This distributed energy trading model holds enormous promise for the future of the energy sector, offering a more equitable and efficient way to manage and distribute energy.
The emergence of P2P energy trading platforms is not without its challenges. Addressing issues such as grid stability, ensuring fair pricing mechanisms, and developing robust regulatory frameworks are critical to the successful implementation of this new model. However, the potential benefits of P2P energy trading in terms of cost savings, energy efficiency, and sustainability make it a key component of the future energy landscape.

AI-powered search engines are revolutionizing how we find information online. Instead of simply matching keywords, these advanced systems understand the context and intent behind user queries, delivering more relevant and accurate results. This shift from keyword-matching to semantic understanding drastically improves the user experience, allowing users to find precisely what they're looking for with greater speed and efficiency. This sophisticated approach is crucial in today's information-saturated world.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization and Trust in Energy Trading
Blockchain technology fundamentally alters the energy trading landscape by enabling a decentralized system. Traditional energy markets often rely on intermediaries, creating potential points of failure and opacity. A blockchain-based system, however, facilitates direct peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating intermediaries and fostering trust among participants. This inherent trust mechanism, built on cryptographic security, enhances transparency and reduces the risk associated with fraud or manipulation.
This decentralization is crucial for empowering individuals and communities. By removing the need for centralized control, blockchain enables smaller players to participate in the energy market, fostering greater competition and potentially driving down costs.
Enhanced Transparency and Security
The immutable nature of blockchain records ensures complete transparency in energy transactions. Every transaction, from generation to consumption, is recorded on a shared, publicly accessible ledger, making it easy to track energy flows and verify the authenticity of each exchange. This transparency drastically reduces the opportunities for fraud and manipulation, fostering greater trust among participants.
Cryptographic security further strengthens the system by using complex algorithms to secure the transactions and prevent unauthorized access. This robust security prevents tampering and ensures the integrity of the entire energy trading process.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Automation inherent in blockchain technology streamlines energy trading processes. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements embedded on the blockchain, can automatically execute transactions based on predefined conditions. This automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and significantly accelerates the entire trading process.
The elimination of intermediaries also reduces transaction costs. By cutting out unnecessary layers in the energy trading chain, blockchain significantly lowers the overall cost of energy transactions, making energy more accessible and affordable for consumers and businesses alike.
Scalability and Adaptability
One of the significant advantages of blockchain technology is its scalability. Blockchain platforms can support a high volume of transactions without compromising the security or efficiency of the system. This scalability is crucial for accommodating the increasing demands of the energy sector as renewable energy sources become more prominent.
Moreover, blockchain's adaptability allows for the seamless integration of new technologies and protocols into the energy trading ecosystem. As energy technologies evolve, blockchain's flexibility ensures that the system can easily adapt to accommodate these changes without disrupting the core functionality.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Blockchain's decentralized nature perfectly complements the distributed nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. By enabling direct transactions between producers and consumers of renewable energy, blockchain fosters a more efficient and sustainable energy system.
This integration encourages the adoption of renewable energy by allowing individuals and communities to participate directly in the generation and distribution of clean energy, contributing to a greener future.
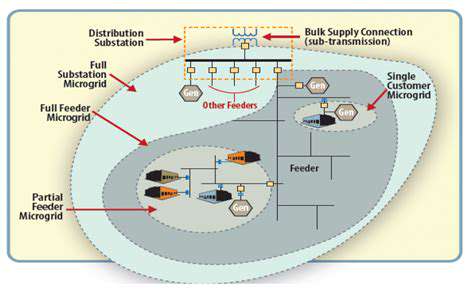
Potential for Microgrids and Decentralized Energy Systems
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the design and management of microgrids. By enabling direct energy trading between participants in a microgrid, blockchain can optimize energy distribution and ensure reliable energy access, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, the implementation of blockchain in energy trading requires careful consideration of regulatory and legal frameworks. Establishing clear regulations and guidelines is crucial to ensure the security, transparency, and accountability of the system.
Collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and blockchain developers is essential for navigating the legal complexities and establishing a robust regulatory environment for blockchain-based energy trading.
The Future of Energy: A Decentralized Landscape

Decentralized Energy Systems: A Paradigm Shift
The future of energy is increasingly leaning towards decentralized systems, moving away from large, centralized power plants. This shift is driven by a multitude of factors, including the need for greater resilience, reduced transmission losses, and a growing emphasis on renewable energy sources. Decentralized energy systems, powered by distributed generation, offer a more sustainable and adaptable energy infrastructure. This approach allows for greater community participation and control over energy production and consumption.
These systems leverage smaller-scale power generation units, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and micro-hydro systems, located closer to the end-users. This proximity drastically reduces transmission losses, leading to significant energy savings and a more efficient energy grid. The integration of smart technologies further enhances the efficiency and reliability of decentralized systems, enabling real-time monitoring and management of energy flow.
Technological Advancements: Driving the Transition
Several key technological advancements are fueling the transition to decentralized energy systems. These advancements include improvements in battery storage technologies, allowing for the efficient storage and use of intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind. This crucial element is essential for ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply.
Smart grids, with their advanced communication and control capabilities, are essential for managing the complexities of decentralized energy systems. These grids enable real-time monitoring and optimization of energy flow, ensuring a stable and efficient energy distribution network. Smart meters and other advanced monitoring technologies are critical for optimizing energy consumption patterns and providing valuable data for system management.
Furthermore, the development of advanced energy storage solutions, such as pumped hydro storage and thermal energy storage, is crucial for addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources. These advancements are necessary to balance the supply and demand in a decentralized system. The combination of these technologies creates a more robust and reliable energy infrastructure.
Economic and Societal Impacts: Shaping the Future
Decentralized energy systems are poised to have a profound impact on both the economy and society. The creation of new jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of distributed energy generation equipment will drive economic growth in local communities.
Increased energy independence and resilience will benefit communities, particularly those in remote areas or with unreliable grid access. This enhanced resilience to outages and disruptions is a significant advantage in the face of natural disasters or other unforeseen events. Furthermore, the transition to decentralized systems can lead to a more sustainable and equitable energy future.
Reduced reliance on fossil fuels and a shift towards renewable energy sources will contribute to a cleaner environment, improving public health and reducing carbon emissions. This transition will have a positive impact on the environment and society as a whole. Moreover, the greater community participation in energy production and consumption fostered by decentralized systems can create a sense of shared responsibility and ownership.