Sustainable Resource Extraction for Renewable Energy Components
Circular Economy Principles and Material Life Cycle Assessment
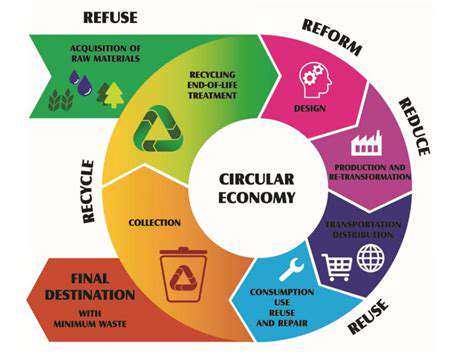
Circular Economy Principles
A circular economy is a systemic approach to economic development designed to decouple growth from the consumption of finite resources. It aims to keep products, components, and materials at their highest utility and value at all times, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. This approach contrasts sharply with the traditional linear take-make-dispose model, which often leads to significant environmental damage and resource depletion.
At its core, the circular economy focuses on principles of reuse, repair, and recycling. This shift in thinking requires a fundamental reimagining of product design, manufacturing processes, and consumer behavior. Instead of designing products for a single use, companies are encouraged to create durable, repairable, and easily recyclable products.
Material Recovery and Recycling
Material recovery and recycling are crucial components of a circular economy. Efficient recycling processes are essential to extract valuable materials from waste streams, reducing the demand for virgin resources. This process not only conserves resources but also minimizes the environmental impact of waste disposal. Recycling facilities need to be strategically located and equipped with advanced technologies to maximize material recovery rates.
Proper sorting and processing of recyclable materials are critical to ensure high-quality recycled products. This requires careful planning and education initiatives to raise public awareness about the importance of proper waste disposal.
Product Design for Durability and Reusability
Designing products for durability and reusability is paramount to a circular economy. This approach focuses on creating products that can be easily repaired, upgraded, or reused, extending their lifespan significantly. Innovative design strategies, like modularity and standardized components, can facilitate easier disassembly and reuse of parts. This approach reduces the need for frequent replacements and minimizes the generation of waste.
Product design should also consider the entire lifecycle of a product, from raw material extraction to disposal. By incorporating circular economy principles from the outset, companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and create more sustainable products.
Waste Reduction and Prevention
Waste reduction and prevention are fundamental principles of a circular economy. Preventing waste in the first place is more environmentally friendly and cost-effective than managing it later. This involves optimizing production processes to minimize waste generation, adopting design approaches that prioritize durability and reusability, and promoting product lifecycles that extend beyond a single use.
Developing strategies for waste prevention requires a collaborative approach involving businesses, policymakers, and consumers. Educating consumers about the benefits of reducing waste and promoting responsible consumption habits is vital for achieving waste reduction targets.
Sustainable Consumption and Production
Sustainable consumption and production practices are essential for a circular economy's success. Consumers play a vital role in reducing waste and promoting reuse by making conscious purchasing decisions. Supporting businesses that adopt circular economy principles is critical to driving wider adoption.
Businesses need to adopt sustainable production practices, minimizing their environmental impact through resource efficiency and waste reduction. Transparency in supply chains is essential to ensure accountability and traceability of materials throughout the product lifecycle. These practices will help reduce pollution and conserve resources.
Policy and Infrastructure Support
Robust policy and infrastructure support are crucial for facilitating the transition to a circular economy. Government policies, such as extended producer responsibility schemes and incentives for recycling, can drive significant change. Clear regulations and standards for sustainable products and practices are needed to ensure a level playing field for businesses adopting circular economy principles.
Investing in infrastructure, such as advanced recycling facilities and waste management systems, is also necessary to support the effective implementation of circular economy principles. This requires a multi-stakeholder approach, involving collaboration between governments, businesses, and research institutions.
Collaboration and Policy Frameworks for Responsible Resource Management
Defining the Scope of Collaboration
A robust collaboration framework requires a clear definition of the scope of collaboration. This encompasses identifying the specific areas where collaboration is deemed necessary and beneficial. Clearly outlining the objectives and expected outcomes is crucial for aligning all participants and ensuring focused efforts. This step also involves defining the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder, minimizing ambiguity and fostering a shared understanding of individual contributions.
Furthermore, establishing clear parameters around the timeframe for the collaboration is important. This includes setting realistic deadlines and milestones to track progress and ensure accountability. A well-defined scope also helps in managing expectations and preventing potential conflicts or misunderstandings later on.
Policy Development for Effective Collaboration
Policies are fundamental to successful collaboration. These policies must address issues such as data sharing protocols, intellectual property rights, and confidentiality agreements. Establishing clear guidelines on these crucial aspects helps maintain trust and transparency among collaborators. Furthermore, policies should outline dispute resolution mechanisms in case disagreements arise.
Effective policies also need to address the handling of sensitive information, including compliance with regulations and ethical considerations. This is vital to protect the interests of all parties involved. Robust policies create a predictable and equitable environment for collaboration.
Building Trust and Transparency
Trust and transparency are essential pillars of any successful collaboration. Building trust involves fostering open communication channels, actively listening to diverse perspectives, and demonstrating respect for each other's ideas and contributions. Creating an environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and concerns is critical to the success of the project.
Transparency, in turn, involves ensuring that all relevant information is shared openly and honestly. This includes sharing data, progress reports, and any potential challenges. Openness and honesty are fundamental to maintaining trust throughout the collaboration process.
Establishing Clear Communication Protocols
Effective communication is paramount for successful collaboration. This necessitates establishing clear communication protocols, including designated channels for different types of communication, such as formal meetings, email exchanges, or instant messaging platforms. This ensures that information flows efficiently and effectively among participants.
Establishing consistent communication schedules is equally important. This might involve regular meetings, progress reports, or feedback sessions. It's important to set expectations regarding response times and communication frequency to optimize workflow and ensure everyone stays informed.
Managing Conflicts and Addressing Challenges
Conflicts and challenges are inevitable in any collaborative environment. Therefore, having a proactive approach to conflict resolution is crucial. This includes establishing clear guidelines for addressing disagreements and establishing a mechanism for mediating disputes. Having a plan in place helps in handling conflicts constructively and efficiently.
Furthermore, anticipating potential challenges and developing contingency plans is vital for maintaining the momentum and productivity of the collaboration. This involves acknowledging potential obstacles, assessing their impact, and strategizing ways to mitigate them. This proactive approach ensures that the collaboration remains on track despite unexpected roadblocks.