Sustainable Practices in Energy Storage Manufacturing
Material Sourcing Strategies for a Circular Economy
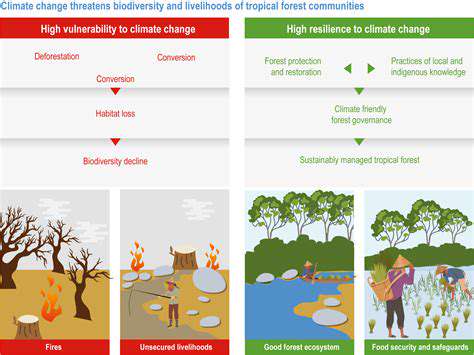
Sustainable material sourcing is paramount in a circular economy model. This involves prioritizing materials with minimal environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. Companies must actively seek out recycled content, renewable resources, and materials that are easily recyclable or compostable. This proactive approach reduces reliance on virgin resources, lowers carbon emissions, and minimizes waste generation, thereby fostering a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
Careful consideration must be given to the entire supply chain. This includes evaluating the environmental footprint of each material from extraction to manufacturing, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the process. Traceability is key to understanding the origin and journey of materials, allowing for informed decisions and the implementation of responsible sourcing policies.
Recycling Infrastructure and Technologies
Robust recycling infrastructure is essential for the successful implementation of a circular economy. This includes the development and improvement of collection systems, sorting facilities, and recycling plants. Investing in advanced technologies like automated sorting and material recovery facilitates higher quality recycling rates and minimizes contamination, thereby maximizing the value of recovered materials.
Furthermore, research and development in recycling technologies are crucial to address the challenges of processing complex materials and improving the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling processes. This includes breakthroughs in chemical recycling, which can convert non-recyclable plastics into valuable feedstocks.
Promoting Consumer Engagement in Recycling
Consumer behavior plays a significant role in material recycling. Educating consumers about the importance of proper waste disposal and recycling methods is vital for maximizing recycling rates. Clear labeling and communication strategies about what materials are recyclable and how to correctly dispose of them empower consumers to participate effectively in the circular economy.
The Economic Benefits of Recycling and Circularity
Implementing circular economy principles can generate substantial economic benefits beyond environmental gains. Recycling materials reduces the need for new raw materials, leading to cost savings in the long run. The recovered materials can also be used as feedstocks for manufacturing processes, creating new markets and opportunities for businesses. This can strengthen local economies and promote sustainable job creation.
Designing for Reusability and Durability
Product design plays a critical role in fostering a circular economy. Products should be designed with reusability and durability in mind. This means considering features like modularity, repairability, and the use of easily replaceable components. By extending the lifespan of products and facilitating their reuse or repair, we reduce the demand for new materials and minimize waste generation.
Collaboration and Policy Support for Circularity
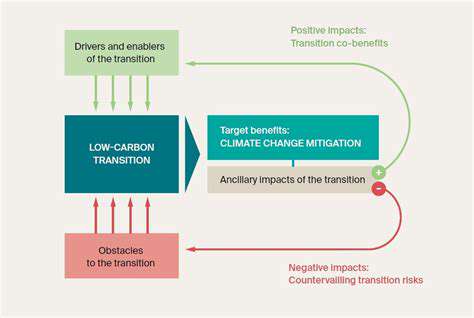
Success in achieving a circular economy necessitates collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers. Policy support, such as tax incentives for recycling and extended producer responsibility schemes, can encourage the development and implementation of circular economy practices. This collaborative approach promotes the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices, accelerating the transition towards a more sustainable future.

Employee Training and Stakeholder Engagement: Fostering Sustainable Practices
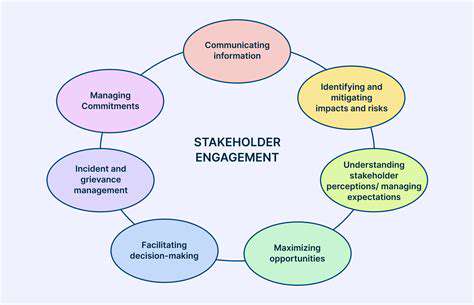
Employee Training Programs
Effective employee training programs are crucial for fostering a skilled and engaged workforce. These programs should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and its employees, ensuring that individuals gain the knowledge and skills required to perform their roles efficiently and effectively. Investing in employee training demonstrates a commitment to professional development and career advancement, which can lead to increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
A comprehensive training program should cover essential skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Beyond these fundamental skills, specific industry-relevant training can be implemented to meet evolving business demands. This could include software training, technical skills development, or product knowledge workshops, depending on the specific roles and functions within the company.
Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
Engaging stakeholders effectively is paramount for successful project implementation and long-term organizational success. Stakeholder engagement is not a one-time event but a continuous process that requires a deep understanding of each stakeholder's needs, concerns, and perspectives. By actively listening to and responding to stakeholder input, organizations can build trust and foster collaboration, ultimately leading to more positive outcomes.
Identifying key stakeholders and understanding their interests is critical for successful engagement. This involves mapping stakeholder influence and impact, and then designing tailored engagement strategies that address their specific concerns and expectations. This process will help to mitigate potential conflicts and build stronger relationships with all stakeholders.
Furthermore, maintaining open communication channels and providing regular updates on project progress are essential to keep stakeholders informed and engaged. This transparency fosters trust and allows for timely feedback, preventing misunderstandings and enabling collaborative problem-solving.
Alignment of Training with Stakeholder Needs
A crucial aspect of successful employee training is aligning it with the needs of stakeholders. This involves understanding the specific skills and knowledge required to meet stakeholder expectations, and tailoring training programs accordingly. By demonstrating a clear connection between employee development and stakeholder value, organizations can strengthen their overall performance and build stronger relationships with their key partners.
Integrating stakeholder feedback into the design of training programs is essential for ensuring relevance and effectiveness. This allows for a dynamic approach to learning, where training is shaped by the needs of both employees and stakeholders. This approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and ensures that training initiatives remain aligned with the evolving needs of the organization and its external partners.