Renewable Energy and Climate Adaptation Strategies
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, utilizing steam and hot water resources to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is particularly well-suited for regions with high geothermal activity, offering a consistent and reliable energy supply.
The technology for harnessing geothermal energy is constantly evolving, with improvements in drilling and extraction techniques leading to more efficient and sustainable operations. This renewable energy source can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Biomass Energy: Utilizing Organic Matter
Biomass energy, derived from organic matter, offers a diverse and versatile approach to renewable energy production. This includes using agricultural residues, wood chips, and other organic materials to produce energy. Biomass energy conversion processes, such as combustion and gasification, can generate electricity or heat.
The sustainable management of biomass resources is crucial for ensuring that this renewable energy source remains environmentally friendly. Careful consideration must be given to the impact of biomass harvesting on ecosystems and the use of sustainable forestry practices.
The Interdependence of Renewable Energy Sources
The various renewable energy sources – solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass – are not mutually exclusive. In fact, combining these sources creates a more robust and resilient energy system. Integrating these diverse sources can help to balance fluctuating energy production and ensure a reliable supply to meet energy demands. This interconnectedness allows for a more comprehensive and sustainable energy mix.
Furthermore, the development of advanced energy storage technologies is crucial for smoothing out the fluctuations in renewable energy production and ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply. The integration of these storage solutions will be essential for the successful transition to a fully renewable energy future.
Renewable Energy Sources: A Foundation for Adaptation
Harnessing Solar Power
Solar energy, derived from the sun's radiant light, is a remarkably abundant and sustainable resource. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, offering a clean alternative to fossil fuels. The vast potential of solar power extends beyond residential applications, with large-scale solar farms playing a crucial role in meeting growing energy demands and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The ongoing advancements in solar technology, including improved efficiency and cost reductions, are making solar power increasingly accessible and economically viable for a wide range of users.
Furthermore, advancements in energy storage technologies are crucial to maximizing the benefits of solar energy. Storing excess solar energy generated during peak hours allows for its utilization during periods of low solar irradiance, thus ensuring a more reliable and consistent energy supply. This integration of solar energy with energy storage systems represents a significant step toward creating a truly sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
Tapping into Wind Power
Wind energy, harnessed through wind turbines, converts kinetic energy from moving air into electricity. Wind farms, strategically located in areas with consistent wind patterns, generate significant amounts of clean energy. The technology behind wind turbines has evolved considerably, with modern designs exhibiting higher efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Offshore wind farms, positioned in the vast expanse of oceans, further expand the potential for wind energy production, offering access to stronger and more consistent winds.
The Promise of Hydropower
Hydropower, utilizing the energy of flowing water, is a well-established renewable energy source. Hydroelectric dams harness the potential energy of water to generate electricity, offering a reliable and consistent energy supply. While large-scale hydroelectric dams can have environmental implications, smaller-scale hydropower projects, such as micro-hydropower plants, can be more environmentally friendly and provide localized energy solutions.
The sustainable management of water resources is crucial for the long-term viability of hydropower projects. Careful consideration of environmental impacts, including the effect on aquatic ecosystems and migratory patterns, is essential for responsible development and operation of hydropower facilities.
Exploring Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth's internal heat, harnessing the heat from the Earth's core to produce steam or hot water that can be used to generate electricity. Geothermal power plants offer a reliable and continuous energy source, particularly in geologically active regions. The technology for extracting and utilizing geothermal energy is constantly evolving, leading to improvements in efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
While geothermal energy is a sustainable energy source, careful consideration needs to be given to the potential for ground subsidence and other localized environmental impacts associated with the extraction of geothermal fluids. Responsible development practices are essential to minimize these impacts and ensure the long-term sustainability of geothermal energy projects.
Bioenergy: A Sustainable Solution from Organic Sources
Bioenergy, derived from organic matter such as biomass, offers a versatile renewable energy source. This includes utilizing agricultural residues, wood waste, and dedicated energy crops to produce biofuels and bioelectricity. Bioenergy offers a potential pathway to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and create a circular economy, where waste materials are transformed into valuable energy resources.
However, the sustainability of bioenergy production depends on careful consideration of land use, resource management, and the potential for competition with food production. Sustainable agricultural practices and careful environmental assessments are crucial for ensuring that bioenergy production does not contribute to deforestation or other negative environmental impacts.
Adapting Infrastructure for Renewable Integration
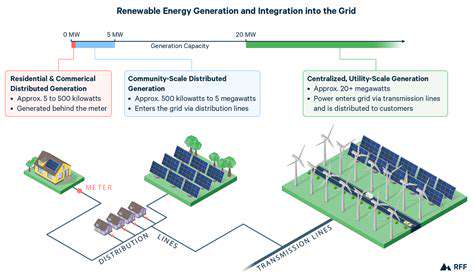
Adapting Existing Infrastructure
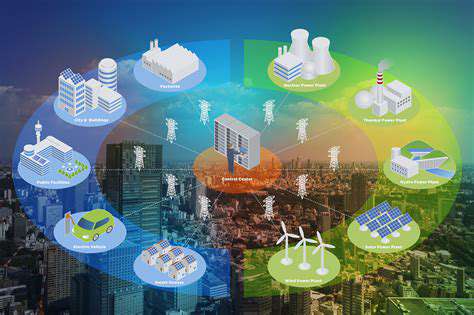
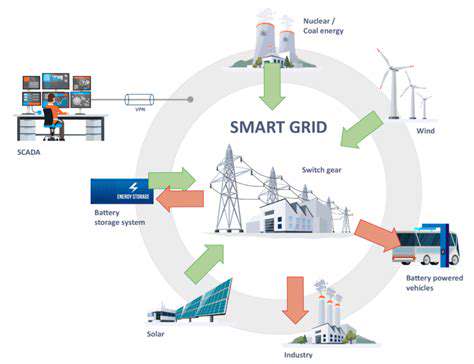
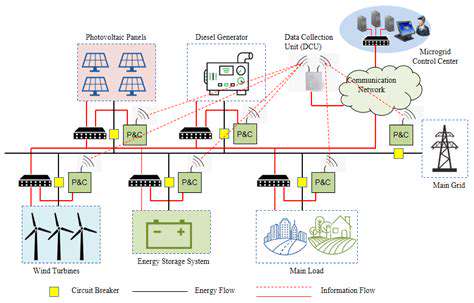
Modernizing existing infrastructure to support renewable energy sources requires careful planning and execution. This involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing not only the physical aspects of the infrastructure but also the regulatory frameworks and public perception surrounding the integration of these new technologies. The critical aspect is to identify and address potential bottlenecks in the existing grid systems to ensure seamless integration of renewable energy sources. This includes upgrading transmission lines, transformers, and substations to handle the fluctuating nature of renewable energy production. Furthermore, existing distribution networks must be assessed and potentially modified to accommodate the anticipated increase in energy flow from renewable sources. This process demands careful consideration of the potential impacts on the existing infrastructure and the development of strategies to mitigate any negative consequences.
Implementing smart grid technologies is crucial for managing the variable output of renewable energy sources. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flows, optimizing energy distribution and minimizing waste. By integrating advanced sensors and communication systems, the grid can respond dynamically to fluctuations in renewable energy generation. Implementing these solutions will lead to greater grid stability and efficiency, improving the overall reliability of the energy supply. Ultimately, this adaptability will allow for a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure, capable of handling the evolving needs of a future powered by renewable energy.
Enhancing Regulatory Frameworks and Public Support
Successfully integrating renewable energy requires a supportive regulatory environment. This includes policies that incentivize the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies, while simultaneously establishing clear guidelines for grid integration. These regulations should address issues like interconnection standards, renewable energy portfolio standards, and net metering policies to facilitate a smooth transition. Establishing clear and consistent regulations will create a predictable and attractive investment environment for renewable energy projects.
Public engagement and education are equally important. Engaging the public in discussions about the benefits and challenges of renewable energy integration is crucial for building public support and addressing concerns. Transparent communication about the benefits of clean energy, including job creation, economic growth, and environmental protection, can foster a positive attitude towards the transition. Community participation in planning and decision-making processes can help ensure that renewable energy projects are socially acceptable and meet the needs of local communities.
Addressing concerns about potential impacts on existing industries and infrastructure, while offering solutions and incentives, is vital for a smooth transition. Open dialogue and engagement will help mitigate potential conflicts and ensure that the transition to renewable energy is inclusive and equitable for all stakeholders.
Community Engagement and Policy Support for Renewable Energy Adaptation
Community Engagement Strategies
Effective community engagement is crucial for successful renewable energy adaptation. This involves more than just informing residents; it requires actively listening to their concerns, understanding their needs, and incorporating their perspectives into the planning process. Community workshops, town hall meetings, and focus groups can provide valuable platforms for dialogue and feedback. Furthermore, establishing transparent communication channels, such as newsletters and online forums, is essential for keeping the community informed about project updates and addressing any emerging concerns. This proactive approach fosters trust and ensures that the renewable energy projects align with the community's values and aspirations.
Building relationships with local community leaders, organizations, and businesses is also critical. Collaborating with these stakeholders can help streamline the permitting process, identify potential challenges early on, and leverage existing resources. Encouraging participation from diverse community members, including those who may be traditionally underrepresented, is vital for ensuring that the benefits of renewable energy are accessible and equitable for all.
Policy Support Frameworks
Robust policy frameworks are essential for incentivizing and facilitating the adoption of renewable energy technologies. These policies should encompass various aspects, such as streamlining permitting procedures, establishing clear timelines for project implementation, and providing financial incentives for renewable energy investments. Incentives can include tax credits, grants, and rebates, which can significantly reduce the initial costs associated with renewable energy projects and make them more attractive to investors.
Policies should also address potential environmental impacts, ensuring that renewable energy projects are developed sustainably and in accordance with environmental regulations. This includes considering the potential effects on wildlife, water resources, and local ecosystems. A comprehensive policy framework should also promote public-private partnerships to leverage resources and expertise from both sectors, fostering innovation and project implementation.
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Equity
Implementing renewable energy projects can present various challenges, including potential impacts on local economies, concerns about job displacement, and concerns regarding visual impacts on the landscape. Addressing these concerns proactively through community engagement and transparent communication is crucial for successful project implementation. It is important to carefully consider the potential economic and social consequences of renewable energy projects and develop strategies to mitigate any negative impacts.
Ensuring that the benefits of renewable energy are distributed equitably is also paramount. This means actively working to involve marginalized communities in the planning and implementation processes, and ensuring that any economic opportunities generated by the projects are accessible to all community members. Addressing potential disparities in access to technology and resources is vital for sustainable and equitable renewable energy transitions.
Furthermore, policies should be designed to mitigate any potential negative impacts on existing industries and employment opportunities. This might involve workforce retraining programs or initiatives to support the transition of workers into new roles related to renewable energy development.
Strong community engagement and thoughtful policies are key to successful renewable energy adaptation. By incorporating these elements, we can foster a transition that is both environmentally sound and socially equitable.
Beyond Energy: The Ripple Effect of Renewable Energy Adaptation
The Impact on Industries
Beyond simply powering our homes and businesses, the transition to sustainable energy sources is fundamentally altering entire industries. The demand for renewable energy technologies is driving innovation and creating new job opportunities across manufacturing, engineering, and installation. This ripple effect extends to traditional energy sectors, forcing them to adapt and invest in new technologies to remain competitive.
From electric vehicle manufacturing to smart grid development, the shift towards a sustainable energy future is creating a dynamic and rapidly evolving marketplace. This transformation is impacting everything from the materials used in construction to the design of our cities, fostering a new era of technological advancement and economic growth.
Environmental Benefits
The transition to sustainable energy sources is paramount for mitigating climate change. Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, thereby slowing the rate of global warming. This, in turn, protects ecosystems and biodiversity, mitigating the devastating effects of climate change on our planet.
The long-term benefits of clean energy extend to improved air quality, reduced water pollution, and the preservation of natural resources. By embracing sustainable energy, we are actively working to create a healthier and more sustainable environment for future generations.
Social Equity and Accessibility
The transition to sustainable energy sources presents an opportunity to address social equity concerns. Deployment of renewable energy technologies can create jobs in underserved communities, fostering economic development and improving living standards. This access to clean energy can empower communities and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, thereby fostering economic self-sufficiency and social progress.
Economic Growth and Investment
Investing in renewable energy technologies stimulates economic growth and creates new opportunities for investment. The sector attracts significant capital, fosters innovation, and generates employment across a wide range of industries. This long-term investment creates a positive feedback loop, accelerating the transition to a sustainable economy.
The growth of the renewable energy sector also provides opportunities for small businesses and entrepreneurs, fostering a dynamic and competitive marketplace. This creates a more resilient and sustainable global economy.
Geopolitical Implications
The shift towards sustainable energy sources has significant geopolitical implications. Countries with abundant renewable resources can become major players in the global energy market. This creates new avenues for international cooperation and trade, fostering alliances and partnerships based on shared sustainability goals.
Dependence on fossil fuels can make nations vulnerable to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability. Transitioning to sustainable energy sources can enhance energy security and reduce reliance on volatile global markets.