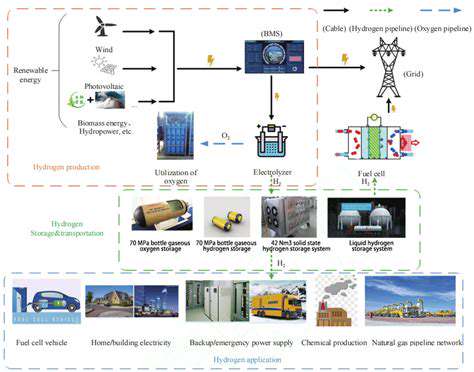
Regulatory Barriers to Renewable Energy Innovation
Standardization and Interoperability Issues: Fragmentation of the Market
Standardization Challenges in Regulatory Environments
Standardization efforts in regulatory environments are often hampered by conflicting priorities and diverse interests among stakeholders. Different jurisdictions may have varying requirements, leading to fragmented approaches and significant challenges for businesses operating across multiple markets. This lack of consistency creates a complex and often unpredictable regulatory landscape, increasing compliance costs and hindering innovation.
Harmonizing standards across borders is a complex process that requires significant collaboration and compromises. Reaching consensus on key technical specifications, data formats, and reporting requirements can be difficult, particularly when dealing with deeply entrenched national or regional regulatory traditions.
Interoperability Concerns in Regulatory Systems
Interoperability, the ability of different systems to exchange information seamlessly, is crucial for regulatory compliance. However, existing regulatory systems often lack the necessary interoperability features. This can lead to data silos, making it difficult to track and analyze compliance across various agencies and jurisdictions. In many cases, legacy systems and incompatible technologies impede the smooth flow of information, hindering effective regulatory oversight.
The lack of interoperability can also increase the risk of errors and inconsistencies in data collection, analysis, and enforcement. This can lead to delays in regulatory processes, reduced transparency, and potentially harmful consequences for businesses and consumers.
Fragmentation of Market Access for Businesses
The fragmented nature of regulatory frameworks can create significant barriers to market access for businesses, particularly those operating internationally. Navigating the maze of different standards, procedures, and requirements in various jurisdictions can be incredibly challenging and time-consuming. This can lead to increased operational costs, delays in market entry, and reduced competitiveness.
Businesses often face substantial hurdles in demonstrating compliance across multiple jurisdictions, requiring significant resources and expertise to ensure adherence to diverse regulatory frameworks. This can disproportionately affect smaller companies, limiting their ability to compete in global markets.
Impact on Consumer Protection and Market Transparency
Standardization and interoperability issues can negatively impact consumer protection and market transparency. Lack of harmonized regulations can lead to inconsistencies in product safety standards, data privacy protections, and other crucial consumer safeguards. This lack of transparency can make it difficult for consumers to make informed decisions and can expose them to potential risks.
The Role of Technology in Bridging the Gap
Emerging technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence have the potential to play a crucial role in bridging the gap between fragmented regulatory systems. These technologies can facilitate data exchange, automate compliance processes, and enhance transparency. However, the effective implementation of these technologies requires careful consideration of data security, privacy, and ethical implications.
Further development of interoperable platforms and standardized data formats are vital for fostering greater collaboration among regulators and stakeholders. Developing robust frameworks for cybersecurity and data protection is also essential to ensure the integrity and reliability of these systems.
Regulatory Cooperation and Harmonization Strategies
Enhanced cooperation and harmonization strategies are crucial for addressing standardization and interoperability issues. International regulatory bodies and organizations can play a vital role in fostering collaboration among different jurisdictions. This includes establishing common standards, facilitating information sharing, and developing best practices for regulatory implementation.
Promoting knowledge sharing and capacity building among regulators can also contribute significantly to the adoption of consistent standards and interoperable systems. This can involve providing training and support to regulators in developing countries, helping them integrate into the global regulatory landscape.
Economic and Social Implications of Fragmentation
The fragmentation of regulatory markets has significant economic and social implications. It can hinder economic growth, limit international trade, and create barriers to investment. Furthermore, this can lead to increased administrative costs for businesses and consumers, reducing overall efficiency and competitiveness.
A lack of standardized regulations can negatively impact consumer confidence and trust, leading to potentially greater social and economic instability. Clearer and more harmonized regulations are crucial for fostering a more stable and predictable environment for businesses and citizens alike.
Policy Uncertainty: A Detriment to Long-Term Investment

Policy Uncertainty and Economic Growth
Policy uncertainty, characterized by unpredictable shifts in government regulations and policies, poses a significant threat to long-term economic growth. This unpredictability creates a climate of fear and hesitation among investors, hindering investment decisions and dampening entrepreneurial spirit. Businesses are less likely to expand, innovate, or take on new projects when they lack confidence in the stability of the regulatory environment. This reduced investment translates directly into slower job creation and a decrease in overall economic output.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Investors, whether domestic or foreign, are crucial for economic development. Uncertainty surrounding government policies directly impacts their willingness to commit capital to long-term projects. When policies are inconsistent or appear arbitrary, investors may delay or abandon their planned investments, fearing that future regulations will negatively impact their returns. This reluctance to invest can lead to a decline in capital formation, hindering productivity growth and potentially triggering a recession.
The lack of clarity in policymaking also discourages foreign direct investment. International investors are more likely to direct their capital towards countries with stable and predictable policy environments. Policy uncertainty undermines the appeal of a country as a desirable investment destination.
Consequences for Entrepreneurial Activity
Entrepreneurs, the driving force behind innovation and job creation, are particularly vulnerable to policy uncertainty. The risk of sudden policy changes makes it difficult for them to plan and execute their business strategies. The fear of facing unforeseen regulations and taxes can discourage new ventures from emerging and existing businesses from expanding. This stagnation in entrepreneurial activity ultimately leads to a decrease in economic dynamism and a slower rate of technological advancement.
Effect on Consumer Confidence
Policy uncertainty can also have a significant impact on consumer confidence. When consumers perceive a high degree of unpredictability in government policies, they may postpone major purchases and investments. This reduced consumer spending can lead to a decline in economic activity and potentially trigger a recession. Furthermore, the uncertainty can create a sense of anxiety and instability, which can negatively affect overall well-being.
Policy Recommendations
To mitigate the detrimental effects of policy uncertainty, governments must prioritize transparency and predictability in their policymaking processes. Clear communication of policy intentions and consistent implementation are crucial. This creates a stable and predictable environment for businesses, investors, and consumers. Furthermore, fostering dialogue and consultation with stakeholders can help policymakers anticipate and address potential concerns before implementing changes.